
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it is convenient for areas in frequent communication to keep the same time.

The history of standard time in the United States began November 18, 1883, when United States and Canadian railroads instituted standard time in time zones. Before then, time of day was a local matter, and most cities and towns used some form of local solar time, maintained by some well-known clock. The standard time system was not immediately embraced by all. Standard time in time zones was established in U.S. law in the Standard Time Act on March 19, 1918, at which time daylight saving time was also instituted.

The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, and the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico.

The Alaska Time Zone observes standard time by subtracting nine hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC−09:00). During daylight saving time its time offset is eight hours (UTC−08:00). The clock time in this zone is based on mean solar time at the 135th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory.
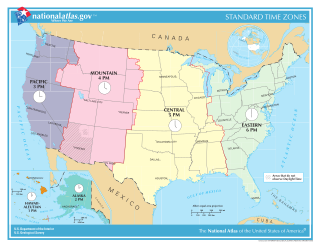
In the United States, time is divided into nine standard time zones covering the states, territories and other US possessions, with most of the country observing daylight saving time (DST) for approximately the spring, summer, and fall months. The time zone boundaries and DST observance are regulated by the Department of Transportation, but no single map of those existed until the agency announced intentions to make one in September 2022. Official and highly precise timekeeping services (clocks) are provided by two federal agencies: the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) ; and the United States Naval Observatory (USNO). The clocks run by these services are kept synchronized with each other as well as with those of other international timekeeping organizations.

The Uniform Time Act of 1966, Pub. L.Tooltip Public Law 89–387, 80 Stat. 107, enacted April 13, 1966, was a Law of the United States to "promote the adoption and observance of uniform time within the standard time zones" prescribed by the Standard Time Act of 1918. Its intended effect was to simplify the official pattern of where and when daylight saving time (DST) is applied within the U.S. Prior to this law, each state had its own scheme for when DST would begin and end, and in some cases, which parts of the state should use it.

Standard time is the synchronization of clocks within a geographical region to a single time standard, rather than a local mean time standard. Generally, standard time agrees with the local mean time at some meridian that passes through the region, often near the centre of the region. Historically, standard time was established during the 19th century to aid weather forecasting and train travel. Applied globally in the 20th century, the geographical regions became time zones. The standard time in each time zone has come to be defined as an offset from Universal Time. A further offset is applied for part of the year in regions with daylight saving time.

The Atlantic Time Zone is a geographical region that keeps standard time—called Atlantic Standard Time (AST)—by subtracting four hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), resulting in UTC−04:00. AST is observed in parts of North America and some Caribbean islands. During part of the year, some portions of the zone observe daylight saving time, referred to as Atlantic Daylight Time (ADT), by moving their clocks forward one hour to UTC−03:00. The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time of the 60th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory.

South African Standard Time (SAST) is the time zone used by all of South Africa as well as Eswatini and Lesotho. The zone is two hours ahead of UTC (UTC+02:00) and is the same as Central Africa Time. Daylight saving time is not observed in either time zone. Solar noon in this time zone occurs at 30° E in SAST, effectively making Pietermaritzburg at the correct solar noon point, with Johannesburg and Pretoria slightly west at 28° E and Durban slightly east at 31° E. Thus, most of South Africa's population experience true solar noon at approximately 12:00 daily.

The time in China follows a single standard time offset of UTC+08:00 based on the National Time Service Center of Chinese Academy of Sciences located in Mount Li, Lintong District, Xi'an City, Shaanxi Province, even though the country spans five geographical time zones. The official national standard time is called Beijing Time domestically because it is based on the 120th meridian east, where Beijing City is located, and China Standard Time (CST) internationally. Daylight saving time has not been observed since 1991. China Standard Time (UTC+8) is consistent across Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, as well as equivalent with Philippines, Singapore, Brunei, most of Mongolia, Malaysia, Irkutsk Time (Russia), Western Australia and Central Indonesia.

Canada is divided into six time zones. Most areas of the country's provinces and territories operate on standard time from the first Sunday in November to the second Sunday in March and daylight saving time the rest of the year.

The U.S. state of Indiana is divided into Eastern and Central time zones. The official dividing line has generally moved progressively west from its original location on the Indiana–Ohio border, to a position dividing Indiana down the middle, and finally to its current location along much of the Indiana–Illinois border. This change primarily occurred to ease communications with Indiana and New York. In April 2006, several southwestern and northwestern counties reverted to Central time.

Most of the United States observes daylight saving time (DST), the practice of setting the clock forward by one hour when there is longer daylight during the day, so that evenings have more daylight and mornings have less. Exceptions include Arizona, Hawaii, and the territories of American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, and the United States Virgin Islands. The Uniform Time Act of 1966 established a uniform set of rules for states opting to observe daylight saving time.
Hawaii is in the Hawaii–Aleutian Time Zone and does not observe daylight saving time.

Time in Arizona, as in all U.S. states, is regulated by the United States Department of Transportation as well as by state and tribal law.

Time in Massachusetts, as in all US states, is regulated by the United States Department of Transportation. Massachusetts is in the Eastern Time Zone (ET) and observes daylight saving time (DST).

Time in New Hampshire, as in all US states, is regulated by the United States Department of Transportation. New Hampshire is in the Eastern Time Zone (ET) and observes daylight saving time (DST).

Time in Rhode Island, as in all US states, is regulated by the United States Department of Transportation. Rhode Island is in the Eastern Time Zone (ET) and observes daylight saving time (DST).

Time in Connecticut, as in all US states, is regulated by the United States Department of Transportation. Connecticut is in the Eastern Time Zone (ET) and observes daylight saving time (DST).

Time in Vermont, as in all US states, is regulated by the United States Department of Transportation. Vermont is in the Eastern Time Zone (ET) and observes daylight saving time (DST).













