Related Research Articles
Activities of daily living (ADLs) is a term used in healthcare to refer to an individual's daily self-care activities. Health professionals often use a person's ability or inability to perform ADLs as a measure of their functional status. The concept of ADLs was originally proposed in the 1950s by Sidney Katz and his team at the Benjamin Rose Hospital in Cleveland, Ohio. Since then, numerous researchers have expanded on the concept of ADLs. For instance, many indexes that assess ADLs now incorporate measures of mobility.
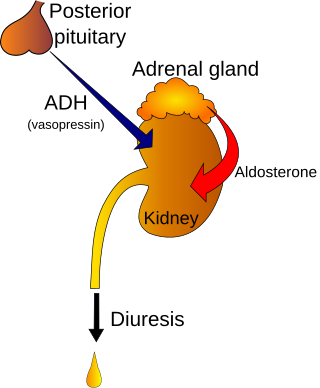
Polyuria is excessive or an abnormally large production or passage of urine. Increased production and passage of urine may also be termed as diuresis. Polyuria often appears in conjunction with polydipsia, though it is possible to have one without the other, and the latter may be a cause or an effect. Primary polydipsia may lead to polyuria. Polyuria is usually viewed as a symptom or sign of another disorder, but it can be classed as a disorder, at least when its underlying causes are not clear.

Geriatrics, or geriatric medicine, is a medical specialty focused on providing care for the unique health needs of the elderly. The term geriatrics originates from the Greek γέρων geron meaning "old man", and ιατρός iatros meaning "healer". It aims to promote health by preventing, diagnosing and treating disease in older adults. There is no defined age at which patients may be under the care of a geriatrician, or geriatric physician, a physician who specializes in the care of older people. Rather, this decision is guided by individual patient need and the caregiving structures available to them. This care may benefit those who are managing multiple chronic conditions or experiencing significant age-related complications that threaten quality of daily life. Geriatric care may be indicated if caregiving responsibilities become increasingly stressful or medically complex for family and caregivers to manage independently.

Hypovolemia, also known as volume depletion or volume contraction, is a state of abnormally low extracellular fluid in the body. This may be due to either a loss of both salt and water or a decrease in blood volume. Hypovolemia refers to the loss of extracellular fluid and should not be confused with dehydration.
Nursing assessment is the gathering of information about a patient's physiological, psychological, sociological, and spiritual status by a licensed Registered Nurse. Nursing assessment is the first step in the nursing process. A section of the nursing assessment may be delegated to certified nurses aides. Vitals and EKG's may be delegated to certified nurses aides or nursing techs. It differs from a medical diagnosis. In some instances, the nursing assessment is very broad in scope and in other cases it may focus on one body system or mental health. Nursing assessment is used to identify current and future patient care needs. It incorporates the recognition of normal versus abnormal body physiology. Prompt recognition of pertinent changes along with the skill of critical thinking allows the nurse to identify and prioritize appropriate interventions. An assessment format may already be in place to be used at specific facilities and in specific circumstances.
Abnormal posturing is an involuntary flexion or extension of the arms and legs, indicating severe brain injury. It occurs when one set of muscles becomes incapacitated while the opposing set is not, and an external stimulus such as pain causes the working set of muscles to contract. The posturing may also occur without a stimulus. Since posturing is an important indicator of the amount of damage that has occurred to the brain, it is used by medical professionals to measure the severity of a coma with the Glasgow Coma Scale and the Pediatric Glasgow Coma Scale.
eMedicine is an online clinical medical knowledge base founded in 1996 by doctors Scott Plantz and Jonathan Adler, and computer engineer Jeffrey Berezin. The eMedicine website consists of approximately 6,800 medical topic review articles, each of which is associated with a clinical subspecialty "textbook". The knowledge base includes over 25,000 clinically multimedia files.

Nezelof syndrome is an autosomal recessive congenital immunodeficiency condition due to underdevelopment of the thymus. The defect is a type of purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency with inactive phosphorylase, this results in an accumulation of deoxy-GTP which inhibits ribonucleotide reductase. Ribonucleotide reductase catalyzes the formation of deoxyribonucleotides from ribonucleotides, thus, DNA replication is inhibited.

Gerontological nursing is the specialty of nursing pertaining to older adults. Gerontological nurses work in collaboration with older adults, their families, and communities to support healthy aging, maximum functioning, and quality of life. The term gerontological nursing, which replaced the term geriatric nursing in the 1970s, is seen as being more consistent with the specialty's broader focus on health and wellness, in addition to illness.
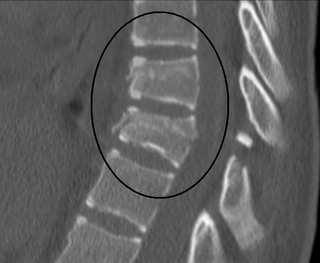
A Chance fracture is a type of vertebral fracture that results from excessive flexion of the spine. Symptoms may include abdominal bruising, or less commonly paralysis of the legs. In around half of cases there is an associated abdominal injury such as a splenic rupture, small bowel injury, pancreatic injury, or mesenteric tear. Injury to the bowel may not be apparent on the first day.
Brief psychotic disorder—according to the classifications of mental disorders DSM-IV-TR and DSM-5—is a psychotic condition involving the sudden onset of at least one psychotic symptom lasting 1 day to 1 month, often accompanied by emotional turmoil. Remission of all symptoms is complete with patients returning to the previous level of functioning. It may follow a period of extreme stress including the loss of a loved one. Most patients with this condition under DSM-5 would be classified as having acute and transient psychotic disorders under ICD-10. Prior to DSM-IV, this condition was called "brief reactive psychosis." This condition may or may not be recurrent, and it should not be caused by another condition.

A pediatric intensive care unit, usually abbreviated to PICU, is an area within a hospital specializing in the care of critically ill infants, children, teenagers, and young adults aged 0–21. A PICU is typically directed by one or more pediatric intensivists or PICU consultants and staffed by doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists who are specially trained and experienced in pediatric intensive care. The unit may also have nurse practitioners, physician assistants, physiotherapists, social workers, child life specialists, and clerks on staff, although this varies widely depending on geographic location. The ratio of professionals to patients is generally higher than in other areas of the hospital, reflecting the acuity of PICU patients and the risk of life-threatening complications. Complex technology and equipment is often in use, particularly mechanical ventilators and patient monitoring systems. Consequently, PICUs have a larger operating budget than many other departments within the hospital.
An androgen-dependent condition, disease, disorder, or syndrome, is a medical condition that is, in part or full, dependent on, or is sensitive to, the presence of androgenic activity in the body.
A chemical restraint is a form of medical restraint in which a drug is used to restrict the freedom or movement of a patient or in some cases to sedate the patient. Chemical restraint is used in emergency, acute, and psychiatric settings to perform surgery or to reduce agitation, aggression or violent behaviours; it may also be used to control or punish unruly behaviours. Chemical restraint is also referred to as a "Psychopharmacologic Agent", "Psychotropic Drug" or "Therapeutic Restraints" in certain legal writing.

Trauma in children, also known as pediatric trauma, refers to a traumatic injury that happens to an infant, child or adolescent. Because of anatomical and physiological differences between children and adults the care and management of this population differs.

J. B. Lippincott & Co. was an American publishing house founded in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in 1836 by Joshua Ballinger Lippincott. It was incorporated in 1885 as J. B. Lippincott Company.
The JumpSTART pediatric triage MCI triage tool is a variation of the simple triage and rapid treatment (START) triage system. Both systems are used to sort patients into categories at mass casualty incidents (MCIs). However, JumpSTART was designed specifically for triaging children in disaster settings. Though JumpSTART was developed for use in children from infancy to age 8, where age is not immediately obvious, it is used in any patient who appears to be a child.

Suresh Samuel David is an Indian physician specializing in emergency medicine. The first Indian physician to be formally trained in emergency medicine, David pioneered the practice of emergency medicine in India and is credited with founding the department of emergency medicine at Christian Medical College, Vellore. He is the first person to hold the position of a professor in the discipline of Emergency Medicine in India.
Mark Charles Rogers is an American physician, medical entrepreneur, professor, and hospital administrator. He is a pediatrician, anesthesiologist, and cardiologist with a specialty in critical care medicine. With a medical career focused on pediatric intensive care, Rogers was founder of the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit at Johns Hopkins Hospital, working there from 1977 to 1991. He concurrently served as chairman of the Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine beginning in 1980 and was a professor of anesthesiology and pediatrics throughout his tenure at Johns Hopkins.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Avner JR (2006). "Altered States of Consciousness". Pediatrics in Review. 27 (9): 331–338. doi:10.1542/pir.27-9-331. PMID 16950938 . Retrieved January 31, 2016.
- 1 2 3 Teitelbaum, Jonathan; Deantonis, Kathleen; Kahan, Scott (June 24, 2004). Pediatric Signs and Symptoms (1st ed.). Blackwell Publishing. pp. 177–180. ISBN 978-1405104272.
- 1 2 3 Akbary S; Kannikeswaran N (2012). "Acute Onset Altered Mental Status in a Previously Healthy Teenager". Pediatric Emergency Care. 28 (4). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc.: 376–379. doi:10.1097/PEC.0b013e31824d9d3f. PMID 22472657.
- 1 2 3 Melillo KD (1991). "Mnemonics: Use in Gerontological Nursing Practice". Journal of Gerontological Nursing. 17 (7): 40–43. doi:10.3928/0098-9134-19910701-13. PMID 2071857.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Wolfson, Allan B.; Hendey, Gregory W.; et al. (2009). Clinical Practice of Emergency Medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. p. 1121. ISBN 9780781789431.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Sanders, Mick J.; McKenna, Kim D.; et al. (2011). Mosby's Paramedic Textbook. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. p. 778. ISBN 9780323072755.
- 1 2 3 4 Forgey, M.D., William W. (November 6, 2012). Wilderness Medicine: Beyond First Aid (6th ed.). Morris Book Publishing, Inc. ISBN 978-0762780709.
- ↑ Stokes, H.; Ihidero, O.; Fox, G.; O'Neill, M. (2011). "Case 2: Coma in an apparently well toddler". Paediatrics & Child Health. 16 (8): 465–467. doi:10.1093/pch/16.8.465. PMC 3202383 . PMID 23024582.