Related Research Articles
The Global 200 is the list of ecoregions identified by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), the global conservation organization, as priorities for conservation. According to WWF, an ecoregion is defined as a "relatively large unit of land or water containing a characteristic set of natural communities that share a large majority of their species dynamics, and environmental conditions". For example, based on their levels of endemism, Madagascar gets multiple listings, ancient Lake Baikal gets one, and the North American Great Lakes get none.

The Valdivian temperate forests (NT0404) is an ecoregion on the west coast of southern South America, in Chile and Argentina. It is part of the Neotropical realm. The forests are named after the city of Valdivia. The Valdivian temperate rainforests are characterized by their dense understories of bamboos, ferns, and for being mostly dominated by evergreen angiosperm trees with some deciduous specimens, though conifer trees are also common.

When the Spanish arrived, they divided Peru into three main regions: the coastal region, that is bounded by the Pacific Ocean; the highlands, that is located on the Andean Heights, and the jungle, that is located on the Amazonian Jungle. But Javier Pulgar Vidal, a geographer who studied the biogeographic reality of the Peruvian territory for a long time, proposed the creation of eight Natural Regions. In 1941, he presented his thesis "Las Ocho Regiones Naturales del Perú" at the III General Assembly of the Pan-American Institute of Geography and History.

The puna grassland ecoregion, part of the Andean montane grasslands and shrublands biome, is found in the central Andes Mountains of South America. It is considered one of the eight Natural Regions in Peru, but extends south, across Chile, Bolivia, and western northwest Argentina. The term puna encompasses diverse ecosystems of the high Central Andes above 3200–3400 m.

Because Chile extends from a point about 625 kilometers north of the Tropic of Capricorn to a point hardly more than 1,400 kilometers north of the Antarctic Circle, within its territory can be found a broad selection of the Earth's climates.

The Patagonian Desert, also known as the Patagonian Steppe, is the largest desert in Argentina and is the eighth-largest desert in the world by area, occupying approx. 673,000 square kilometres. It is located primarily in Argentina and is bounded by the Andes, to its west, and the Atlantic Ocean to its east, in the region of Patagonia, southern Argentina and areas of Chile. To the north the desert grades into the Cuyo Region and the Monte. The central parts of the steppe are dominated by shrubby and herbaceous plant species albeit to the west, where precipitation is higher, bushes are replaced by grasses. Topographically the deserts consist of alternating tablelands and massifs dissected by river valleys and canyons. The more western parts of the steppe host lakes of glacial origin and grades into barren mountains or cold temperate forests along valleys.

The Monte Desert is a South American desert, lying entirely within Argentina and covering approximately the submontane areas of Catamarca, La Rioja, San Juan, San Luis and Mendoza Provinces, plus the western half of La Pampa Province and the extreme north of Río Negro Province. The desert lies southeast of the Atacama Desert in Chile and Peru, north of the larger Patagonian Desert, east of the Andes and west of the Sierra de Córdoba.
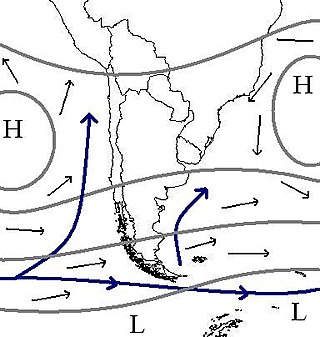
The climate of Chile comprises a wide range of weather conditions across a large geographic scale, extending across 38 degrees in latitude, making generalizations difficult. According to the Köppen system, Chile within its borders hosts at least seven major climatic subtypes, ranging from low desert in the north, to alpine tundra and glaciers in the east and southeast, tropical rainforest in Easter Island, Oceanic in the south and Mediterranean climate in central Chile. There are four seasons in most of the country: summer, autumn, winter, and spring.

The Chilean Matorral (NT1201) is a terrestrial ecoregion of central Chile, located on the west coast of South America. It is in the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome, part of the Neotropical realm.

The variable hawk is a polymorphic species of bird of prey in the family Accipitridae.

The wildlife of Chile is very diverse because of the country's slender and elongated shape, which spans a wide range of latitude, and altitude, ranging from the windswept coastline of the Pacific coast on the west to northern Andes to the sub-Antarctic, high Andes mountains in the east. There are many distinct ecosystems.

The Southern Andean steppe is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion occurring along the border of Chile and Argentina in the high elevations of the southern Andes mountain range.

Environmental issues in Chile include deforestation, water scarcity, pollution, soil erosion, climate change, and biodiversity loss, especially in its industry-heavy "sacrifice zones". The country of Chile is a virtual continental island that spans over 4,200 kilometers. It is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the Andes Mountains on the east, and the Atacama Desert in the north; it is home to several important eco-regions, such as the Chilean Winter Rainfall-Valdivian Forests, a biodiversity hot-spot that harbors richly endemic flora and fauna, and the Tropical Andes, which stretches into northern Chile. The country has a wide variety of climates due to its large size and extreme geographical features including glaciers, volcanoes, rain forests, and deserts. Chile faces many environmental issues that impact both its people and economy.

The Arid Diagonal is a contiguous zone of arid and semi-arid climate that traverses South America from coastal Peru in the Northwest to Argentine Patagonia in the Southeast including large swathes of Bolivia and Chile. The Arid Diagonal encompasses a number of deserts, for example: Sechura, Atacama, Monte and the Patagonian Desert.

Bosque Andino Patagónico, also known as Patagonian Andean forest, is a type of temperate to cold forest located in western Patagonia in Argentina and also in southern Chile, at the southern end of South America. The climate here is influenced by humid air masses moving in from the Pacific Ocean which lose most of their moisture as they rise over the Andes. The flora is dominated by trees, usually of the genus Nothofagus.
References
- Olson, D., Dinerstein, E., Canevari, P., Davidson, I., Castro, G., Morisset, V., Abell, R., and Toledo, E.; eds. (1998). Freshwater biodiversity of Latin America and the Caribbean: A conservation assessment. Biodiversity Support Program, Washington, D.C..