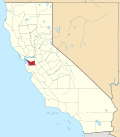
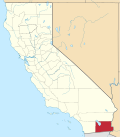
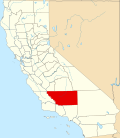
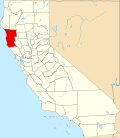
| Counties of California | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | State of California |
| Created |
|
| Number | 58 counties |
| Populations | Minimum: Alpine, 1,204 Maximum: Los Angeles, 9,757,179 |
| Areas | Minimum: San Francisco, 47 square miles (120 km2) Maximum: San Bernardino, 20,062 square miles (51,960 km2) |
| Government | |
| Subdivisions | |
The U.S. state of California is divided into 58 counties. [1] The state was first divided into 27 counties on February 18, 1850. These were further sub-divided to form sixteen additional counties by 1860. Another fourteen counties were formed through further subdivision from 1861 to 1893. The most recent county to form was Imperial County, in 1907. California is home to San Bernardino County, the largest county in the contiguous United States, as well as Los Angeles County, the most populous county in the United States.
Contents
The counties of California are local arms of the State of California, described by the Supreme Court of California as agents ("the county is merely a political subdivision of state government, exercising only the powers of the state, granted by the state…'") and the property they hold is held on behalf of all the people of the state. [2] [3] As such, the State Legislature may delegate any of the functions of the State to the counties but likewise can reassume any delegated duties. [4]
California counties are general law counties by default. Still, they may be chartered as provided in Article XI, Section 3 of the California Constitution. [5] A charter county is granted limited home rule powers. Of the 58 counties in California, 14 are governed under a charter. They are Alameda, Butte, El Dorado, Fresno, Los Angeles, Orange, Placer, Sacramento, San Bernardino, San Diego, San Francisco, San Mateo, Santa Clara, and Tehama. [6]
Nine counties in California are named for saints, tied with Louisiana for the largest number. This count omits Santa Cruz ("Holy Cross") County, not named for a saint; Merced County and Los Angeles County, both of whose names refer to Saint Mary (Our Lady of Mercy (Merced) and Our Lady Queen of The Angels (Los Angeles)); and Ventura County, whose name is a shortening of the name of St. Bonaventure, the namesake of the local mission. [7]