
The Boston and Maine Railroad was a U.S. Class I railroad in northern New England. Originally chartered in 1835, it became part of what is now the Pan Am Railways network in 1983.
The Pennsylvania Railroad was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and was headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was so named because it was established in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania.
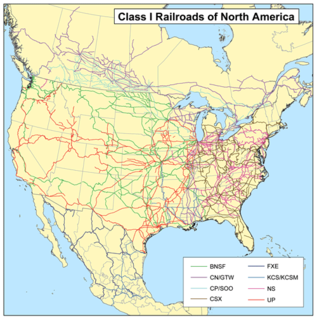
In the United States, railroad carriers are designated as Class I, II, or III, according to annual revenue criteria originally set by the Surface Transportation Board in 1992. With annual adjustments for inflation, the 2019 thresholds were US$504,803,294 for Class I carriers and US$40,384,263 for Class II carriers.

The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad, commonly known as The Consolidated or simply as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in the New England region of the United States from 1872 to December 31, 1968. Founded by the merger of the New York and New Haven and Hartford and New Haven railroads, the company had near-total dominance of railroad traffic in Southern New England for the first half of the 20th century.

The Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad (CMStP&P), often referred to as the "Milwaukee Road", was a Class I railroad that operated in the Midwest and Northwest of the United States from 1847 until 1986.

The Pittsburgh Locomotive and Car Works was a railroad equipment manufacturing company founded by Andrew Carnegie and T.N. Miller in 1865. It was located in Allegheny, Pennsylvania, a suburb of Pittsburgh and since 1907 part of that city.

The Chicago and North Western Transportation Company was a Class I railroad in the Midwestern United States. It was also known as the "North Western". The railroad operated more than 5,000 miles (8,000 km) of track at the turn of the 20th century, and over 12,000 miles (19,000 km) of track in seven states before retrenchment in the late 1970s. Until 1972, when the employees purchased the company, it was named the Chicago and North Western Railway.

The Illinois Central Railroad, sometimes called the Main Line of Mid-America, was a railroad in the central United States, with its primary routes connecting Chicago, Illinois, with New Orleans, Louisiana, and Mobile, Alabama. A line also connected Chicago with Sioux City, Iowa (1870). There was a significant branch to Omaha, Nebraska (1899), west of Fort Dodge, Iowa, and another branch reaching Sioux Falls, South Dakota (1877), starting from Cherokee, Iowa. The Sioux Falls branch has been abandoned in its entirety.

The Atlantic Coast Line Railroad is a former U. S. Class I railroad formed in 1900, though predecessor railroads had used the ACL brand since 1871. In 1967 it merged with long-time rival Seaboard Air Line Railroad to form the Seaboard Coast Line Railroad. Much of the original ACL network has been part of CSX Transportation since 1986.

The Louisville and Nashville Railroad, commonly called the L&N, was a Class I railroad that operated freight and passenger services in the southeast United States.

The Pennsylvania-Reading Seashore Lines was a railroad that operated in southern New Jersey in the 20th century. It was created in 1933 as a joint consolidation venture between two competing railroads in the region.

Conrail, formally the Consolidated Rail Corporation, was the primary Class I railroad in the Northeastern United States between 1976 and 1999. The trade name Conrail is a portmanteau based on the company's legal name. It continues to do business as an asset management and network services provider in three Shared Assets Areas that were excluded from the division of its operations during its acquisition by CSX Corporation and the Norfolk Southern Railway.
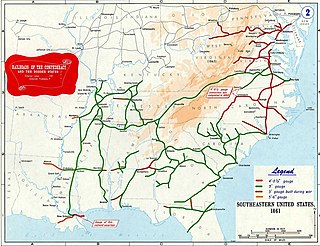
The American Civil War was the first in which large armies depended heavily on railroads to bring supplies. For the Confederate States Army, the system was fragile and was designed for short hauls of cotton to the nearest river or ocean port. During the war, new parts were hard to obtain, and the system deteriorated from overuse, lack of maintenance, and systematic destruction by Union raiders.

Hawleyville is an unincorporated community in Fairfield County in the town of Newtown, Connecticut, about 1 mile outside the borough of Newtown. It was listed as a census-designated place prior to the 2020 census.

The Toledo, St. Louis and Western Railroad, often abbreviated TStL&W and commonly known as the Clover Leaf, was a railroad company that operated in northwestern Ohio, north central Indiana, and south central Illinois during the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
A shortline railroad is a small or mid-sized railroad company that operates over a relatively short distance relative to larger, national railroad networks. The term is used primarily in the United States and Canada. In the U.S., railroads are categorized by operating revenue, and most shortline railroads fall into the Class III or Class II categorization defined by the Surface Transportation Board. Shortlines generally exist for one of three reasons: to link two industries requiring rail freight together ; to interchange revenue traffic with other, usually larger, railroads; or to operate a tourist passenger train service. Often, short lines exist for all three of these reasons.

The Vandalia Railroad Company was incorporated January 1, 1905, by a merger of several lines in Indiana and Illinois that formed a 471-mile railroad consisting of lines mostly west of Indianapolis.














