
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it is convenient for areas in frequent communication to keep the same time.
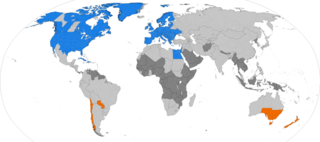
Daylight saving time (DST), also referred to as daylight savings time or simply daylight time, and summer time, is the practice of advancing clocks during warmer months so that darkness falls at a later clock time. The typical implementation of DST is to set clocks forward by one hour in the spring, and to set clocks back by one hour in the fall to return to standard time. As a result, there is one 23-hour day in late winter or early spring and one 25-hour day in autumn.

Japan Standard Time, or Japan Central Standard Time, is the standard time zone in Japan, 9 hours ahead of UTC (UTC+09:00). Japan does not observe daylight saving time, though its introduction has been debated on several occasions. During World War II, the time zone was often referred to as Tokyo Standard Time.

The history of standard time in the United States began November 18, 1883, when United States and Canadian railroads instituted standard time in time zones. Before then, time of day was a local matter, and most cities and towns used some form of local solar time, maintained by some well-known clock. The new standard time system was not immediately embraced by all.

The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico, Panama, Colombia, mainland Ecuador, Peru, and a small portion of westernmost Brazil in South America, along with certain Caribbean and Atlantic islands.
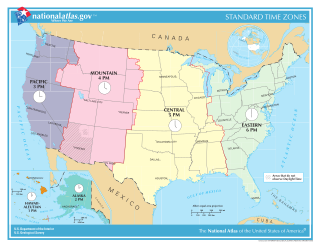
Time in the United States, by law, is divided into nine standard time zones covering the states, territories and other US possessions, with most of the United States observing daylight saving time (DST) for approximately the spring, summer, and fall months. The time zone boundaries and DST observance are regulated by the Department of Transportation, but no single map of those existed until the agency announced intentions to make one in September 2022. Official and highly precise timekeeping services (clocks) are provided by two federal agencies: the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) ; and the United States Naval Observatory (USNO). The clocks run by these services are kept synchronized with each other as well as with those of other international timekeeping organizations.

The Atlantic Time Zone is a geographical region that keeps standard time—called Atlantic Standard Time (AST)—by subtracting four hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), resulting in UTC−04:00. AST is observed in parts of North America and some Caribbean islands. During part of the year, some portions of the zone observe daylight saving time, referred to as Atlantic Daylight Time (ADT), by moving their clocks forward one hour to result in UTC−03:00. The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time of the 60th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory.

Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Western Standard Time, Australian Central Standard Time, and Australian Eastern Standard Time. Time is regulated by the individual state governments, some of which observe daylight saving time (DST). Australia's external territories observe different time zones.

The U.S. state of Indiana is divided between Eastern and Central time zones. The official dividing line has generally moved progressively west from its original location on the Indiana–Ohio border, to a position dividing Indiana down the middle, and finally to its current location along much of the Indiana–Illinois border. In April 2006, several southwestern and northwestern counties reverted to Central time, although by late 2007 all but two had returned to Eastern time.

Iran Standard Time (IRST) or Iran Time (IT) is the time zone used in Iran. Iran uses a UTC offset UTC+03:30. IRST is defined by the 52.5 degrees east meridian, the same meridian which defines the Iranian calendar and is the official meridian of Iran.

The time zone in Germany is Central European Time and Central European Summer Time. Daylight saving time is observed from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October. The doubled hour during the switch back to standard time is named 2A and 2B.

The majority of the United States observes daylight saving time, the practice of setting the clock forward by one hour when there is longer daylight during the day, so that evenings have more daylight and mornings have less. Exceptions include Arizona, Hawaii, and the overseas territories of American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, and the United States Virgin Islands. The Uniform Time Act of 1966 established the system of uniform daylight saving time throughout the US.

Time in Arizona, as in all U.S. states, is regulated by the United States Department of Transportation as well as by state and tribal law.

Spain has two time zones and observes daylight saving time. Spain mainly uses CET (UTC+01:00) and CEST (UTC+02:00) in Peninsular Spain, the Balearic Islands, Ceuta, Melilla and plazas de soberanía. In the Canary Islands, the time zone is WET (UTC±00:00) and WEST (UTC+01:00). DST is observed from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October throughout Spain.

Time in Maine, as in all US states, is regulated by the United States Department of Transportation. All of Maine is in the Eastern Time Zone (ET) and observes daylight saving time (DST).

Time in Massachusetts, as in all US states, is regulated by the United States Department of Transportation. Massachusetts is in the Eastern Time Zone (ET) and observes daylight saving time (DST).

Time in Rhode Island, as in all US states, is regulated by the United States Department of Transportation. Rhode Island is in the Eastern Time Zone (ET) and observes daylight saving time (DST).

Time in Connecticut, as in all US states, is regulated by the United States Department of Transportation. Connecticut is in the Eastern Time Zone (ET) and observes daylight saving time (DST).

Time in Vermont, as in all US states, is regulated by the United States Department of Transportation. Vermont is in the Eastern Time Zone (ET) and observes daylight saving time (DST).

Permanent standard time refers to the year-round observation of standard time. Likewise, permanent daylight saving time refers to the year-round observation of daylight saving time (DST). Both permanent standard time and permanent DST eliminate the practice of semi-annual clock changes, specifically the advancement of clocks by one hour from standard time to DST in spring and the retraction of clocks by one hour from DST to standard time in fall.














