
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the first common carrier railroad and the oldest railroad in the United States. It operated as B&O from 1830 until 1987, when it was merged into the Chessie System; its lines are today controlled by CSX Transportation.

The Washington–Baltimore combined metropolitan statistical area is a statistical area including the overlapping metropolitan areas of Washington, D.C. and of Baltimore. The region includes Central Maryland, Northern Virginia, three counties in the Eastern Panhandle of West Virginia, and one county in south-central Pennsylvania. It is the most educated, highest-income, and third-largest combined statistical area in the United States behind New York City–Newark, NJ and Los Angeles–Long Beach.

MARC is a commuter rail system in the Washington–Baltimore area. MARC is administered by the Maryland Transit Administration (MTA) and operated under contract by Alstom and Amtrak on track owned by CSX Transportation (CSXT) and Amtrak. In 2023, the system had a ridership of 3,860,600, or about 12,400 per weekday as of the fourth quarter of 2023, less than pre-COVID-19 pandemic weekday ridership of 40,000.

The Western Maryland Railway was an American Class I railroad (1852–1983) that operated in Maryland, West Virginia, and Pennsylvania. It was primarily a coal hauling and freight railroad, with a small passenger train operation.
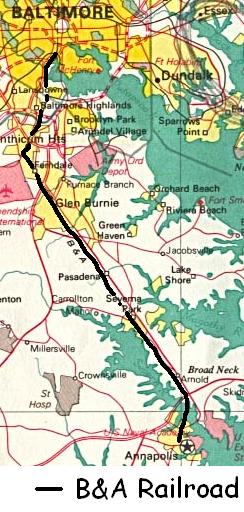
The Baltimore & Annapolis Railroad was an American railroad of central Maryland built in the 19th century. The railroad, the second to serve Annapolis, ran between Annapolis and Clifford along the north shore of the Severn River. From Clifford, just north of the present day Patapsco Light Rail Stop, it connected with the B&O's Curtis Bay branch so that trains could travel to Baltimore. In 1921, when it was called the Annapolis and Baltimore Short Line, it was purchased by the larger Washington, Baltimore and Annapolis Electric Railway (WB&A), and then emerged from the WB&A's 1935 bankruptcy and closure as the Baltimore & Annapolis Railroad. B&A electric passenger operation between the two cities continued until 1950, at which time the rail line became solely a freight carrier, operating buses for passenger service. Freight service to Annapolis continued until June 1968 when the Severn River Trestle was declared unsafe. In the 1980s, the line was completely shut down. The right-of-way now serves as part of Baltimore's light rail system and as the Baltimore & Annapolis Trail.

The Maryland and Pennsylvania Railroad, colloquially known as the "Ma and Pa", was an American short-line railroad between York and Hanover, Pennsylvania, formerly operating passenger and freight trains on its original line between York and Baltimore, Maryland, from 1901 until the 1950s. The Ma and Pa was popular with railfans in the 1930s and 1940s for its antique equipment and curving, picturesque right-of-way through the hills of rural Maryland and Pennsylvania. Reflecting its origin as the unintended product of the merger of two 19th-century narrow-gauge railways, the meandering main line took 77.2 miles (124 km) to connect Baltimore and York, although the two cities are only 45 miles (72 km) apart.

Streetcars and interurbans operated in the Maryland suburbs of Washington, D.C., between 1890 and 1962.

The Baltimore–Columbia–Towson Metropolitan Statistical Area, also known as Central Maryland, is a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) in Maryland as defined by the United States Office of Management and Budget (OMB). It is part of the larger Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area. As of 2022, the combined population of the seven counties is 2,985,871, making it the 20th-largest metropolitan statistical area in the nation.

U.S. Route 40 in the U.S. state of Maryland runs from Garrett County in Western Maryland to Cecil County in the state's northeastern corner. With a total length of 221 miles (356 km), it is the longest numbered highway in Maryland. Almost half of the road overlaps or parallels with Interstate 68 (I-68) or I-70, while the old alignment is generally known as US 40 Alternate, US 40 Scenic, or Maryland Route 144. West of Baltimore, in the Piedmont and Appalachian Mountains / Blue Ridge region of the Western Maryland panhandle of the small state, the portions where it does not overlap an Interstate highway are mostly two-lane roads. The portion northeast of Baltimore going toward Wilmington in northern Delaware and Philadelphia in southeastern Pennsylvania is a four-lane divided highway, known as the Pulaski Highway. This section crosses the Susquehanna River at the north end of the Chesapeake Bay on the Thomas J. Hatem Memorial Bridge.
The Hagerstown and Frederick Railway, now defunct, was an American railroad of central Maryland built in the 19th and 20th centuries.
The Chambersburg, Greencastle & Waynesboro Street Railway, now defunct, was an American railroad of south central Pennsylvania built in the 19th and 20th centuries.

The Queen Anne’s Railroad was a railroad that ran between Love Point, Maryland, and Lewes, Delaware, with connections to Baltimore via ferry across the Chesapeake Bay. The Queen Anne's Railroad company was formed in Maryland in 1894, and received legislative authorization from Delaware in February 1895. The railroad's original western terminus was in Queenstown, Maryland, and was moved via a 13-mile (21 km) extension to Love Point in 1902, which shortened the ferry trip to Baltimore.

The Washington, Baltimore and Annapolis Electric Railway (WB&A) was an American railroad of central Maryland and Washington, D.C., built in the 19th and 20th century. The WB&A absorbed two older railroads, the Annapolis and Elk Ridge Railroad and the Baltimore & Annapolis Short Line, and added its own electric streetcar line between Baltimore and Washington. It was built by a group of Cleveland, Ohio, electric railway entrepreneurs to serve as a high-speed, showpiece line using the most advanced technology of the time. It served Washington, Baltimore, and Annapolis, Maryland, for 27 years before the "Great Depression" and the rise of the automobile forced an end to passenger service during the economic pressures of the 1930s "Depression" southwest to Washington from Baltimore & west from Annapolis in 1935. Only the Baltimore & Annapolis portion between the state's largest city and its state capital continued to operate electric rail cars for another two decades, replaced by a bus service during the late 1950s into 1968. Today, parts of the right-of-way are used for the light rail line, rail trail for hiking - biking trails, and roads through Anne Arundel County.
The Fuller Syndicate was a group of American financiers that invested in railroads in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.

John Mifflin Hood (1843–1906) was an American railroad and electric streetcar system executive.
The Baltimore, Chesapeake and Atlantic railroad, nicknamed Black Cinders & Ashes, ran from Claiborne, Maryland, to Ocean City, Maryland. It operated 87 miles (140.0 km) of center-line track and 15.6 miles (25.11 km) of sidings. Chartered in 1886, the railroad started construction in 1889 and cost $2.356 million ($2024=79,895,000).










