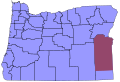
State Time Offsets DST Details Map Alabama UTC−06:00 CT Yes Central Standard Time (Phenix City observes Eastern time on a de facto basis) Alaska UTC−09:00 AKT Yes Most of state: UTC−09:00 AKST Alaska Standard Time UTC−10:00 HT Aleutian Islands (west of 169°30' W): UTC−10:00 HST Hawaii–Aleutian Standard Time American Samoa UTC−11:00 ST No Samoa Standard Time Arizona UTC−07:00 MT Part Mountain Standard Time . Except for the Navajo Nation , Arizona does not observe DST. Arkansas UTC−06:00 CT Yes Central California UTC−08:00 PT Yes Pacific Standard Time Colorado UTC−07:00 MT Yes Mountain Connecticut UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern Standard Time Delaware UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern District of Columbia UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern Florida UTC−05:00 ET Yes Big Bend and peninsula regions east of the Apalachicola River along with the portion of Gulf County south of the Intracoastal Waterway : UTC−05:00 EST Eastern Standard Time UTC−06:00 CT Florida Panhandle West of the Apalachicola River except for the portion of Gulf County south of the Intracoastal Waterway: UTC−06:00 CST Central Standard Time Georgia UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern Guam UTC+10:00 ChT No Chamorro Standard Time Hawaii UTC−10:00 HT No Hawaii–Aleutian Idaho UTC−07:00 MT Yes Most of state: UTC−07:00 MST Mountain Standard Time (A legislative error in 1923 in the Calder Act seemingly put this area at UTC−06:00 CST, and was corrected by Congress in 2007. [ 1] ) 15 U.S.C. ch. 6 , § 264. MST has been observed since 1923. UTC−08:00 PT North of the Salmon River, that is between the Oregon state border and the Idaho County/Lemhi County border; west of the Idaho County/Lemhi County border, that is between the Salmon River and the Montana state border: UTC−08:00 PST Pacific Standard Time Illinois UTC−06:00 CT Yes Central Indiana UTC−05:00 ET Yes Most of state: UTC−05:00 EST Eastern Standard Time UTC−06:00 CT Northwest and southwest corners: UTC−06:00 CST Central Standard Time (See Time in Indiana for more information) Iowa UTC−06:00 CT Yes Central Kansas UTC−06:00 CT Yes Most of state: UTC−06:00 CST Central Standard Time UTC−07:00 MT Greeley , Hamilton , Sherman and Wallace counties: UTC−07:00 MST Mountain Standard Time Kentucky UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern 60% of state: UTC−05:00 EST Eastern Standard Time UTC−06:00 CT Western 40% of state: UTC−06:00 CST Central Standard Time Louisiana UTC−06:00 CT Yes Central Maine UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern Maryland UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern Massachusetts UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern Michigan UTC−05:00 ET Yes Most of state: UTC−05:00 EST Eastern Standard Time UTC−06:00 CT Upper Peninsula counties bordering Wisconsin : UTC−06:00 CST Central Standard Time Minnesota UTC−06:00 CT Yes Central Mississippi UTC−06:00 CT Yes Central Missouri UTC−06:00 CT Yes Central Montana UTC−07:00 MT Yes Mountain Nebraska UTC−06:00 CT Yes Most of state: UTC−06:00 CST Central Standard Time UTC−07:00 MT Nebraska Panhandle , counties with Colorado as a western boundary, and the western Sand Hills : UTC−07:00 MST Mountain Standard Time Nevada UTC−07:00 MT Yes West Wendover city limits: UTC−07:00 MST Mountain Standard Time UTC−08:00 PT Most of state: UTC−08:00 PST Pacific Standard Time New Hampshire UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern New Jersey UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern New Mexico UTC−07:00 MT Yes Mountain New York UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern North Carolina UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern North Dakota UTC−06:00 CT Yes Most of state: UTC−06:00 CST Central Standard Time UTC−07:00 MT West of the Missouri River (except Morton and Oliver counties, and parts of Dunn , McKenzie , and Sioux counties: UTC−07:00 MST Mountain Standard Time Northern Mariana Islands UTC+10:00 ChT No Chamorro Ohio UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern Oklahoma UTC−06:00 CT Yes Central (Kenton observes Mountain time on a de facto basis) Oregon UTC−07:00 MT Yes Northern 80% of Malheur County : UTC−07:00 MST Mountain Standard Time UTC−08:00 PT Most of state: UTC−08:00 PST Pacific Standard Time Pennsylvania UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern Puerto Rico UTC−04:00 AT No Atlantic Standard Time Rhode Island UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern South Carolina UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern South Dakota UTC−06:00 CT Yes Eastern half of state: UTC−06:00 CST Central Standard Time UTC−07:00 MT Western half of state: UTC−07:00 MST Mountain Standard Time Tennessee UTC−05:00 ET Yes East Tennessee , except Bledsoe , Cumberland , and Marion Counties: UTC−05:00 EST Eastern Standard Time UTC−06:00 CT Most of state: UTC−06:00 CST Central Standard Time Texas UTC−06:00 CT Yes Most of state: UTC−06:00 CST Central Standard Time UTC−07:00 MT El Paso and Hudspeth counties: UTC−07:00 MST Mountain Standard Time U.S. Minor Outlying Islands UTC+12:00 UTC−12:00 UTC−11:00 STUTC−10:00 HTUTC−05:00 ET No Wake Island : UTC+12:00 (Wake Island Time Zone )Baker Island and Howland Island : UTC−12:00 Jarvis Island , Kingman Reef , Midway Atoll , and Palmyra Atoll : UTC−11:00 (Samoa Time )Johnston Atoll : UTC−10:00 (Hawaii–Aleutian Time ) Utah UTC−07:00 MT Yes Mountain Vermont UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern U.S. Virgin Islands UTC−04:00 AT No Atlantic Virginia UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern Washington UTC−08:00 PT Yes Pacific West Virginia UTC−05:00 ET Yes Eastern Wisconsin UTC−06:00 CT Yes Central Wyoming UTC−07:00 MT Yes Mountain