 |
|---|
This article lists the heads of government of Norfolk Island .
 |
|---|
This article lists the heads of government of Norfolk Island .
(Dates in italics indicate de facto continuation of office, irrespective of continuation of status of that office)
| Term | Incumbent | Title | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1896 to 15 January 1897 | Oliver Masey Quintal | President of the Council of Elders | |
| 15 January 1897 | Self-government revoked | ||
| 15 January 1897 to 1899 | Oliver Masey Quintal | President of the Council of Elders | |
| 1899 to 1900 | John Buffett | ||
| 1900 to 1903 | John Forrester Young | ||
| 1903 to 1909 | Francis Mason Nobbs | President of the Executive Council | |
| 1909 to 1915 | Joseph Allen McCleave Buffett | ||
| 1915 to 1 July 1916 | Charles Chase Ray Nobbs | 1st term | |
| Norfolk Island Territory of The Commonwealth of Australia | |||
| 1916 | Charles Chase Ray Nobbs | President of the Executive Council | 1st term (contd.) |
| 1916 to 1919 | Matthew Frederick Howard Christian | ||
| 1919 to 1920 | Albert Randall | 1st term | |
| 1921 to 1922 | Enoch Cobbcroft Robinson | 1st term | |
| 1922 to 1923 | Albert Randall | 2nd term | |
| 1924 to 1928 | Eustace Buffett Christian | 1st term | |
| 1928 to 1933 | Enoch Cobbcroft Robinson | 2nd term | |
| 1933 to 19 May 1934 | Charles Chase Ray Nobbs | 2nd term | |
| 1934 to 1934 | Eustace Buffett Christian | 2nd term | |
| 1934 to 20 July 1935 | Francis Rawdon M. Crozier | ||
| 1 August 1935 to 31 July 1936 | Charles Chase Ray Nobbs | President of the Advisory Council | |
| 1 August 1936 to 31 July 1937 | Enoch Cobbcroft Robinson | 1st term | |
| 1 August 1937 to 31 July 1941 | William McLachlan | ||
| 1 August 1941 to 31 July 1947 | George Hunn Nobbs Buffett | ||
| 1 August 1947 to 31 July 1948 | Ray Herbert Hastings Nobbs | 1st term | |
| 1 August 1948 to 31 July 1949 | David Campbell Dunsmere Buffett | ||
| 1 August 1949 to 31 July 1950 | Ray Herbert Hastings Nobbs | 2nd term | |
| 1 August 1950 to 31 July 1951 | Leonard Dixon Holloway | 1st term | |
| 1 August 1951 to 5 June 1952 | Enoch Cobcroft Robinson | 2nd term | |
| 1 August 1952 to 31 October 1952 | Leonard Dixon Holloway | 2nd term | |
| 1 November 1952 to 31 July 1953 | Charles Marie Gustav Adams | ||
| 1 August 1953 to 31 July 1956 | Ray Herbert Hastings Nobbs | 3rd term | |
| 1 August 1956 to 15 June 1959 | Wilfrid Metcalfe Randall | ||
| 15 June 1959 to 22 June 1960 | vacant | ||
| 22 June 1960 to 1967 | Frederick James Needham | President of the Island Council | |
| 1967 to 1974 | William M. Randall | ||
| 1974 to 1976 | Richard Albert Bataille | ||
| 1976 to 1978 | William Arthur Blucher | ||
| 10 August 1978 | Restoration of self-government | ||
| 10 August 1979 to 21 May 1986 | David Buffett | Chief Minister | |
| 21 May 1986 to 22 May 1989 | John Terence Brown | President of the Legislative Assembly | |
| 22 May 1989 to 20 May 1992 | David Buffett | ||
| 20 May 1992 to 4 May 1994 | John Terence Brown | Head of Government | |
| 4 May 1994 to 5 May 1997 | Mike King | ||
| 5 May 1997 to 28 February 2000 | George Charles Smith | Chief Minister | |
| 28 February 2000 to 5 December 2001 | Ronald Coane Nobbs | ||
| 5 December 2001 to 1 June 2006 | Geoff Gardner | ||
| 2 June 2006 to 28 March 2007 | David Buffett | ||
| 28 March 2007 to 24 March 2010 | Andre Nobbs | ||
| 24 March 2010 to 20 March 2013 | David Buffett | ||
| 20 March 2013 to 17 June 2015 | Lisle Snell | ||
| 18 June 2015 [1] | Self-government abolished; under Commonwealth and New South Wales laws [2] | ||
| 6 July 2016 to 4 February 2021 [3] | Robin Adams | Mayor | |
| 4 February 2021 to present [3] | Mike Colreavy | Interim administrator | |

Norfolk Island is an external territory of Australia located in the Pacific Ocean between New Zealand and New Caledonia, 1,412 kilometres (877 mi) directly east of Australia's Evans Head and about 900 kilometres (560 mi) from Lord Howe Island. Together with the neighbouring Phillip Island and Nepean Island, the three islands collectively form the Territory of Norfolk Island. At the 2021 census, it had 2,188 inhabitants living on a total area of about 35 km2 (14 sq mi). Its capital is Kingston.

Politics of Norfolk Island takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic entity. Norfolk Island is the only non-mainland Australian territory to have achieved self-governance. The Norfolk Island Act 1979, passed by the Parliament of Australia in 1979, is the Act under which the island is governed.

This is a list of local government areas (LGAs) in New South Wales, sorted by region. As of September 2024 there were 128 local government areas in New South Wales, there are 33 local government areas in Greater Sydney and 95 local government areas and 12 regions in Regional NSW. All councils are listed below in alphabetical order by region. There is also the Unincorporated Far West Region which is not part of any local government area, in the sparsely inhabited Far West, and Lord Howe Island, which is also unincorporated but self-governed by the Lord Howe Island Board.

Broadland is a local government district in Norfolk, England, named after the Norfolk Broads. Its council is based at the Broadland Business Park on the outskirts of Norwich. The district includes the towns of Acle, Aylsham, Reepham, Sprowston and Thorpe St Andrew. Several of the district's settlements form part of the Norwich built-up area, lying outside the city's boundaries to the north-west and north-east. The district also includes numerous villages and surrounding rural areas. Some eastern parts of the district lie within The Broads.

Breckland is a local government district in Norfolk, England. Its council is based in Dereham, although the largest town is Thetford. The district also includes the towns of Attleborough, Swaffham and Watton, along with numerous villages and surrounding rural areas.

North Norfolk is a local government district in Norfolk, England. Its council is based in Cromer, and the largest town is North Walsham. The district also includes the towns of Fakenham, Holt, Sheringham, Stalham and Wells-next-the-Sea, along with numerous villages and surrounding rural areas.
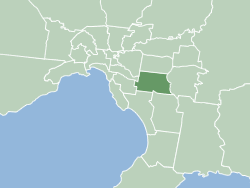
The City of Monash is a local government area in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia in the south-eastern suburbs of Melbourne with an area of 81.5 square kilometres and a population of 200,077 people in 2016.

The City of Banyule is a local government area in Victoria, Australia in the north-eastern suburbs of Melbourne. It was created under the Local Government Act 1989 and established in 1994 as an amalgamation of former councils. It has an area of 63 square kilometres (24.3 sq mi) and lies between 7 and 21 km from central Melbourne. In 1994 it had a population of 116,000. In June 2018 Banyule had a population of 130,237. The Yarra River runs along the City's southern border while its western border is defined by Darebin Creek.

The Borough of Great Yarmouth is a local government district with borough status in Norfolk, England. It is named after its main town, Great Yarmouth, and also contains the town of Gorleston-on-Sea and a number of villages and rural areas, including part of The Broads. Other notable settlements include Caister-on-Sea, Hemsby, Hopton-on-Sea and Winterton-on-Sea.
Kingborough Council is a local government body in Tasmania, and one of the five municipalities that constitutes the Greater Hobart Area. Kingborough is classified as an urban local government area and has a population of 37,734, it covers the transition from the southern urban areas of Hobart through Kingston, as well as encompassing Bruny Island.

Norfolk Island elects on territorial level a legislature. The Norfolk Island Legislative Assembly has 9 members, elected for a three-year term. The last assembly was the 14th, elected on 13 March 2013. On 17 June 2015, the Australian government abolished the assembly, ending self-government on the island. Norfolk Island Regional Council, a local government body with significantly-restricted powers, was established in July 2016 to perform local-level governance on the island.

Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Eastern Standard Time, Australian Central Standard Time and Australian Western Standard Time.

The visa policy of Australia deals with the requirements that a foreign national wishing to enter Australia must meet to obtain a visa, which is a permit to travel, to enter and remain in the country. A visa may also entitle the visa holder to other privileges, such as a right to work, study, etc. and may be subject to conditions.

The states and territories are the second level of government of Australia. The states are partially sovereign, administrative divisions that are self-governing polities, having ceded some sovereign rights to the federal government. They have their own constitutions, legislatures, executive governments, judiciaries and law enforcement agencies that administer and deliver public policies and programs. Territories can be autonomous and administer local policies and programs much like the states in practice, but are still legally subordinate to the federal government.

The Shire of Torres is a local government area located in Far North Queensland, Australia, covering large sections of the Torres Strait Islands and the northern tip of Cape York Peninsula north of 11°S latitude. It holds two distinctions—it is the northernmost Local Government Area in Australia, and is the only one to abut an international border – it is at one point just 73 kilometres (45 mi) from Papua New Guinea. It is administered from Thursday Island.

The Northern Peninsula Area Region is a local government area in Far North Queensland, Australia, covering areas on the northwestern coast of Cape York Peninsula. It was created in March 2008 out of three Aboriginal Shires and two autonomous Island Councils during a period of statewide local government reform.
The Torres Strait Island Region is a local government area in Far North Queensland, Australia, covering part of the Torres Strait Islands. It was created in March 2008 out of 15 autonomous Island Councils during a period of statewide local government reform. It has offices in each of its 15 communities, and satellite services in Thursday Island and in Cairns.

Laws regarding euthanasia or assisted suicide in Australia are matters for state and territory governments. As of June 2024 all states and the Australian Capital Territory have passed legislation creating an assisted suicide and euthanasia scheme for eligible individuals. These laws typically refer to the practices as "voluntary assisted dying".

The Norfolk Island Act 1979 is an act of the Parliament of Australia. It acknowledged the sovereign British Possession of Norfolk Islands' powers of self-government in conjunction to standing Australian policy. The Act formally recognised the Norfolk Island Legislative Assembly and the Assembly's powers to pass, amend, and repeal laws, and – subject to the assent of the Administrator of Norfolk Island – executive powers. The Act was made under the powers granted to Parliament in section 122 of the Constitution of Australia.