| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|
 | 1492–1500 | Royal Flag of The Crown of Castile | quartered banner of arms of Castile, represented by a castle, and León, represented by a lion. |
 | 1500–1516 | Royal Flag of The Crown of Castile | the same design of the previous flag in a slightly different shape. |
 | 1516–1785 | Flag of the Captaincy General of Santo Domingo | The Cross of Burgundy flag represents the Spanish Empire. |
 | 1785–1795, 1810–1821, 1861–1865 | Flag of Santo Domingo | A Tricolour of Red, Yellow and Red with the coat of arms off-centred toward the hoist. In 1861, general Pedro Santana asked queen Isabella II of Spain to retake control of the Dominican Republic, after a period of only 17 years of independence. Spain, which had not come to terms with the loss of its American colonies 30 years earlier, accepted his proposal and made the country a colony again. |
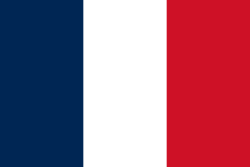 | 1795–1809 | Flag of the Saint-Domingue | The tricolour flag of the French First Republic. France came to own the whole island by the Treaty of Basel, as Spain ceded Santo Domingo as a consequence of the French Revolutionary Wars. |
 | 1809–1813 | Flag of Spain under Joseph Bonaparte | A White Banner with the coat of arms off-centred toward the hoist. |
 | 1821–1822 | Flag of Spanish Haiti | On 9 February 1822 Jean-Pierre Boyer annexed the Spanish out of the colony of Santo Domingo, which a few months before had proclaimed its independence from Spain (30 November 1821) under the name The Republica del Haiti Español . An attempt to declare its alliance to Gran Colombia, the flag was raised in the early weeks of 1822, but it was short-lived when nine weeks later Boyer had ended the republic. |
 | 1822–1844 | Flag of the Unification of Hispaniola | |
 | 1844–1849 | Flag of the Dominican War of Independence | It was developed from the flag of Haiti and was added a white symmetric cross. |
 | 1849–1861 | Flag of the First Dominican Republic | A crossed two-colored flag with the country's coat of arms in the center |
 | 1905–1908 | Flag of The United States | Thirteen horizontal stripes alternating red and white; in the canton, 45 white stars on a blue field. |
 | 1908–1912 | Flag of The United States | Thirteen horizontal stripes alternating red and white; in the canton, 46 white stars on a blue field. |
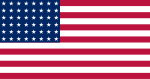 | 1912–1924 | Flag of The United States | Thirteen horizontal stripes alternating red and white; in the canton, 48 white stars on a blue field. |
|

































