| Flag | Date | Description |
|---|
 | 1534–1820 | The Cross of Burgundy flag of the Spanish colonial empire flew over Ecuador for many years. |
 | 1809–1812 | The leaders of a rebellion against the Spanish authorities raised a reversed Cross of Burgundy flag in Quito on 10 August 1809. The uprising was defeated in 1812. |
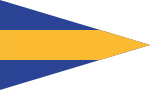
 | 1820–1822 | A flag with five horizontal stripes and three stars in the middle stripe. This flag subsequently became that of the Guayas Province, and was first raised by the patriots in the liberation of 9 October 1820. |
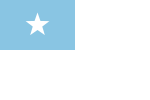 | 1822 | The previous flag was changed by decree of 2 June 1822: "The flag of the free province of Guayaquil shall be white and its first quarter blue with a centered star." |
 | 1822–1830 | Ecuador was subsumed into Gran Colombia, during which time the Colombian horizontal tricolour became definitive. Although Ecuador seceded from that union in 1830, the flag was retained until 1845. |
 | 1830–1835 | Provisional flag of the State of Ecuador, decreed on 19 November 1830. |
 | 1835–1845 | First flag used officially by Ecuador after its separation from Gran Colombia. |
 | 1845 | During the 1845 Marcist Revolution the pale blue and white colours return, but as a vertical tricolour of white, blue, white, with three white stars in the central stripe. |
 | 1845–1860 | The Cuenca Convention ratified, by decree of 6 November 1845, a change to a deeper blue, and the increase in the number of stars to seven "as symbols of the seven provinces which make up the Republic". |
 | 1860–1900 | Gabriel García Moreno, upon assuming power two days after the Battle of Guayaquil, reinstated the tricolor flag of Greater Colombia on 26 September 1860. In 1900, the flag was made the definitive national standard, and the coat of arms was added for official state use. The plain flag was established as the merchant ensign in 1900. |
 | 1900–2009 | The flag from 31 October 1900. In 1900, the flag was made the definitive national standard, and the coat of arms was added for official state use. The plain flag was established as the merchant ensign in 1900 a modification in November 2009. |