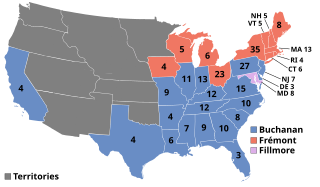
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 4, 1856. Democratic nominee James Buchanan defeated Republican nominee John C. Frémont and Know Nothing/Whig nominee Millard Fillmore. The main issue was the expansion of slavery as facilitated by the Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854. Buchanan defeated President Franklin Pierce at the 1856 Democratic National Convention for the nomination. Pierce had become widely unpopular in the North because of his support for the pro-slavery faction in the ongoing civil war in territorial Kansas, and Buchanan, a former Secretary of State, had avoided the divisive debates over the Kansas–Nebraska Act by being in Europe as the Ambassador to the United Kingdom.

The Territory of Kansas was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 30, 1854, until January 29, 1861, when the eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the free state of Kansas. The territory extended from the Missouri border west to the summit of the Rocky Mountains and from the 37th parallel north to the 40th parallel north. Originally part of Missouri Territory, it was unorganized from 1821 to 1854. Much of the eastern region of what is now the State of Colorado was part of Kansas Territory. The Territory of Colorado was created to govern this western region of the former Kansas Territory on February 28, 1861.

The 33rd United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1853, to March 4, 1855, during the first two years of Franklin Pierce's presidency. During this session, the Kansas–Nebraska Act was passed, an act that soon led to the creation of the Republican Party. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1850 United States census. Both chambers had a Democratic majority.

The 34th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from March 4, 1855, to March 4, 1857, during the last two years of Franklin Pierce's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1850 United States census. The Whig Party, one of the two major parties of the era, had largely collapsed, although many former Whigs ran as Republicans or as members of the "Opposition Party." The Senate had a Democratic majority, and the House was controlled by a coalition of Representatives led by Nathaniel P. Banks, a member of the American Party.

The 1854–55 United States House of Representatives elections were held in 31 states for all 234 seats between August 4, 1854, and November 6, 1855, during President Franklin Pierce's term. Each state legislature separately set a date to elect representatives to the House of Representatives before the 34th Congress convened its first session on December 3, 1855.

Bernhart Henn was a pioneer lawyer and businessman, and a two-term Democratic U.S. Representative from Iowa's 1st congressional district during Iowa's first decade of statehood.

David Addison Noble was a politician and judge from the U.S. state of Michigan who served a term in Congress from 1853 to 1855.
The Vermont Republican Party is the affiliate of the Republican Party in Vermont and has been active since its foundation in the 1860s. The party is the second largest in the state behind the Vermont Democratic Party, but ahead of the Vermont Progressive Party. The party historically dominated Vermont politics until the mid-20th century, but was replaced by the Vermont Democratic Party. The party currently has very weak federal electoral power in the state, controlling none of Vermont's federal elected offices. The two statewide offices that the party currently controls are the governorship, held by Phil Scott, and the lieutenant governorship, held by John S. Rodgers.

The American Party, known as the Native American Party before 1855 and colloquially referred to as the Know Nothings, or the Know Nothing Party, was an Old Stock nativist political movement in the United States in the 1850s. Members of the movement were required to say "I know nothing" whenever they were asked about its specifics by outsiders, providing the group with its colloquial name.

This is the electoral history of Abraham Lincoln. Lincoln served one term in the United States House of Representatives from Illinois (1847–1849). He later served as the 16th president of the United States (1861–1865).

The 1855 United States Senate election in New York was held on February 6, 1855, by the New York State Legislature to elect a U.S. Senator to represent the State of New York in the United States Senate.
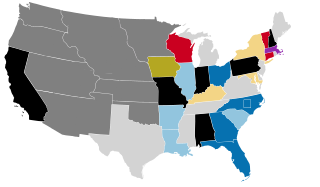
The 1854–55 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1854 and 1855, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 3.
The 1854 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held on November 7, 1854, to elect 33 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 34th United States Congress, and two representatives to fill vacancies in the 33rd United States Congress.
The 1855 United States Senate special election in Massachusetts was held during January 1855. Henry Wilson was elected to fill the remainder of the term left vacant by the resignation of Edward Everett.

The 1854 United States House of Representatives election in Florida was held on Monday, October 2, 1854 to elect the single United States Representative from the state of Florida, one from the state's single at-large congressional district, to represent Florida in the 34th Congress. The election coincided with the elections of other offices, including the senatorial election and various state and local elections.
The 1854 United States elections was the midterm election choosing members of the 34th United States Congress during the middle of Democratic President Franklin Pierce's term. It was part of the transition from the Second Party System to the Third Party System, as the Whigs collapsed as a national party and were replaced by a coalition running on the Opposition Party ticket and the nascent Republican Party.

The Eighth Wisconsin Legislature convened from January 10, 1855, to April 2, 1855, in regular session.

The 1855 Massachusetts gubernatorial election was held on November 6. Know-Nothing candidate Henry J. Gardner was re-elected to a second term as Governor in a multi-partisan race, defeating Republican Julius Rockwell and Democrat Erasmus Beach.
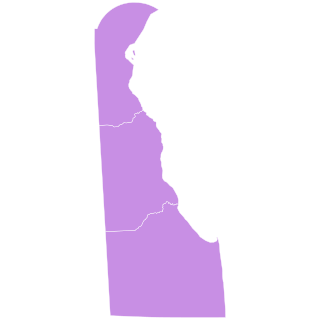
The 1854 Delaware gubernatorial election was held on November 7, 1854. Incumbent Democratic Governor William H. H. Ross was unable to seek re-election. His 1850 opponent, former State Representative Peter F. Causey, ran as the American Party candidate, and faced former Kent County Sheriff William Burton, the Democratic nominee. Causey ultimately defeated Burton by a slim, but decisive, margin.