
The United States had an official estimated resident population of 334,914,895 on July 1, 2023, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. This figure includes the 50 states and the District of Columbia but excludes the population of five unincorporated U.S. territories as well as several minor island possessions. The United States is the third most populous country in the world. The Census Bureau showed a population increase of 0.4% for the twelve-month period ending in July 2022, below the world average annual rate of 0.9%. The total fertility rate in the United States estimated for 2022 is 1.665 children per woman, which is below the replacement fertility rate of approximately 2.1.
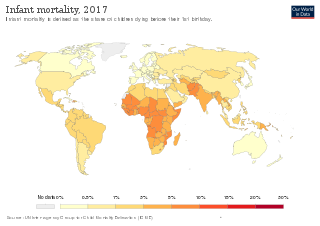
Infant mortality is the death of an infant before the infant's first birthday. The occurrence of infant mortality in a population can be described by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the number of deaths of infants under one year of age per 1,000 live births. Similarly, the child mortality rate, also known as the under-five mortality rate, compares the death rate of children up to the age of five.
The maternal mortality ratio is a key performance indicator (KPI) for efforts to improve the health and safety of mothers before, during, and after childbirth per country worldwide. Often referred to as MMR, it is the annual number of female deaths per 100,000 live births from any cause related to or aggravated by pregnancy or its management. It is not to be confused with the maternal mortality rate, which is the number of maternal deaths in a given period per 100,000 women of reproductive age during the same time period. The statistics are gathered by WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA, World Bank Group, and the United Nations Population Division. The yearly report started in 1990 and is called Trends in Maternal Mortality. As of the 2015 data published in 2016, the countries that have seen an increase in the maternal mortality ratio since 1990 are the Bahamas, Georgia, Guyana, Jamaica, Dem. People’s Rep. Korea, Serbia, South Africa, St. Lucia, Suriname, Tonga, United States, Venezuela, RB Zimbabwe. But according to Sustainable Development Goals report 2018, the overall maternal mortality ratio has declined by 37 percent since 2002. Nearly 303,000 women died due to complications during pregnancy.

Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to pregnancy, underlying conditions worsened by the pregnancy or management of these conditions. This can occur either while she is pregnant or within six weeks of resolution of the pregnancy. The CDC definition of pregnancy-related deaths extends the period of consideration to include one year from the resolution of the pregnancy. Pregnancy associated death, as defined by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), are all deaths occurring within one year of a pregnancy resolution. Identification of pregnancy associated deaths is important for deciding whether or not the pregnancy was a direct or indirect contributing cause of the death.

Sexual and reproductive health (SRH) is a field of research, health care, and social activism that explores the health of an individual's reproductive system and sexual well-being during all stages of their life. Sexual and reproductive health is more commonly defined as sexual and reproductive health and rights, to encompass individual agency to make choices about their sexual and reproductive lives.
The 2010 census estimated Alabama's population at 4,802,740, an increase of 332,636 or 7.5% since 2000. This includes a natural increase of 87,818 and a net migration of 73,178 people into the state. Immigration from outside the United States resulted in a net increase of 30,537 and migration within the country produced a net increase of 42,641.

Child mortality is the mortality of children under the age of five. The child mortality rate refers to the probability of dying between birth and exactly five years of age expressed per 1,000 live births.
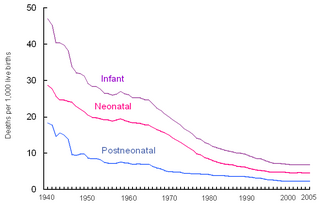
Perinatal mortality (PNM) is the death of a fetus or neonate and is the basis to calculate the perinatal mortality rate. Perinatal means "relating to the period starting a few weeks before birth and including the birth and a few weeks after birth."
Maternal health is the health of women during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. In most cases, maternal health encompasses the health care dimensions of family planning, preconception, prenatal, and postnatal care in order to ensure a positive and fulfilling experience. In other cases, maternal health can reduce maternal morbidity and mortality. Maternal health revolves around the health and wellness of pregnant women, particularly when they are pregnant, at the time they give birth, and during child-raising. WHO has indicated that even though motherhood has been considered as a fulfilling natural experience that is emotional to the mother, a high percentage of women develop health problems and sometimes even die. Because of this, there is a need to invest in the health of women. The investment can be achieved in different ways, among the main ones being subsidizing the healthcare cost, education on maternal health, encouraging effective family planning, and ensuring progressive check up on the health of women with children. Maternal morbidity and mortality particularly affects women of color and women living in low and lower-middle income countries.

This is a list of US states by gun deaths and rates of violence. In 2021, there were 26,000 gun suicides and 21,000 gun homicides, together making up a sixth of deaths from external causes. Gun deaths make up about half of all suicides, but over 80% of homicides.

Niger is a landlocked country located in West Africa and has Libya, Chad, Nigeria, Benin, Mali, Burkina Faso, and Algeria as its neighboring countries. Niger was French territory that got its independence in 1960 and its official language is French. Niger has an area of 1.267 million square kilometres, nevertheless, 80% of its land area spreads through the Sahara Desert.

Modern social statistics of Native Americans serve as defining characteristics of Native American life, and can be compared to the average United States citizens’ social statistics. Areas from their demographics and economy to health standards, drug and alcohol use, and land use and ownership all lead to a better understanding of Native American life. Health standards for Native Americans have notable disparities from that of all United States racial and ethnic groups. They have higher rates of disease, higher death rates, and a lack of medical coverage.

Lesotho's Human development index value for 2018 was 0.518—which put the country in the low human development category—positioning it at 164 out of 189 countries and territories. Health care services in Lesotho are delivered primarily by the government and the Christian Health Association of Lesotho. Access to health services is difficult for many people, especially in rural areas. The country's health system is challenged by the relentless increase of the burden of disease brought about by AIDS, and a lack of expertise and human resources. Serious emergencies are often referred to neighbouring South Africa. The largest contribution to mortality in Lesotho are communicable diseases, maternal, perinatal and nutritional conditions.
According to the Constitution of Albania, citizens are entitled to healthcare. The healthcare system in Albania is primarily public. The public system is made up of three tiers: primary care, secondary care, and tertiary care. Primary healthcare covers basic health needs. Secondary healthcare is needed when seeing a specialist after being referred to by a general practitioner. Tertiary healthcare funds are dedicated for highly specialized medical care that is needed over a long duration of time. There are over 400 public clinics that offer both primary and secondary healthcare services, along with over 40 public hospitals that offer tertiary healthcare services.
Compared with other neighbouring countries, Guyana ranks poorly in regard to basic health indicators. Basic health services in the interior are primitive to non-existent, and some procedures are not available at all. Although Guyana's health profile falls short in comparison with many of its Caribbean neighbours, there has been remarkable progress since 1988, and the Ministry of Health is working to upgrade conditions, procedures, and facilities. Many Guyanese seek medical care in the United States, Trinidad and Tobago or Cuba.
Health indicators are quantifiable characteristics of a population which researchers use as supporting evidence for describing the health of a population. Typically, researchers will use a survey methodology to gather information about a population sample, use statistics in an attempt to generalize the information collected to the entire population, and then use the statistical analysis to make a statement about the health of the population. Health indicators are often used by governments to guide health care policy or to make goals for improving population health.
Zimbabwe was once a model functional healthcare system in post colonial Africa, boasting a strong primary healthcare system and skilled healthcare workers under the Mugabe administration. In 2008, Zimbabwe had a 76.9 billion percent inflation rate and this worsened the state of the healthcare system which has not recovered today and is relying mostly on donor funding to keep running.

Maternal mortality refers to the death of a woman during her pregnancy or up to a year after her pregnancy has terminated; this metric only includes causes related to the pregnancy, and does not include accidental causes. Some sources will define maternal mortality as the death of a woman up to 42 days after the pregnancy has ended, instead of one year. In 1986, the CDC began tracking pregnancy-related deaths to gather information and determine what was causing these deaths by creating the Pregnancy-Related Mortality Surveillance System. According to a 2010-2011 report although the United States was spending more on healthcare than any other country in the world, more than two women died during childbirth every day, making maternal mortality in the United States the highest when compared to 49 other countries in the developed world.

Maternity care deserts in the United States, also known as maternal care deserts, are counties that lack maternity care resources. The March of Dimes defines a maternity care desert as a county that has no hospitals or birth centers offering obstetric care and no obstetric providers. As of 2020 March of Dimes classified 1095 of 3139 of U.S. counties (34.9%) as maternity care deserts. Its 2022 report indicated an increase of nearly 2%, with 1119 of 3142 US counties (35.6%) considered maternity care deserts, affecting a population of over 5.6 million women. People living in maternity care deserts may have to travel longer distances to receive care, which is associated with higher costs and a greater risk of pregnancy complications.












