
The Alþingi, anglicised as Althingi or Althing, is the supreme national parliament of Iceland. It is one of the oldest surviving parliaments in the world. The Althing was founded in 930 at Þingvellir, about 45 kilometres (28 mi) east of what later became the country's capital, Reykjavík. After Iceland's union with Norway in 1262, the Althing lost its legislative power, which was not restored until 1904 when Iceland gained home rule from Denmark. For 641 years, the Althing did not serve as the parliament of Iceland; ultimate power rested with the Norwegian, and subsequently the Danish throne. Even after Iceland's union with Norway in 1262, the Althing still held its sessions at Þingvellir until 1800, when it was discontinued. It was restored in 1844 by royal decree and moved to Reykjavík. The restored unicameral legislature first came together in 1845 and after 1874 operated in two chambers with an additional third chamber taking on a greater role as the decades passed until 1991 when Althing became once again unicameral. The present parliament building, the Alþingishús, was built in 1881, made of hewn Icelandic stone. The unicameral parliament has 63 members, and is elected every four years based on party-list proportional representation. The current speaker of the Althing is Birgir Ármannsson.

Mixed-member proportional representation is a type of representation provided by some mixed electoral systems which combine local winner-take-all elections with a compensatory tier with party lists, in a way that produces proportional representation overall. Like proportional representation, MMP is not a single system, but a principle and goal of several similar systems. Some systems designed to achieve proportionality are still called mixed-member proportional, even if they generally fall short of full proportionality. In this case, they provide semi-proportional representation.
In the United Kingdom, the boundary commissions are non-departmental public bodies responsible for determining the boundaries of parliamentary constituencies for elections to the House of Commons. There are four boundary commissions: one each for England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.

The House of Assembly, or Lower House, is one of the two chambers of the Parliament of Tasmania in Australia. The other is the Legislative Council or Upper House. It sits in Parliament House in the state capital, Hobart.

An electoral district in Canada is a geographical constituency upon which Canada's representative democracy is based. It is officially known in Canadian French as a circonscription but frequently called a comté (county). In Canadian English it is also colloquially and more commonly known as a riding or constituency.
Over the history of the House of Commons, the number of Members of Parliament (MPs) has varied for assorted reasons, with increases in recent years due to increases in the population of the United Kingdom. There are currently 650 constituencies, each sending one MP to the House of Commons, corresponding to approximately one for every 92,000 people, or one for every 68,000 parliamentary electors.

Elections in Barbados are held to choose members to fill elective offices in the House of Assembly. Elections are held on Election Day. These general elections do not have fixed dates, but must be called within five years of the opening of parliament following the last election. A former minister of the DLP, Warwick Franklin summed up the general elections process in Barbados as saying it is really just, "30 by-elections on the same day."

There are three types of elections in Nepal: elections to the federal parliament, elections to the provincial assemblies and elections to the local government. Within each of these categories, there may be by-elections as well as general elections. Currently three electoral systems are used: parallel voting for the House of Representatives and provincial assemblies, single transferable vote for the National Assembly, and first-past-the-post for local elections.

In the United Kingdom (UK), each of the electoral areas or divisions called constituencies elects one member to the House of Commons.

An electorate or electoral district is a geographic constituency used for electing a member (MP) to the New Zealand Parliament. The size of electorates is determined such that all electorates have approximately the same electoral population.

The House of Assembly of Barbados is the lower house of the bicameral Parliament of Barbados. It has 30 Members of Parliament (MPs), who are directly elected in single member constituencies using the simple-majority system for a term of five years. The House of Assembly sits roughly 40–45 days a year and is presided over by a Speaker.
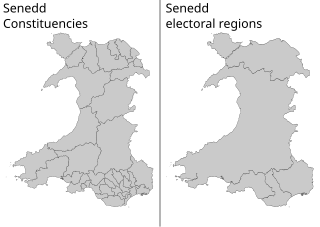
The Senedd constituencies and electoral regions are the electoral districts used to elect members of the Senedd to the Senedd, and have been used in some form since the first election of the then National Assembly for Wales in 1999. New boundaries were introduced for the 2007 elections and currently consist of forty constituencies and five regions. The five electoral regions are: Mid and West Wales, North Wales, South Wales Central, South Wales East, and South Wales West, with the forty constituencies listed below. Voting last took place in all districts in the 2021 Senedd election, and is not used for local government.

The 2008 Western Australian state election was held on Saturday 6 September 2008 to elect 59 members to the Legislative Assembly and 36 members to the Legislative Council. The incumbent centre-left Labor Party government, in power since the 2001 election and led since 25 January 2006 by Premier Alan Carpenter, was defeated by the centre-right Liberal Party opposition, led by Opposition Leader Colin Barnett since 6 August 2008.
Electoral districts go by different names depending on the country and the office being elected.
The Electoral Boundaries Readjustment Act, commonly known by its acronym EBRA, is an act of the Parliament of Canada that was passed by the 26th Canadian Parliament in 1964.
By-elections were held in the Barbadian constituencies of St. Philip North and the city of Bridgetown on 26 February 1976 and 12 May 1976 respectively. Both elections were triggered based on the resignations of House of Assembly representatives Elliot Mottley and Neville Maxwell. It was the first by-election held under the new single-member first-past-the-post system.










