Historical

The "Panhandle and Plains" section of Texas is now in the Central Time Zone, but had a two-year period of being in the Mountain Time Zone between 1919 and 1921. [2]
Current time for most counties:10:07, September 11, 2024 CDT [refresh]
Current time for El Paso and Hudspeth counties:09:07, September 11, 2024 MDT [refresh]
Most of Texas is in the Central Time Zone with the exception being the two westernmost counties.
Northwestern Culberson County near Guadalupe Mountains National Park unofficially observes Mountain Time Zone. [1]
The 2 zones for Texas as given by zone.tab of the IANA time zone database. Columns marked * are from the zone.tab.
| c.c.* | coordinates* | TZ* | comments* | UTC offset | UTC offset DST | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US | +415100−0873900 | America/Chicago | Central (most areas) | −06:00 | −05:00 | |
| US | +394421−1045903 | America/Denver | Mountain (most areas) | −07:00 | −06:00 |

The "Panhandle and Plains" section of Texas is now in the Central Time Zone, but had a two-year period of being in the Mountain Time Zone between 1919 and 1921. [2]

Hudspeth County is a county located in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, the population was 3,202. Its county seat is Sierra Blanca, and the largest community is Fort Hancock. The county is named for Claude Benton Hudspeth, a state senator and United States Representative from El Paso. It is northeast of the Mexico–U.S. border.

El Paso County is the westernmost county in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, the population was 865,657, making it the ninth-most populous county in the state of Texas. Its seat is the city of El Paso, the sixth-most populous city in Texas and the 22nd-most populous city in the United States. The county was created in 1850 and later organized in 1871.

Culberson County is a county located in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 2,188. The county seat is Van Horn. Culberson County was founded in 1911 and organized the next year. It is named for David B. Culberson, a Confederate soldier and U.S. representative.

Dell City is a city in Hudspeth County, Texas, United States. The population was 365 at the time of the 2010 census, down from 413 at the time of the 2000 census. The population is now at 245 by the 2020 census. It is near the former location of Paulville, a failed Ron Paul-inspired Libertarian cooperative and planned community.

Sierra Blanca is an unincorporated area in Hudspeth County, Texas, United States. It is also the county seat of the county and the namesake of a census-designated place (CDP) in which it is located. The town is part of the Trans-Pecos region of far West Texas, is located northeast of the Mexican border and is within the Mountain Time Zone. As of the 2020 census, its population was 315.

The North American Central Time Zone (CT) is a time zone in parts of Canada, the United States, Mexico, Central America, and some Caribbean islands.

The Mountain Time Zone of North America keeps time by subtracting seven hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) when standard time (UTC−07:00) is in effect, and by subtracting six hours during daylight saving time (UTC−06:00). The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time at the 105th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory. In the United States, the exact specification for the location of time zones and the dividing lines between zones is set forth in the Code of Federal Regulations at 49 CFR 71.
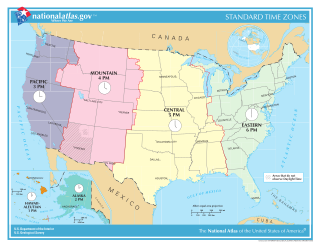
In the United States, time is divided into nine standard time zones covering the states, territories and other US possessions, with most of the country observing daylight saving time (DST) for approximately the spring, summer, and fall months. The time zone boundaries and DST observance are regulated by the Department of Transportation, but no single map of those existed until the agency announced intentions to make one in September 2022. Official and highly precise timekeeping services (clocks) are provided by two federal agencies: the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) ; and the United States Naval Observatory (USNO). The clocks run by these services are kept synchronized with each other as well as with those of other international timekeeping organizations.

West Texas is a loosely defined region in the U.S. state of Texas, generally encompassing the arid and semiarid lands west of a line drawn between the cities of Wichita Falls, Abilene, and Del Rio.

U.S. Route 54 is an east–west United States Highway that runs northeast–southwest for 1,197 miles (1,926 km) from El Paso, Texas, to Griggsville, Illinois. The Union Pacific Railroad's Tucumcari Line runs parallel to US 54 from El Paso to Pratt, Kansas, which comprises about two-thirds of the route. Truckers refer to this road as "The Bee Line."
The Central United States is sometimes conceived as between the Eastern and Western as part of a three-region model, roughly coincident with the U.S. Census's definition of the Midwestern United States plus the western and central portions of the U.S. Census's definition of the Southern United States. The Central States are typically considered to consist of North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas, Minnesota, Iowa, Missouri, Arkansas, Louisiana, Wisconsin, Illinois, Michigan, Indiana, Ohio, Kentucky, Tennessee, West Virginia, Mississippi and Alabama.

State Highway 20 is a 78.1-mile (125.7 km) highway maintained by the Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT) that runs from New Mexico State Road 460 at the state line between Texas and New Mexico at Anthony in El Paso County to Interstate 10 at McNary in Hudspeth County. It largely follows a former alignment of U.S. Route 80. The route passes through the city of El Paso as well as suburban and rural farming communities along the Rio Grande. With the exception of a stretch north of central El Paso where the route crosses north of I-10, the route generally runs in a narrow belt between I-10 and the Rio Grande. The route has connections to every international border crossing with Mexico in the El Paso area and has important intersections with US 54, US 62, US 85, and US 180.
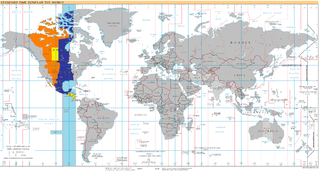
UTC−06:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of −06:00. In North America, it is observed in the Central Time Zone during standard time, and in the Mountain Time Zone during the other eight months. Several Latin American countries and a few other places use it year-round.

The Trans-Pecos, as originally defined in 1887 by the Texas geologist Robert T. Hill, is the distinct portion of Texas that lies west of the Pecos River. The term is considered synonymous with Far West Texas, a subdivision of West Texas. The Trans-Pecos is part of the Chihuahuan Desert, the largest desert in North America. It is the most mountainous and arid portion of the state, and most of its vast area is sparsely populated. Among the nine counties in the region are the five largest counties by area in Texas and eight of the eleven largest in the state. The area is known for the natural environment of the Big Bend and the gorge of the Rio Grande, part of which has been designated a National Wild and Scenic Rivers System. With the notable exceptions of Big Bend Ranch State Park, Big Bend National Park and the Guadalupe Mountains National Park, the vast majority of the Trans-Pecos region consists of privately owned ranchland. However, most of the region's population reside in the El Paso metropolitan area. Besides El Paso and its metropolitan area, the major cities are Pecos (12,916), Fort Stockton (8,466), and Alpine (6,035). All other settlements have under 5,000 people.
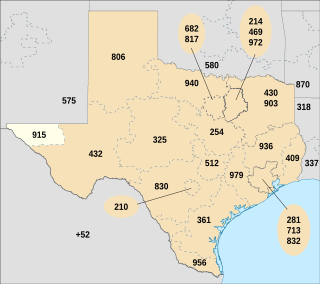
Area code 915 is a telephone area code in the North American Numbering Plan for the area around El Paso, Texas, U.S. It is one of the original North American area codes established in October 1947, when it was assigned to the north-western part of the state, north of Austin and west of Fort Worth, and stretched from the Oklahoma border to the Mexican border.
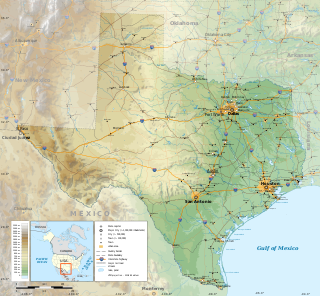
The geography of Texas is diverse and large. Occupying about 7% of the total water and land area of the U.S., it is the second largest state after Alaska, and is the southernmost part of the Great Plains, which end in the south against the folded Sierra Madre Oriental of Mexico. Texas is in the South Central United States of America, and is considered to form part of the U.S. South and also part of the U.S. Southwest.
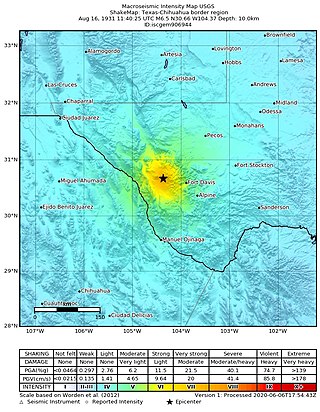
In the early morning hours of August 16, 1931, a powerful earthquake occurred in West Texas with a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). Estimates of its magnitude range between 5.8 and 6.4 mb, making it the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Texas history. Its epicenter was near the town of Valentine, Texas; there, the earthquake caused damage to many homes and buildings. The earthquake may have been caused by movement along oblique-slip faulting in West Texas, the most seismically-active region in the state. Shaking from the earthquake was perceptible within a 400 mi (640 km) radius of the epicenter, affecting four U.S. states and northern Mexico. Several foreshocks and aftershocks accompanied the primary temblor, with the aftershocks continuing until at least November 3, 1931. The main earthquake caused no fatalities, though several people sustained minor injuries; the damage in Valentine amounted to $50,000–$75,000.

Cornudas is an unincorporated community in Hudspeth County, Texas, United States. Cornudas is located near the intersection of Ranch to Market Road 2317 and the concurrent U.S. Highways 62 and 180, 42 miles (68 km) northwest of the county seat, Sierra Blanca. Cornudas was located in 1929 strategically on the most direct route between El Paso and Carlsbad, New Mexico as a natural rest and resupply station. It was directly or indirectly named for the Cornudas Mountains that can be seen behind the Cornudas Cafe.

The Hudspeth County Courthouse is located in the town of Sierra Blanca, the seat of Hudspeth County in the U.S. state of Texas. The courthouse was constructed in 1919 and added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1975. The Texas Historical Commission (THC) has also designated the building as a Recorded Texas Historic Landmark since 1962 and as a State Antiquities Landmark since 1981. The county is named for Claude Benton Hudspeth who served as a U.S. representative from El Paso and previously in both houses of the Texas Legislature where, as a member of the Texas Senate, he was influential in the county's creation.