The following is a list of flags of Belarus.
Contents
- State flag
- Presidential flag
- Presidential institutions
- Military flags
- Governmental flags
- Subdivision flags
- Political flags
- Minority flags
- Historical flags
- See also
- References
- External links
The following is a list of flags of Belarus.
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | June 7, 1995 [1] –present (ornament pattern modified in 2012) [2] | State flag and civil ensign | Proportions: 1:2 |
 | Vertical flag |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | December 11, 1997–2012 | Presidential flag | |
 | 2012–present | Presidential flag | Proportions: 5:6 |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Flag of Academy of Public Administration under the aegis of the President of the Republic of Belarus | ||
 | Flag of National Academy of Sciences of Belarus | ||
 | Flag of State Forensic Examination Committee of the Republic of Belarus |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 2007–present | Flag of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of Belarus | |
 | 2000–2012 | Flag of the Armed Forces | |
 | 2012–present | Flag of the Armed Forces | Ornament pattern modified in 2012 |
 | ?–present | Flag of the Presidential Security Service of Belarus | The obverse of the flag bears the coat of arms of Belaurs and the inscription "Служба бяспекі прэзідэнта" (Presidential Security Service). |
 | | The reverse of the flag bears the emblem of the Presidential Secret Service of Belarus and the inscription "Абавязак. Гонар. Айчына." (Duty. Honor. Fatherland.). | |
 | March 8, 2005–present | Flag of the Land Forces | Red, with emblem of the Land Forces in full colors in the center |
 | 2005–present | Flag of the Air Forces | Air force emblem corresponding to 2/5 of the total flag-width, placed on a blue field with yellow beams |
 | 2003–present | Flag of DOSAAF | Emblem of the Voluntary Society of Assistance to the Army, the Air Force and the Navy of the Republic of Belarus, centered on a sky-blue background |
 | Flag of the Special Forces of Belarus |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 2018–present | Ministry of Foreign Affairs | |
 | 2018–present | Ministry of Labour and Social Protection | |
 | 2018–present | Ministry of Economy | |
 | 2018–present | Ministry of Agriculture and Food | |
 | December 9, 1991–present | Ministry for Emergency Situations | |
 | 2000–2009 | Border Guard | Green with a red saltire |
 | 2000–2009 | Chairman of State Committee of the Border Guard | Green with a red saltire with the State coat of arms in the center. |
 | 2000–2009 | Chief of Staff of Border Guard | Green with a red saltire with the Border Guard emblem in the center. |
 | March 5, 2001–present | State Committee of Aviation | Blue with a triangle, in the center of which the symbol of the SCA is placed. |
 | 1991–1995 | Customs | White-red-white flag with a Pahonia with a green border on the fly. |
 | March 5, 2001–present | Customs | Green flag with the emblem of the Belarusian customs in the center. |
 | March 5, 2001–present | Vitebsk Customs |
| Flag | Administrative division | Adopted | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  | Minsk City | 2001 | Blue with the Minsk Coat of Arms of 1591 in the center. |
 |  | Brest Region | 2004 | Blue with a yellow zoubre (Bison bonasus) on a red stylized tower (coat of arms of the Region of Brest). |
 |  | Gomel Region | 2005 | Green with the coat of arms of the Region of Homyel (Gomel) (only in the centre of an obverse side of the flag). Ratio: 1:2. |
 |  | Grodno Region | 2007 | Red with the coat of arms of the Region of Hrodna (only in the centre of an obverse side of the flag). Ratio 1:2 |
 |  | Mogilev Region | 2005 | Red with the coat of arms of the Region of Mogilyov (only in the centre of an obverse side of the flag). Ratio: 1:2. |
 |  | Minsk Region | 2007 | Red with the coat of arms of the Region of Minsk (only in the centre of an obverse side of the flag). Ratio 1:2 |
 |  | Vitebsk Region | 2009 | Green with the coat of arms of the Region of Vitsebsk (only in the centre of an obverse side of the flag). Ratio 1:2 |
| Flag | Date | Party | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Current | |||
 | 2018–present | Combat Organization of Anarcho-Communists | |
 | 2007–present | Belaya Rus | |
 | 2005–present | Belarusian Social Democratic Party | |
 | 2004–present | Right Alliance and Belarusian Freedom Party | |
 | 1999–present | Conservative Christian Party – BPF | |
 | 1996–present | Communist Party of Belarus | Flag of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (1951–1991) |
  | 1994–present | Liberal Democratic Party of Belarus | |
 | 1994–present | Republican Party | |
 | 1992–present | Belarusian Agrarian Party | |
 | ?–present | National Bolshevik Party of Belarus | |
Former | |||
 | 1995–1999 | Belarusian Peasant Party | |
  | 1919–1930s | Belarusian Peasant Party "Green Oak" be | |
Other | |||
 | 2020 | A variant of the 1991–1995 flag of Belarus, used by pro-democracy protestors. | A white-red-white flag with the Pahonia coat of arms in the centre. |
 | 2017–present | Flag of Veyshnoria, used as an element of satire. | |
 | 2000s | Pro-Union State flag | |
 | Flag used by some Belarusian anarchists [3] | ||
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
  | Flags of Lipka Tatars | Top: A white-red-white flag with a crescent moon and a five-pointed star. Bottom: Flag is based on the flag of the Golden Horde. |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | since 1918 (in exile after 1919) | White-red-white flag Belarusian Democratic Republic | Proportions: 1:2 |
 | 1919–1925 | Belarusian Democratic Republic (in exile) | White with a red horizontal band of red, the central red stripe being bordered by a thin black stripes. In use besides the regular white-red-white flag. Black stripes are believed to symbolize mourning. |
 | 1918–1919 | Lithuanian–Byelorussian SSR | Plain red flag |
 | 1919 | Flag of The Second Polish Republic | |
 | 1919–1937 | Flag of the Soviet Socialist Republic of Belarus | Plain red flag |
 | 1937–1940 | Flag of the Byelorussian SSR | |
 | 1942–1944 | Belarusian Central Council | |
 | 1943–1945 | Union of Belarusian Youth | |
 | 1944–1951 | Flag of the Byelorussian SSR | |
 | 1951–1991 | Flag of the Byelorussian SSR | |
 | | All flags of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union did not bear the hammer and sickle on their reverse side. | |
 | 1991–1995 | State flag and civil ensign; today the white-red-white flag is used in opposition to the current government | Proportions: 1:2 |
 | 1995–2012 |

The Armed Forces of the Republic of Belarus are the military forces of Belarus. It consists of the Ground Forces and the Air Force and Air Defence Forces, all under the command of the Ministry of Defence. As a landlocked country, Belarus has no navy, however the Belarusian military does have control over some small Soviet inherited naval vessels in its rivers and lakes.

The Byelorussian SSR was one of only two Soviet republics to be separate members of the United Nations. Both republics and the Soviet Union joined the UN when the organization was founded in 1945.

Brest region, also known as Brest oblast or Brest voblasts, is one of the six regions of Belarus. Its administrative center is Brest. Other major cities in the region include Baranavichy, and Pinsk. As of 2024, it has a population of 1,308,569.
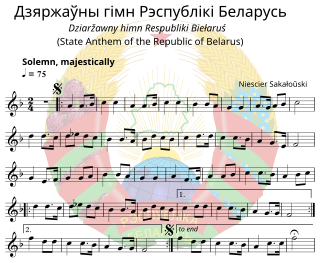
The State Anthem of the Republic of Belarus, better known as "We Belarusians", is the national anthem of Belarus. It was originally written in the 1940s and adopted in 1955 for use in the Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic. The music of the Belarusian SSR anthem was composed by Niescier Sakałowski and the lyrics were written by Michas Klimkovič. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the music composed by Sakalowski was kept and the lyrics were discarded. New lyrics, which were written by Klimkovič and Uładzimir Karyzna, were adopted by a presidential decree issued on 2 July 2002.

The national flag of Belarus is an unequal red-green bicolour with a red-on-white ornament pattern placed at the hoist (staff) end. The current design was introduced in 2012 by the State Committee for Standardisation of the Republic of Belarus, and is adapted from a design approved in a May 1995 referendum. It is a modification of the 1951 flag used while the country was a republic of the Soviet Union. Changes made to the Soviet-era flag were the removal of communist symbols – the hammer and sickle and the red star – as well as the reversal of the colours in the ornament pattern. Since the 1995 referendum, several flags used by Belarusian government officials and agencies have been modelled on this national flag.

The national emblem of Belarus features a ribbon in the colors of the national flag, a silhouette of Belarus, wheat ears and a red star. It is sometimes referred to as the coat of arms of Belarus, although in heraldic terms this is inaccurate as the emblem does not respect the rules of conventional heraldry. The emblem is an allusion to one that was used by the Byelorussian SSR, designed by Ivan Dubasov in 1950, with the biggest change being a replacement of the Communist hammer and sickle with a silhouette of Belarus. The Belarusian name is Dziaržaŭny hierb Respubliki Biełaruś, and the name in Russian is Gosudarstvennyĭ gerb Respubliki Belarusʹ.

Hero of Belarus is the highest title that can be bestowed on a citizen of Belarus. The title is awarded to those "who perform great deeds in the name of freedom, independence and prosperity of the Republic of Belarus". The deed can be for military performance, economic performance or great service to the State and society. The design of the medal is similar to that of its predecessor, Hero of the Soviet Union. Similar titles to the Hero of Belarus include the Hero of the Russian Federation, Hero of Ukraine, and Hero of Uzbekistan. Since its creation, the title has been awarded to eleven people.

The prime minister of the Republic of Belarus is the deputy head of government of Belarus. Until 1991, it was known as the Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic as the head of the government of the constituent republic of the Soviet Union.

The National Assembly of the Republic of Belarus is the bicameral parliament of Belarus. The two chambers of the National Assembly are:

The Council of the Republic of the National Assembly of the Republic of Belarus is the upper house of the parliament of Belarus.

The Party of Freedom and Progress is a liberal political party in Belarus. Since 2003, it has continuously failed to reach the minimum threshold to get an official registration by the electoral commission.

Currently, Belarus has an embassy in Riga, while Latvia has an embassy in Minsk. The countries share 161 km as it relates to their common border.

Visitors to Belarus must obtain a visa from one of the Belarusian diplomatic missions unless they are citizens of one of the visa-exempt countries.

Military Academy of the Republic of Belarus is higher military educational institution in the national education system of the Republic of Belarus and the leading institution in the education system of training, retraining and advanced training of military personnel. It is located on Independence Avenue in the Belarusuan capital of Minsk. It has 10 departments that train officers of 38 specialties for all arms of service.

The Ministry of Defence of the Republic of Belarus is the government organisation that is charged with the duties of raising and maintaining the Armed Forces of Belarus.

The Military Band Service of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Belarus is the central military band service of the Armed Forces of Belarus. The band was formed on 1 April 1950 as the Band of the Belorussian Military District. It was expanded into a service in the 1990s after the Independence of Belarus occurred. Its bands participate in military parades, military tattoos, and official ceremonies of Belarus. They perform domestically, regularly performing in the Central Officers House in Minsk, as well as other garrison clubs. The massed bands of the Minsk Garrison is an annual participant in the parades of the Minsk Garrison on Victors Avenue since 2004. The repertoire of the band includes more than 500 compositions of the most important classical music composers and contemporary ones. Bands have performed in festivals in Great Britain, Ireland, Germany, France, Poland, Sweden, and Russia. The band has also played in the Spasskaya Tower military tattoo in 2013, 2016, and 2017. The band is commanded by its Senior Director of Music/Chief Conductor, Lieutenant Colonel Igor Khlebus, since 2019. The artistic director of the band is Colonel Evgueny Dovzhik.

Pavel Pavlovich Latushko is a Belarusian politician and diplomat. He was the Minister of Culture of the Republic of Belarus from 2009 to 2012.

The Ministry of Economy of the Republic of Belarus or Minekonomiki (Минэкономики) is the Belarusian government ministry which oversees the economic policy of Belarus.

Belarus–NATO relations refers to relations between the Republic of Belarus and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).

The Order of Friendship of Peoples is a state award of the Republic of Belarus. It is the highest award of the Republic of Belarus for foreign citizens.