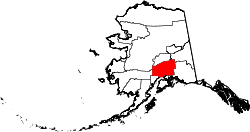
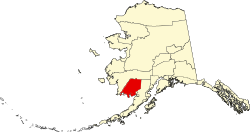
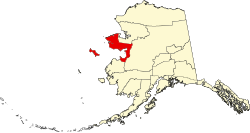
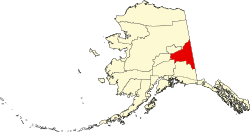
| Boroughs and census areas of Alaska | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | State of Alaska |
| Number | 19 organized boroughs 11 census areas |
| Populations | (Organized boroughs): 690 (Yakutat) – 289,600 (Anchorage) (Census areas): 2,312 (Hoonah-Angoon) – 18,237 (Bethel) |
| Areas | (Organized boroughs): 434 square miles (1,120 km2) (Skagway) – 88,824 square miles (230,050 km2) (North Slope) (Census areas): 4,393 square miles (11,380 km2) (Aleutians West) – 145,576 square miles (377,040 km2) (Yukon-Koyukuk) |
| Government | |
| Subdivisions |
|
The U.S. state of Alaska is divided into 19 organized boroughs and 11 census areas in the Unorganized Borough. [1] Boroughs and census areas are both treated as county-level equivalents by the Census Bureau.
Contents
- List of boroughs
- Census areas in the Unorganized Borough
- See also
- References
- Other sources
- Further reading
Delegates to the Alaska Constitutional Convention wanted to avoid the traditional county system and adopted their own unique model with different classes of boroughs varying in powers and duties. [2] Many of the most densely populated regions of the state are part of Alaska's boroughs, which function similarly to counties in other states. There are four different classifications of organized boroughs: "Unified Home Rule" or "Non-unified Home Rule" (may exercise all legislative powers not prohibited by law or charter); "First Class" (may exercise any power not prohibited by law on a non-area wide basis by adopting ordinances); and "Second Class" (must gain voter approval for authority to exercise many non-area wide powers). [3]
Unlike county-equivalents in the other 49 states, the organized boroughs do not cover the entire land area of the state. The area not part of any organized borough is referred to as the Unorganized Borough. The U.S. Census Bureau, in cooperation with the state, divides the Unorganized Borough into 11 census areas, each roughly corresponding to an election district, thus totaling 30 county equivalents. However, Census Areas exist solely for the purposes of statistical analysis and presentation; they have no government of their own. Some areas in the Unorganized Borough receive limited public services directly from the Alaska state government, usually law enforcement from the Alaska State Troopers and educational funding.
Seven consolidated city-borough governments exist— Juneau City and Borough, Skagway Municipality, Sitka City and Borough, Yakutat City and Borough, Wrangell City and Borough, Haines Borough, as well as the state's largest city, Anchorage. Though its legal name is the Municipality of Anchorage, it is considered a consolidated city-borough under state law.
The Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 55-2,3,4 codes, which are used by the United States Census Bureau to uniquely identify states and counties, is provided with each entry. [4] Alaska's code is 02, so each code is of the format 02XXX. The FIPS code for each county equivalent links to census data for that county equivalent. There are 30 divisions in Alaska.