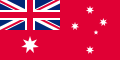
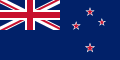
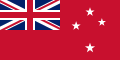
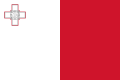
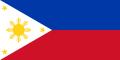
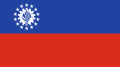
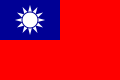
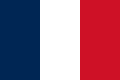
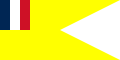
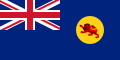
A civil ensign is an ensign (maritime flag) used by civilian vessels to denote their nationality. It can be the same or different from the state ensign and the naval ensign (or war ensign). It is also known as the merchant ensign or merchant flag. Some countries have special civil ensigns for yachts, and even for specific yacht clubs, known as yacht ensigns.
Contents
- Countries having specific civil ensigns
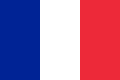
- Civil ensigns with the national flag in the canton
- Civil ensigns that vary greatly from the national flag
- Civil ensigns consisting of the national flag with an additional emblem
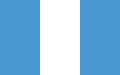
- Civil ensigns that are simplified national flags with coat of arms removed
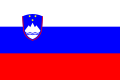
- Civil ensigns with a modified coat of arms
- Civil ensigns differing from the national flag in the proportions
- Former civil ensigns no longer in current use or obsolete
- See also
- Remarks
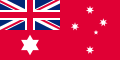
Most countries have only one national flag and ensign for all purposes. In other countries, a distinction is made between the land flag and the civil, state and naval ensigns. The British ensigns, for example, differ from the flag used on land (the Union Flag) and have different versions of plain and defaced Red and Blue ensigns for civilian and state use, as well as the naval ensign (White Ensign) that can also be used by yachts of the Royal Yacht Squadron.