Related Research Articles
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as medications to decrease blood pressure in patients with hypertension. CCBs are particularly effective against large vessel stiffness, one of the common causes of elevated systolic blood pressure in elderly patients. Calcium channel blockers are also frequently used to alter heart rate, to prevent peripheral and cerebral vasospasm, and to reduce chest pain caused by angina pectoris.

Nephrotic syndrome is a collection of symptoms due to kidney damage. This includes protein in the urine, low blood albumin levels, high blood lipids, and significant swelling. Other symptoms may include weight gain, feeling tired, and foamy urine. Complications may include blood clots, infections, and high blood pressure.

A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of migrated gallstones within bile ducts.

Hemolytic anemia or haemolytic anaemia is a form of anemia due to hemolysis, the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs), either in the blood vessels or elsewhere in the human body (extravascular). This most commonly occurs within the spleen, but also can occur in the reticuloendothelial system or mechanically. Hemolytic anemia accounts for 5% of all existing anemias. It has numerous possible consequences, ranging from general symptoms to life-threatening systemic effects. The general classification of hemolytic anemia is either intrinsic or extrinsic. Treatment depends on the type and cause of the hemolytic anemia.

Combined hyperlipidemia is a commonly occurring form of hypercholesterolemia characterised by increased LDL and triglyceride concentrations, often accompanied by decreased HDL. On lipoprotein electrophoresis it shows as a hyperlipoproteinemia type IIB. It is the most commonly inherited lipid disorder, occurring in around one in 200 persons. In fact, almost one in five individuals who develop coronary heart disease before the age of 60 have this disorder.

Chlortalidone, also known as chlorthalidone, is a thiazide-like diuretic drug used to treat high blood pressure, swelling including that due to heart failure, liver failure, and nephrotic syndrome, diabetes insipidus, and renal tubular acidosis. Because chlortalidone is reliably effective in most patients with high blood pressure, it is considered a preferred initial treatment. It is also used to prevent calcium-based kidney stones. It is taken by mouth. Effects generally begin within three hours and last for up to three days. Chlortalidone is more effective than hydrochlorothiazide for prevention of heart attack or stroke.

Xylazine is a pharmaceutical drug used for sedation, anesthesia, muscle relaxation, and analgesia in animals such as horses, cattle, and other non-human mammals. Veterinarians also use xylazine as an emetic, especially in cats. It is an analog of clonidine and an agonist at the α2 class of adrenergic receptor.

Glucuronic acid is a uronic acid that was first isolated from urine. It is found in many gums such as gum arabic, xanthan, and kombucha tea and is important for the metabolism of microorganisms, plants and animals.

A hypertensive emergency is very high blood pressure with potentially life-threatening symptoms and signs of acute damage to one or more organ systems. It is different from a hypertensive urgency by this additional evidence for impending irreversible hypertension-mediated organ damage (HMOD). Blood pressure is often above 200/120 mmHg, however there are no universally accepted cutoff values. Signs of organ damage are discussed below.

Aminoglutethimide (AG), sold under the brand names Elipten, Cytadren, and Orimeten among others, is a medication which has been used in the treatment of seizures, Cushing's syndrome, breast cancer, and prostate cancer, among other indications. It has also been used by bodybuilders, athletes, and other men for muscle-building and performance- and physique-enhancing purposes. AG is taken by mouth three or four times per day.
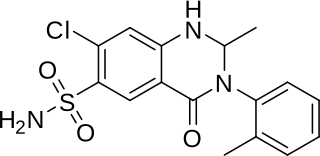
Metolazone is a thiazide-like diuretic marketed under the brand names Zytanix, Metoz, Zaroxolyn, and Mykrox. It is primarily used to treat congestive heart failure and high blood pressure. Metolazone indirectly decreases the amount of water reabsorbed into the bloodstream by the kidney, so that blood volume decreases and urine volume increases. This lowers blood pressure and prevents excess fluid accumulation in heart failure. Metolazone is sometimes used together with loop diuretics such as furosemide or bumetanide, but these highly effective combinations can lead to dehydration and electrolyte abnormalities.
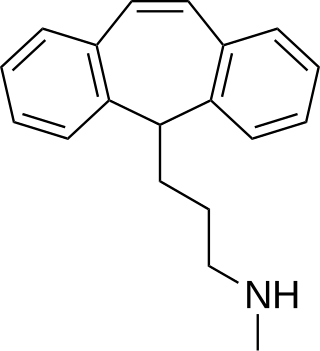
Protriptyline, sold under the brand name Vivactil among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA), specifically a secondary amine, indicated for the treatment of depression and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Uniquely among most of the TCAs, protriptyline tends to be energizing instead of sedating, and is sometimes used for narcolepsy to achieve a wakefulness-promoting effect.

Mephentermine is a cardiac stimulant.

Xipamide is a sulfonamide diuretic drug marketed by Eli Lilly under the trade names Aquaphor and Aquaphoril. It is used for the treatment of oedema and hypertension.
Glomerulonephrosis is a non-inflammatory disease of the kidney (nephrosis) presenting primarily in the glomerulus as Nephrotic Syndrome. The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney and it contains the glomerulus, which acts as a filter for blood to retain proteins and blood lipids. Damage to these filtration units results in important blood contents being released as waste in urine. This disease can be characterized by symptoms such as fatigue, swelling, and foamy urine, and can lead to chronic kidney disease and ultimately end-stage renal disease, as well as cardiovascular diseases. Glomerulonephrosis can present as either primary glomerulonephrosis or secondary glomerulonephrosis.

Butizide is a diuretic of the thiazide class.
References
- ↑ Biochemistry Mnemonics for Health Sciences Students & Professionals. Examville Study Guides. p. 6.
- ↑ "Clinical Cases Cholelithiasis (Gallstones)". University of Michigan. Retrieved 12 May 2015.
- 1 2 Mega List of Mnemonics for Nurses & Nursing Students. Examville Study Guides. 2010.
- ↑ Causes of pancreatitis (mnemonic)
- ↑ "Hepatology Mnemonics - Oxford Medical Education" . Retrieved 2015-08-23.