
The economy of Georgia is an emerging free market economy. Its gross domestic product fell sharply following the dissolution of the Soviet Union but recovered in the mid-2000s, growing in double digits thanks to the economic and democratic reforms brought by the peaceful Rose Revolution. Georgia continued its economic progress since, "moving from a near-failed state in 2003 to a relatively well-functioning market economy in 2014". In 2007, the World Bank named Georgia the World's number one economic reformer, and has consistently ranked the country at the top of its ease of doing business index.

Customs is an authority or agency in a country responsible for collecting tariffs and for controlling the flow of goods, including animals, transports, personal effects, and hazardous items, into and out of a country. Traditionally, customs has been considered as the fiscal subject that charges customs duties and other taxes on import and export. In recent decades, the views on the functions of customs have considerably expanded and now covers three basic issues: taxation, security, and trade facilitation.
A free-trade zone (FTZ) is a class of special economic zone. It is a geographic area where goods may be imported, stored, handled, manufactured, or reconfigured and re-exported under specific customs regulation and generally not subject to customs duty. Free trade zones are generally organized around major seaports, international airports, and national frontiers—areas with many geographic advantages for trade.

A duty-free shop is a retail outlet whose goods are exempt from the payment of certain local or national taxes and duties, on the requirement that the goods sold will be sold to travelers who will take them out of the country, who will then pay duties and taxes in their destination country. Which products can be sold duty-free vary by jurisdiction, as well as how they can be sold, and the process of calculating the duty or refunding the duty component.
Tax-free shopping (TFS) is the buying of goods in another country or state and obtaining a refund of the sales tax which has been collected by the retailer on those goods. The sales tax may be variously described as a sales tax, goods and services tax (GST), value added tax (VAT), or consumption tax.
Taxation in the Netherlands is defined by the income tax, the wage withholding tax, the value added tax and the corporate tax.
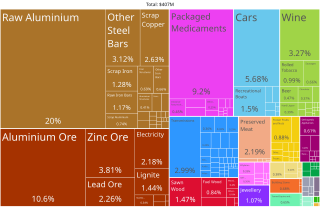
The economy of Montenegro is currently in a process of transition, as it navigates the impacts of the Yugoslav Wars, the decline of industry following the dissolution of the Yugoslavia, and economic sanctions imposed by the United Nations. Montenegro joined the World Trade Organization on 29 April 2012. Montenegro joined the North Atlantic Treaty Organization on 5 June 2017. The accession of Montenegro to the European Union is planned for 2025.
Taxation in Iran is levied and collected by the Iranian National Tax Administration under the Ministry of Finance and Economic Affairs of the Government of Iran. In 2008, about 55% of the government's budget came from oil and natural gas revenues, the rest from taxes and fees. An estimated 50% of Iran's GDP was exempt from taxes in FY 2004. There are virtually millions of people who do not pay taxes in Iran and hence operate outside the formal economy. The fiscal year begins on March 21 and ends on March 20 of the next year.
Taxation in Greece is based on the direct and indirect systems. The total tax revenue in 2017 was €47.56 billion from which €20.62 billion came from direct taxes and €26.94 billion from indirect taxes. The total tax revenue represented 39.4% of GDP in 2017. Taxes in Greece are collected by the Independent Authority for Public Revenue.

The European Union value-added tax is a value added tax on goods and services within the European Union (EU). The EU's institutions do not collect the tax, but EU member states are each required to adopt in national legislation a value added tax that complies with the EU VAT code. Different rates of VAT apply in different EU member states, ranging from 17% in Luxembourg to 27% in Hungary. The total VAT collected by member states is used as part of the calculation to determine what each state contributes to the EU's budget.
In Bangladesh, the principal taxes are Customs duties, Value-Added-Tax (VAT), supplementary duty, income tax and corporation tax.

Sughd free economic zone is an industrial-innovative type, which was established in 2009 according to the Decree of the Government of the Republic of Tajikistan dated May 2, 2008.
Taxation in Norway is levied by the central government, the county municipality and the municipality. In 2012 the total tax revenue was 42.2% of the gross domestic product (GDP). Many direct and indirect taxes exist. The most important taxes – in terms of revenue – are VAT, income tax in the petroleum sector, employers' social security contributions and tax on "ordinary income" for persons. Most direct taxes are collected by the Norwegian Tax Administration and most indirect taxes are collected by the Norwegian Customs and Excise Authorities.

In the United Kingdom, the value added tax (VAT) was introduced in 1973, replacing Purchase Tax, and is the third-largest source of government revenue, after income tax and National Insurance. It is administered and collected by HM Revenue and Customs, primarily through the Value Added Tax Act 1994.
The United Arab Emirates is a federation of seven Emirates, with autonomous federal and local governments. The UAE has historically been a low-tax jurisdiction. The federal government and local governments are entitled to levy taxes on citizens and companies. The federal government currently levies a value added tax, corporate income tax, and excise taxes. Some emirates levy property, transfer, excise and tourism taxes. Some emirates also charge corporate taxes oil companies and foreign banks.
Czech Republic's current tax system was put into administration on 1 January 1993. Since then, an updated VAT act was introduced on 1 May 2004 when Czech Republic joined the EU and the act had to correspond to EU law. In 2008, the administration also introduced Energy Taxation. Changes to tax laws are quite frequent and common in the Czech Republic due to a dynamic economy. The highest levels of revenue are generated from income tax, social security contributions, value-added tax and corporate tax. In 2015, total revenue stood at CZK 670.216 billion which was 36.3% of GDP. The tax quota of the Czech Republic is lower than the EU average. Compared to the averages of the OECD countries, revenues generated from taxes on social security contributions, corporate income and gains and value added taxes account for higher proportions of total taxation revenue. Personal income tax lies on the other end of the spectrum where the revenue is proportionally much lower than the OECD average. Taxes on property also account for lower levels of revenue.
Taxes in Georgia are collected on both national and local levels. The most important taxes are collected on national level, these taxes include an income tax, corporate taxes and value added tax. On local level property taxes as well as various fees are collected. There are 6 flat tax rates in Georgia - Corporate Profit Tax, Value Added Tax, Excise Tax, Personal Income Tax, Import Tax and Property Tax.

A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally. It is levied on the price of a product or service at each stage of production, distribution, or sale to the end consumer. If the ultimate consumer is a business that collects and pays to the government VAT on its products or services, it can reclaim the tax paid. It is similar to, and is often compared with, a sales tax. VAT is an indirect tax because the person who ultimately bears the burden of the tax is not necessarily the same person as the one who pays the tax to the tax authorities.

The Royal Science and Technology Park (RSTP) is a Swazi public enterprise and science park created to foster the conception of inventions and facilitate their patenting and help knit various elements of the R&D cluster together. It is intended to provide a focal point for research, facilitates the links between research and industrial communities and stimulates the development of knowledge-based businesses through the incubation of techno-preneurship and high-tech enterprises.








