
The Arctic National Wildlife Refuge or Arctic Refuge is a national wildlife refuge in northeastern Alaska, United States, on traditional Iñupiaq and Gwich'in lands. The refuge is 19,286,722 acres (78,050.59 km2) of the Alaska North Slope region, with a northern coastline and vast inland forest, taiga, and tundra regions. ANWR is the largest national wildlife refuge in the country, slightly larger than the Yukon Delta National Wildlife Refuge. The refuge is administered from offices in Fairbanks. ANWR is home to a diverse range of endemic mammal species; notably, it is one of the few North American locations with all three endemic American bears—the polar bear, grizzly bear, and American black bear, each of which resides predominantly in its own ecological niche. Besides the bears, other mammal species include the moose, caribou, wolves, red and Arctic fox, Canada lynx, wolverine, pine marten, American beaver, and North American river otter. Further inland, mountain goats may be seen near the slope. Hundreds of species of migratory birds visit the refuge yearly, and it is a vital, protected breeding location for them. Snow geese, eiders and snowy owls may be observed as well.

Prudhoe Bay is a census-designated place (CDP) located in North Slope Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. As of the 2020 census, the population of the CDP was 1,310 people, down from 2,174 residents in the 2010 census, and up from just 5 residents in 2000; however, at any given time, several thousand transient workers support the Prudhoe Bay Oil Field. The airport, lodging and general store are located in Deadhorse, and the rigs and processing facilities are located on scattered gravel pads laid atop the tundra. It is only during winter that the surface is hard enough to support heavy equipment, and new construction happens at that time.

The Colville River is a major river of the Arctic Ocean coast of Alaska in the United States, approximately 350 miles (560 km) long. One of the northernmost major rivers in North America, it drains a remote area of tundra on the north side of the Brooks Range entirely above the Arctic Circle in the southwestern corner of the National Petroleum Reserve-Alaska. The river is frozen for more than half the year and floods each spring.The Colville River and its adjacent hills are home to a variety of Arctic wildlife, including Lake Teshekpuk and Central Arctic caribou herds, and hawks.

Deadhorse is an unincorporated community located within the CDP of Prudhoe Bay in North Slope Borough, Alaska, United States, along the North Slope near the Arctic Ocean. The town consists mainly of facilities for the workers and companies that operate at the nearby Prudhoe Bay Oil Field. Deadhorse is accessible via the Dalton Highway from Fairbanks, 495 miles (797 km) south, or Deadhorse Airport. Limited accommodation is also available for tourists.

The question of whether to drill for oil in the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge (ANWR) has been an ongoing political controversy in the United States since 1977. As of 2017, Republicans have attempted to allow drilling in ANWR almost fifty times, finally being successful with the passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017.

Teshekpuk Lake is the largest lake in Arctic Alaska, at 22 miles (35 km) width on the Alaska North Slope within the National Petroleum Reserve-Alaska, South of Pitt Point, 12 miles (19 km) east of Harrison Bay, 80 miles (130 km) east of Point Barrow. The Teshekpuk Lake region is considered one of the most productive, diverse, and sensitive wetland ecosystems in the entire Arctic, habitat to a variety of arctic wildlife, including the resident Teshekpuk Lake caribou herd of 64,000 animals, large numbers of shorebirds and migratory waterfowl, for whom it is an essential part of the East Asian–Australasian Flyway site network.
The Kokolik River is a stream, 200 miles (320 km) long, in the western North Slope of the U.S. state of Alaska.

The National Petroleum Reserve in Alaska (NPRA) is an area of land on the Alaska North Slope owned by the United States federal government and managed by the Department of the Interior, Bureau of Land Management (BLM). It lies to the west of the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge, which, as a U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service managed National Wildlife Refuge, is also federal land.
Umiat (OO-mee-yat) is an unincorporated community in North Slope Borough, Alaska, United States. It is located on the Colville River, 140 miles southwest of Deadhorse in the Arctic Circle. The town is not accessible by road or rail, only by air or river.
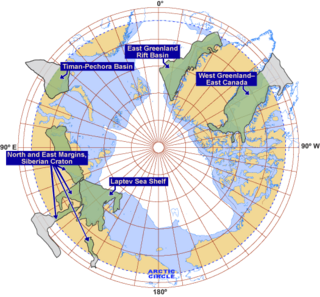
Exploration for petroleum in the Arctic is expensive and challenging both technically and logistically. In the offshore, sea ice can be a major factor. There have been many discoveries of oil and gas in the several Arctic basins that have seen extensive exploration over past decades but distance from existing infrastructure has often deterred development. Development and production operations in the Arctic offshore as a result of exploration have been limited, with the exception of the Barents and Norwegian seas. In Alaska, exploration subsequent to the discovery of the Prudhoe Bay oilfield has focussed on the onshore and shallow coastal waters.
Prudhoe Bay Oil Field is a large oil field on Alaska's North Slope. It is the largest oil field in North America, covering 213,543 acres (86,418 ha) and originally contained approximately 25 billion barrels (4.0×109 m3) of oil. The amount of recoverable oil in the field is more than double that of the next largest field in the United States by acreage (the East Texas Oil Field), while the largest by reserves is the Permian Basin (North America). The field was operated by BP; partners were ExxonMobil and ConocoPhillips until August 2019; when BP sold all its Alaska assets to Hilcorp.

The Chukchi Shelf or Chukchi Sea Shelf is the westernmost part of the continental shelf of the United States and the easternmost part of the continental shelf of Russia. In the west it merges with the Russian Siberian Shelf. Within this shelf, the 50-mile Chukchi Corridor acts as a passageway for one of the largest marine mammal migrations in the world.
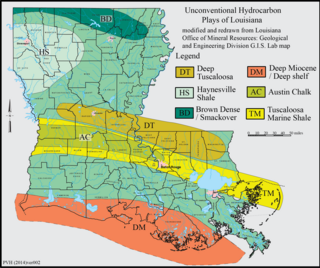
The Haynesville Shale is an informal, popular name for a Jurassic Period rock formation that underlies large parts of southwestern Arkansas, northwest Louisiana, and East Texas. It lies at depths of 10,500 to 13,000 feet below the land’s surface. It is part of a large rock formation which is known by geologists as the Haynesville Formation. The Haynesville Shale underlies an area of about 9,000 square miles and averages about 200 to 300 feet thick. The Haynesville Shale is overlain by sandstone of the Cotton Valley Group and underlain by limestone of the Smackover Formation.

Within the petroleum industry, proven crude oil reserves in the United States were 44.4 billion barrels (7.06×109 m3) of crude oil as of the end of 2021, excluding the Strategic Petroleum Reserve.
Marvin Dale Mangus (1924–2009) was an American geologist and landscape painter. He was giving the honor of driving a purely symbolic wood stake prior to start of drilling the actual oil well by the Atlantic Richfield Corporation, his employer. The focus of his later art career was glorified role of geologist and other exploration of Alaska. He painted animals and birds and was recognized with awards from The National Park Service

The Arctic coastal tundra is an ecoregion of the far north of North America, an important breeding ground for a great deal of wildlife.
Mount Elbert Methane Hydrate Site is a natural gas test site within the Alaska North Slope. The well was first drilled in 2007 as part of a Cooperative Research Agreement with BP Exploration (Alaska), Inc. (BPXA) and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) in collaboration with the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). The aim was to help determine whether natural gas hydrate in the area can become a commercially viable gas resource. Results so far are promising.

The Nanushuk Formation or Nanushuk Group is a geologic group in Alaska in westernmost National Petroleum Reserve in Alaska (NPR-A). Petroleum in these rocks likely was generated beneath Western Alaska North Slope and migrated northeastward into NPR-A. The formation preserves fossils dating back to the Albian-Cenomanian ages of the Cretaceous period. Its thickness varies from about 1500 to about 250 meters. Underneath the Nanushuk lies the Torok Formation.

Smith Bay is an estuary in the Beaufort Sea that supports a wide range of fish, birds, and marine mammals. It is located northeast of Point Barrow, Alaska. The Bureau of Ocean Energy Management recognizes the southeastern portion of Barrow Canyon, which covers some, but not all, of Smith Bay, as an Environmentally Important Area.

The Alaskan North Slope (ANS) is a foreland basin located on the northern edge of the Brooks Range. The Alaska North Slope is bounded on the north by the Beaufort Sea and runs from the Canadian border to the maritime boundary with Russia in the west. The western edge extends into the Chukchi Sea and Chukchi platform where the basin is at its widest. As the basin moves east it narrows towards the Canadian border. The basin is 1000 km long, 600 km at its widest, and covers a total area of 240,000 km2.




















