1775–1777 (the "Continental Union")
1775–1777 (the "Continental Union") Betsy Ross circular 13-star version (1792) *other
Betsy Ross circular 13-star version (1792) *other "Hopkinson" version (1777–1795) *other
"Hopkinson" version (1777–1795) *other Battle of Bennington version (1777) *other
Battle of Bennington version (1777) *other 1795–1818 (the "Star-Spangled Banner", 15 stars, 15 stripes)
1795–1818 (the "Star-Spangled Banner", 15 stars, 15 stripes)
This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2019) |

This is a list of flags in the United States describing the evolution of the flag of the United States, as well as other flags used within the United States, such as the flags of governmental agencies. There are also separate flags for embassies and ships.
Contents
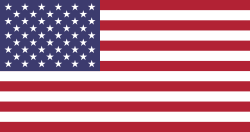
- National flags
- Historical progression of designs
- Other historical versions
- Executive branch flags
- Office of the President
- Office of the Vice President
- Department of State
- Department of the Treasury
- Department of Defense
- Department of Justice
- Department of the Interior
- Department of Agriculture
- Department of Commerce
- Department of Labor
- Department of Health and Human Services
- Department of Housing and Urban Development
- Department of Transportation
- Department of Energy
- Department of Education
- Department of Veterans Affairs
- Department of Homeland Security
- Legislative branch flags
- Congress
- Other federal flags
- State and territory flags
- History
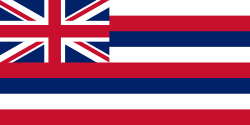
- Current state flags
- Current federal district flag
- Current inhabited territory flags
- County flags
- City flags
- Maritime flags
- Ensigns
- Distinctive marks
- Commissioning pennants
- Native American tribal flags
- Associated state flags
- Historical flags
- Thirteen Colonies
- American Revolutionary War
- Former federal flags
- Other states
- Former territories and administered areas
- See also
- References
- External links