Interstate regions
Census Bureau-designated regions and divisions

Since 1950, the United States Census Bureau defines four statistical regions, with nine divisions. [1] [2] The Census Bureau region definition is "widely used [...] for data collection and analysis", [3] and is the most commonly used classification system. [4] [5] [6] [7]
Puerto Rico and other US territories are not part of any census region or census division. [8]
Federal Reserve Banks

The Federal Reserve Act of 1913 divided the country into twelve districts with a central Federal Reserve Bank in each district. These twelve Federal Reserve Banks together form a major part of the Federal Reserve System, the central banking system of the United States. Missouri is the only U.S. state to have two Federal Reserve locations within its borders, but several other states are also divided between more than one district.
Time zones

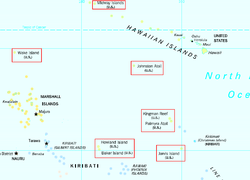
- UTC−12:00 (Baker Island, Howland Island)
- Samoa Time Zone (American Samoa, Jarvis Island, Kingman Reef, Midway Atoll, Palmyra Atoll)
- Hawaii–Aleutian Time Zone (Hawaii, Aleutian Islands (Alaska), Johnston Atoll)
- Alaska Time Zone (Alaska, excluding Aleutian Islands)
- Pacific Time Zone
- Arizona Time Zone (excluding the Navajo Nation) [9]
- Mountain Time Zone (excluding most parts of Arizona)
- Central Time Zone
- Eastern Time Zone
- Atlantic Time Zone (Puerto Rico, U.S. Virgin Islands)
- Chamorro Time Zone (Guam, Northern Mariana Islands)
- Wake Island Time Zone (Wake Island)
Courts of Appeals circuits
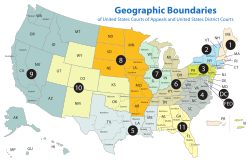
- First Circuit
- Second Circuit
- Third Circuit
- Fourth Circuit
- Fifth Circuit
- Sixth Circuit
- Seventh Circuit
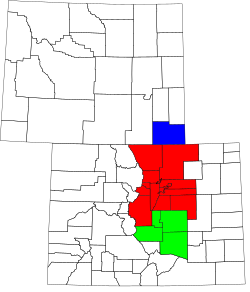
- Eighth Circuit
- Ninth Circuit
- Tenth Circuit
- Eleventh Circuit
- D.C. Circuit
The Federal Circuit is not a regional circuit. Its jurisdiction is nationwide but based on the subject matter.
Agency administrative regions
In 1969, the Office of Management and Budget published a list of ten "Standard Federal Regions", [10] to which federal agencies could be restructured as a means of standardizing government administration nationwide. Despite a finding in 1977 that this restructuring did not reduce administrative costs as initially expected, [11] and the complete rescinding of the standard region system in 1995, [12] several agencies continue to follow the system, including the Environmental Protection Agency [13] [14] and the Department of Housing and Urban Development. [15]
Regions and office locations

Region I
Office location: Boston
States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont
Region II
Office location: New York City
States: New York, New Jersey, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands
Region III
Office location: Philadelphia
States: Delaware, Maryland, Pennsylvania, Virginia, Washington, D.C., and West Virginia
Region IV
Office location: Atlanta
States: Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Tennessee
Region V
Office location: Chicago
States: Illinois, Indiana, Minnesota, Michigan, Ohio, and Wisconsin
Region VI
Office location: Dallas
States: Arkansas, Louisiana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Texas
Region VII
Office location: Kansas City
Region VIII
Office location: Denver
States: Colorado, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Utah, and Wyoming
Region IX
Office location: San Francisco
States: Arizona, California, Hawaii, Nevada, Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, American Samoa, U.S. Minor Outlying Islands in the Pacific, the Freely Associated States of the Federated States of Micronesia, and the Republic of Palau.
Region X
Office location: Seattle
States: Alaska, Idaho, Oregon, and Washington
Bureau of Economic Analysis regions

The Bureau of Economic Analysis defines regions for comparison of economic data. [16]
- New England: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont
- Mideast: Delaware, Maryland, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, and Washington, D.C.
- Great Lakes: Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Ohio, and Wisconsin
- Plains: Iowa, Kansas, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, and South Dakota
- Southeast: Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, and West Virginia
- Southwest: Arizona, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Texas
- Rocky Mountain: Colorado, Idaho, Montana, Utah, and Wyoming
- Far West: Alaska, California, Hawaii, Nevada, Oregon, and Washington