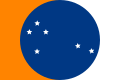
- Flag used to represent the South African team at the 1992 Summer Olympics and at the 1992 Summer Paralympics
- Flag used to represent the South African team at the 1994 Winter Olympics
Overview
The following flags have been used as the national flag of the Union of South Africa and the Republic of South Africa:
| Flag | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
 | 1910–1957 | Blue field on which the Cross of Saint Andrew counterchanged with the Cross of Saint Patrick, over all the Cross of Saint George fimbriated. |
 | 1910–1912 | A British Red Ensign with the shield of the coat of arms of the Union of South Africa. |
 | 1912–1928 | A British Red Ensign with the shield of the coat of arms of the Union of South Africa on a white roundel. |
 | Flag of South Africa 1928–1994 | Orange, white, and blue horizontal stripes, on the white stripe, a backwards Union Flag towards the hoist, the Orange Free State flag hanging vertically and the flag of the South African Republic, towards the fly. Used for both the Union and later Republic of South Africa |
 | Flag of South Africa 1994–present | Two horizontal bands of chilli red (top) and blue (bottom) with a black triangle at the hoist, over all a green horizontal (pall) (Y-shape), fimbriated white against the red and blue and gold against the black. |