This article needs additional citations for verification .(May 2025) |
The following is a list of flags present in Suriname.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(May 2025) |
The following is a list of flags present in Suriname.
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1975-Today | Flag of Suriname | A horizontal triband of green (top and bottom) and red (double width) with large white border with the large yellow five-pointed star centered on the red band. [1] |
 | 1975-Today | Flag of Suriname (Vertical) |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1975-Today | Presidential Flag of Suriname | A horizontal triband of green (top and bottom) and red (double width) with large white border with the coat of arms centered on the red band. [1] |
 | 1975-1988 | Flag of the Prime Minister of Suriname | A white field with a golden border and the coat of arms in the center. |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1593-1629 | Flag of Habsburg Spain | A red saltire resembling two crossed, roughly-pruned (knotted) branches, on a white field. |
| Royal Flag | |||
 | 1593-1629 | Royal Flag of Philip II of Spain | A red field with the royal coat of arms in the center. |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1650-1651 | Flag of the Commonwealth of England | St George's Cross and an Irish Harp juxtaposed. |
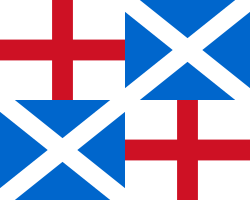 | 1651-1658 | Flag of the Commonwealth of England | St George's Cross and St Andrew's cross quartered. |
 | 1658-1660 | Flag of The Protectorate | The 1606 Union Jack defaced with an Irish Harp. |
 | 1660-1667 1667-1668 | Flag of the Kingdom of England | a red cross on a white field. |
 | 1799-1801 | Flag of the Kingdom of Great Britain | First version of the Union Jack used in England from 1606 and Scotland from 1707 – the Flags of England and Scotland superimposed. |
 | 1801-1802 1804-1816 | flag of the United Kingdom | A superimposition of the flags of England and Scotland with the Saint Patrick's Saltire (representing Ireland). |
| Lord Protector's Flag | |||
 | 1653-1659 | Standard of the Lord Protector | The cross of St. George quartered with the cross of St. Andrew and the Irish Harp, and surmounted by an escutcheon with Cromwell's personal coat of arms. |
| Royal Flags | |||
 | 1660-1667 1667-1668 | Royal Standard of the House of Stuart | A banner of the Royal Coat of Arms of James I, first and fourth quarters representing England and the English claim to the French throne, second quarter representing Scotland, third quarter representing Ireland (This is the first time that Ireland has been represented on the Royal Standard). |
 | 1799-1801 | Royal Standard of Great Britain under the House of Hanover | A banner of the Royal Coat of Arms of Great Britain, first quarter representing England and Scotland, second quarter representing the British claim to the French throne, third quarter representing Ireland, fourth quarter representing the Electorate of Hanover. |
 | 1801-1802 1804-1816 | Royal Standard of the United Kingdom | A banner of the Royal Arms from the creation of the United Kingdom on 1 January 1801; first and fourth quarters for England and Wales, second Scotland, third Ireland, with an inescutcheon for the Electorate of Hanover. |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1795-1799 1802-1804 | Flag of the French First Republic | a vertical tricolour of blue, white and red. |
| Netherlands under French Rule | |||
 | 1795-1799 1802-1804 | Flag of the Batavian Republic | A horizontal triband of red, white and blue with the Republic's emblem in the canton. |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1667 1668-1795 | The Prince's Flag | A horizontal Tricolour of orange, white and blue. |
 | 1667 1668-1796 | States Flag | A horizontal Tricolour of Red, White and Blue. The blue is a lighter shade than that of the current flag. |
 | 1816-1975 | Flag of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and the Kingdom of the Netherlands | A horizontal Tricolour of Red, White and Blue. |
| Royal Flags | |||
 | 1816–1908 | Royal Standard of the Monarch | The colours of the flag of the Netherlands with the royal coat of arms (without the mantle). |
 | 1908–1975 | Royal Standard of the Monarch | A square orange flag, divided in four quarters by a nassau-blue cross with the small coat of arms of the Kingdom, surmounted by a royal crown and surrounded by the insignia of the Grand Cross of the Order of William. Each quarter shows a bugle-horn which originates in arms of the Principality of Orange. |
| Colonial Flags | |||
 | 1920–1966 | Governor's standard of Dutch Guyana | National tricolour, with in the red stripe three white balls. |
 | 1966–1975 | Standard of the governor of Suriname | A white flag with the flag of the Netherlands striped across both the top and the bottom, and the flag of Suriname in the centre. |
 | 1959-1975 | Flag of Suriname | A White Field with 5 five-pointed stars (black, white, brown, red and yellow) in the center. [2] |