This article needs additional citations for verification .(July 2016) |
The following railroads operate in the U.S. state of Maine.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(July 2016) |
The following railroads operate in the U.S. state of Maine.
Maine train stations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

The Downeaster is a 145-mile (233 km) passenger train service operated by Amtrak and managed by the Northern New England Passenger Rail Authority (NNEPRA), an agency of the state of Maine. Named for the Down East region of Maine, the train operates five daily round trips between North Station in Boston, Massachusetts, and Brunswick, Maine, with 10 intermediate stops.

The Maine Central Railroad was a U. S. class 1 railroad in central and southern Maine. It was chartered in 1856 and began operations in 1862. By 1884, Maine Central was the longest railroad in New England. Maine Central had expanded to 1,358 miles (2,185 km) when the United States Railroad Administration assumed control in 1917. The main line extended from South Portland, Maine, east to the Canada–United States border with New Brunswick, and a Mountain Division extended west from Portland to St. Johnsbury, Vermont, and north into Quebec. The main line was double track from South Portland to Royal Junction, where it split into a "lower road" through Brunswick and Augusta and a "back road" through Lewiston, which converged at Waterville into single track to Bangor and points east. Branch lines served the industrial center of Rumford, a resort hotel on Moosehead Lake and coastal communities from Bath to Eastport.

Interstate 95 (I-95) is a part of the Interstate Highway System that runs north–south from Miami, Florida to Houlton, Maine. The highway enters Maine from the New Hampshire state line in Kittery and runs for 303 miles (488 km) to the Canadian border in Houlton. It is the only primary Interstate Highway in Maine. In 2004, the highway's route between Portland and Gardiner was changed so that it encompasses the entire Maine Turnpike, a toll road running from Kittery to Augusta.

The railroad history of Portland, Maine, began in 1842 with the arrival of the Portland, Saco & Portsmouth Railway (PS&P). Most of the rail activity in Portland revolved around agricultural goods bound for export and import freight from Europe. Yet Maine's largest city also enjoyed 125 years of continuous passenger rail service, from 1842 until 1967, and Amtrak began serving the city in 2001. For most of Portland's history, passenger train schedules were designed with intercity travel rather than daily commuting in mind; passenger activities were mostly confined to intercity travel from Portland to Boston, Montreal, Nova Scotia, and points west.

The Rockland Branch is a railroad from Brunswick, Maine to Rockland, Maine. A charter was granted in 1849 to build a railway from the Portland and Kennebec Railroad on the west side of the Kennebec River to Rockland. Construction through the rocky headlands of the Atlantic coast proved more expensive than anticipated. The Knox and Lincoln Railroad commenced service to Rockland in 1871 using a ferry to cross the Kennebec River between Bath and Woolwich. The Knox and Lincoln was leased by Maine Central Railroad in 1891, and became Maine Central's Rockland Branch in 1901. Maine Central purchased the Samoset destination hotel in nearby Glen Cove in 1912, and offered direct passenger service for summer visitors from the large eastern cities. Carlton bridge was completed in 1927 to carry the railroad and U.S. Route 1 over the Kennebec River. Maine Central sold the Samoset hotel in 1941, and the last Maine Central passenger train to Rockland was on 4 April 1959. The State of Maine purchased the branch in 1987 to prevent abandonment. The line has subsequently been operated by the Maine Coast Railroad, the Maine Eastern Railroad, and, beginning in 2016, the Central Maine and Quebec Railway. In 2019, Canadian Pacific Railway agreed to purchase the Central Maine and Quebec, thereby inheriting the operation of the Rockland Branch. The acquisition was completed on June 3, 2020.
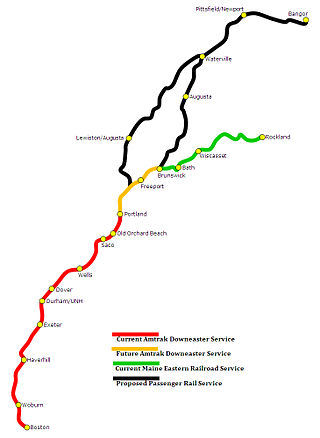
Trainriders Northeast is a non-profit citizens' organization group based out of Portland, Maine, in the United States. It was established in 1989 to advocate for the extension of passenger rail service from Boston to Portland and points north. Today Trainriders Northeast may be most well known for their role in bringing passenger service back to Portland, with the Amtrak Downeaster.

Originally, various track gauges were used in the United States. Some railways, primarily in the northeast, used standard gauge of 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in ; others used gauges ranging from 2 ft to 6 ft. As a general rule, southern railroads were built to one or another broad gauge, mostly 5 ft, while northern railroads that were not standard-gauge tended to be narrow-gauge. The Pacific Railroad Acts of 1863 specified standard gauge.
Below is the list of the 124th Maine Senate, which was sworn into office on December 3, 2008 and left office in December 2010.
William Robinson Miller (1866–1929) was an American architect from Maine. He specialized in richly ornamented Romanesque- and French-Revival buildings. Born in Durham, Maine, Miller attended Bates College and the School of Architecture at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (1891–1892).

The Maine Central Railroad Company main line extended from Portland, Maine, east to the Canada–US border with New Brunswick at the Saint Croix-Vanceboro Railway Bridge. It is the transportation artery linking Maine cities to the national railway network. Sections of the main line had been built by predecessor railroads consolidated as the Maine Central in 1862 and extended to the Canada–US border in 1882. Through the early 20th century, the main line was double track from South Portland to Royal Junction, where it split into a lower road through Brunswick and Augusta and a back road through Lewiston which converged at Waterville into single track to Bangor and points east. Westbound trains typically used the lower road with lighter grades, while eastbound trains of empty cars used the back road. This historical description does not include changes following purchase of the Maine Central Railroad by Guilford Transportation Industries in 1981 and subsequent operation as part of Pan Am Railways.

The Portland–Lewiston Interurban (PLI) was an electric railroad subsidiary of the Androscoggin Electric Company operating from 1914 to 1933 between Monument Square in Portland and Union Square in Lewiston, Maine. Hourly service was offered over the 40-mile (64 km) route between the two cities. Express trains stopping only at West Falmouth, Gray, New Gloucester, Upper Gloucester and Danville made the trip in 80 minutes, while trains making other local stops upon request required 20 minutes more. The line was considered the finest interurban railroad in the state of Maine.

Union Station was a train station in Portland, Maine.
The Maine State League was a Class D level minor league baseball league that played in the 1897, 1907 and 1908 seasons. The eight–team Maine State League consisted of teams based in Maine and New Hampshire. The Maine State League permanently folded after the 1908 season. The Portland (1897), Bangor Cubs (1907) and Bangor White Sox (1908) teams won league championships.
Minor league baseball teams were based in Bangor, Maine between 1894 and 1913, before resuming minor league play in 1994. Playing under numerous nicknames, Bangor teams played as members of the New England League from 1894 to 1896, Maine State League in 1897, New England League in 1901, Maine State League from 1907–1908 and New Brunswick-Maine League in 1913, winning two league championships while hosting early minor league home games at Maplewood Park.
Amos Fitz Gerald was a railroad engineer from Maine, United States. He was nicknamed the "Electric Railway King" of the state due to his building 125 miles of Maine's early railroads.