| Flag | Date | Party | Description |
|---|
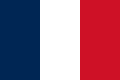
 | 1880–present | The Presidential and Prime Minister Standard of France | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 1:1). |
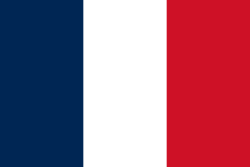 | The Presidential and Prime Minister Standard of France (variant) | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 3:2). |
 | 1887–1894 | Presidential standard of Sadi Carnot | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 1:1) with the golden "C". |
 | 1894–1895 | Presidential standard of Jean Casimir-Perier | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 1:1) with the golden "CP". |
 | 1895–1899 | Presidential standard of Félix Faure | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 1:1) with the golden "FF". |
 | 1899–1906 | Presidential standard of Émile Loubet | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 1:1) with the golden "EL". |
 | 1906–1913 | Presidential standard of Armand Fallières | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 1:1) with the golden "AF". |
 | 1913–1920 | Presidential standard of Raymond Poincaré | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 1:1) with the golden "RP". |
 | 1920 | Presidential standard of Paul Deschanel | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 1:1) with the golden "PD". |
 | 1920–1924 | Presidential standard of Alexandre Millerand | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 1:1) with the golden "AM". |
 | 1924–1931 | Presidential standard of Gaston Doumergue | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 1:1) with the golden "GD". |
 | 1931–1932 | Presidential standard of Paul Doumer | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 1:1) with the golden "PD". |
 | 1932–1940 | Presidential standard of Albert Lebrun | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 1:1) with the golden "AL". |

 | 1940–1944 | Presidential standards of Philippe Pétain | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red with the axe and 7 golden stars. |
 | 1947–1954 | Presidential standard of Vincent Auriol | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 1:1) with the golden "VA". |
 | 1958–1959 | Presidential standard of René Coty | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 1:1) with the golden "RC". |

 | 1959–1969 | Presidential standards of Charles de Gaulle | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 3:2) with the red Cross of Lorraine.
A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red (proportions 1:1) with the golden "CG" and the red Cross of Lorraine. |

 | 1969–1974 | Presidential standards of Georges Pompidou | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red with the golden "GP". |

 | 1974 | Presidential standards of Alain Poher | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red with the golden "AP". |

 | 1975–1981 | Presidential standards of Valéry Giscard d'Estaing | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red with the golden fasces. |

 | 1982–1995 | Presidential standards of François Mitterrand | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red with the golden oak tree. |

 | 1982–1995 | Presidential standards of François Mitterrand | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red with the golden "FM". |