
The Piney Woods is a temperate coniferous forest terrestrial ecoregion in the Southern United States covering 54,400 square miles (141,000 km2) of East Texas, southern Arkansas, western Louisiana, and southeastern Oklahoma. These coniferous forests are dominated by several species of pine as well as hardwoods including hickory and oak. Historically the most dense part of this forest region was the Big Thicket though the lumber industry dramatically reduced the forest concentration in this area and throughout the Piney Woods during the 19th and 20th centuries. The World Wide Fund for Nature considers the Piney Woods to be one of the critically endangered ecoregions of the United States. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) defines most of this ecoregion as the South Central Plains.

The Dissected Till Plains are physiographic sections of the Central Lowlands province, which in turn is part of the Interior Plains physiographic division of the United States, located in southern and western Iowa, northeastern Kansas, the southwestern corner of Minnesota, northern Missouri, eastern Nebraska, and southeastern South Dakota.

The Western Gulf coastal grasslands are a subtropical grassland ecoregion of the southern United States and northeastern Mexico. It is known in Louisiana as the "Cajun Prairie", Texas as "Coastal Prairie," and as the Tamaulipan pastizal in Mexico.
Illinois is in the midwestern United States. Surrounding states are Wisconsin to the north, Iowa and Missouri to the west, Kentucky to the east and south, and Indiana to the east. Illinois also borders Michigan, but only via a northeastern water boundary in Lake Michigan. Nearly the entire western boundary of Illinois is the Mississippi River, except for a few areas where the river has changed course. Illinois' southeastern and southern boundary is along the Wabash River and the Ohio River, whereas its northern boundary and much of its eastern boundary are straight survey lines. Illinois has a maximum north–south distance of 390 miles (630 km) and 210 miles (340 km) east-west. Its total area is 57,918 square miles (150,010 km2).

The Big Muddy River is a 156-mile-long (251 km) river in southern Illinois. It joins the Mississippi River just south of Grand Tower. The Big Muddy has been dammed near Benton, forming Rend Lake.

The term Cross Timbers, also known as Ecoregion 29, Central Oklahoma/Texas Plains, is used to describe a strip of land in the United States that runs from southeastern Kansas across Central Oklahoma to Central Texas. Made up of a mix of prairie, savanna, and woodland, it forms part of the boundary between the more heavily forested eastern country and the almost treeless Great Plains, and also marks the western habitat limit of many mammals and insects.

The Snake River Plain ecoregion is a Level III ecoregion designated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the U.S. states of Idaho and Oregon. It follows the Snake River across Idaho, stretching roughly 400 miles (640 km) from the Wyoming border to Eastern Oregon in the xeric intermontane west. Characterized by plains and low hills, it is considerably lower and less rugged than surrounding ecoregions. Many of the alluvial valleys bordering the Snake River are used for agriculture. Where irrigation water and soil depth are sufficient, sugar beets, potatoes, alfalfa, small grains, and vegetables are grown. Elsewhere, livestock grazing is widespread. Cattle feedlots and dairy operations are found locally.
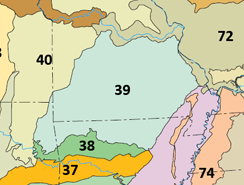
The Ozark Highlands is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in four U.S. states. Most of the region is within Missouri, with a part in Arkansas and small sections in Oklahoma and Kansas. It is the largest subdivision of the region known as the Ozark Mountains, less rugged in comparison to the Boston Mountains in Arkansas, the highest part of the Ozarks.

The environment of Iowa has been heavily affected by agricultural production since it became a U.S. state in 1846. However, there remain natural areas in Iowa that reflect a wide varieties of environmental niches.
The Mississippi Alluvial Plain is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in seven U.S. states, though predominantly in Arkansas, Louisiana, and Mississippi. It parallels the Mississippi River from the Midwestern United States to the Gulf of Mexico.

The North Central Hardwood Forests are a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion in central Minnesota, central Wisconsin, and northwestern Lower Michigan, embedded between (clockwise) the Western Corn Belt Plains in the south, the Northern Glaciated Plains, the Red River Valley, the Northern Minnesota Wetlands, and the Northern Lakes and Forests. It forms the northern part of the upper Midwest forest-savanna transition, which also includes regions 52 and 53.

The Arkansas Valley is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the U.S. states of Arkansas and Oklahoma. It parallels the Arkansas River between the flat plains of western Oklahoma and the Arkansas Delta, dividing the Ozarks and the Ouachita Mountains with the broad valleys created by the river's floodplain, occasionally interrupted by low hills, scattered ridges, and mountains. In Arkansas, the region is often known as the Arkansas River Valley, especially when describing the history and culture of the region.
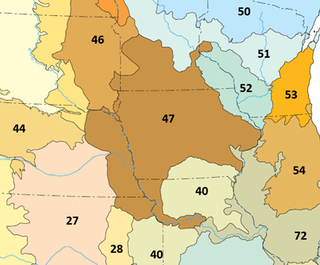
The Western Corn Belt Plains is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in seven U.S. states, though predominantly in Iowa.

The North American Southeastern Plains are a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in ten U.S. states. The region takes a U shape starting in western Tennessee, going south through eastern Mississippi, and forming most of Alabama. On the eastern side, the plains lie between the Appalachian Mountains and the coastal plains, forming central Georgia, South Carolina, and North Carolina. It forms part of eastern Virginia before terminating in Maryland.

The North American Mississippi Valley Loess Plains are a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in six U.S. states. The region lies primarily on the eastern border of the Mississippi Alluvial Plain, from the Ohio River in western Kentucky, through Tennessee and Mississippi, to Louisiana. A separate unit that includes Crowley's Ridge occurs west of the river in Arkansas and Missouri. It has been divided into four Level IV ecoregions.













