National flag
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1962-Present | Flag of Trinidad and Tobago | A red field with a white-fimbriated black diagonal band from the upper hoist-side to the lower fly-side. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] |
==Government's flags SYM
This is the following is a list of flags related with Trinidad and Tobago.
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1962-Present | Flag of Trinidad and Tobago | A red field with a white-fimbriated black diagonal band from the upper hoist-side to the lower fly-side. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] |
==Government's flags SYM
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1962-Present | Flag of The Trinidad and Tobago Air Guard | A Blue field with the national flag in the canton and defaced with The Air Guard's Emblem. |
 | 1962-Present | Flag of The Trinidad and Tobago Regiment | A Green Field with The Regiment's Emblem in the center. |
 | 1962-Present | President's Flag of the Trinidad and Tobago Regiment | Similar to The National Flag, but with a golden border, The Emblem of the president in the center and The Coat of Arms surrounded by Laurels upwards. |
 | 1962-Present | Regimental Flag of the Trinidad and Tobago Regiment | A Green Field with a golden border, The Regiment's Emblem in the center and The Coat of Arms surrounded by Laurels upwards. |
 | 1962-Present | Flag of The Trinidad and Tobago Defence Force | A Horizontal Triband of Red, Blue and Cyan with The Defence Force's Emblem in the center. |
 | 1962-Present | Flag of The Trinidad and Tobago Defence Force Reserves | A Red Field with a small triband of green, white and blue with The Defence Force's Emblem in the center. |
 | 1962-Present | Civil Ensign of Trinidad and Tobago | A red field with a white-edged black diagonal band from the upper hoist-side to the lower fly-side. |
 | 1962-Present | Naval Ensign of Trinidad and Tobago | A White Ensign with the National Flag in the canton. |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1498-1516 | Flag of The Crown of Castile | quartered banner of arms of Castile, represented by a castle, and León, represented by a lion. |
 | 1516-1785 | Flag of The Spanish Empire | A red saltire resembling two crossed, roughly-pruned (knotted) branches, on a white field. |
 | 1785-1797 | Flag of The Kingdom of Spain | A horizontal triband flag of red, yellow (double width) and red; charged with the Spanish coat of arms off-centred toward the hoist. |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1628-1680 | The Prince's Flag | A Horizontal triband of orange, white and blue. |
 | 1652–1672 | States Flag | A Horizontal triband of red, white and blue. |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1654 1680-1693 | Flag of The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth | A horizontal triband of red (top), white and red with the Coat of arms of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in the center. |
 | 1654 1680-1693 | Flag of the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia | A Horizontal Bicolour of Red and White [7] |
 | 1654 1680-1693 | Merchant ensign of the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia | A Red Field with a black crab in the center. also known as The "Crab Flag". |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1662-1667 1781-1790 | Flag of The Kingdom of France | a white banner with several Fleur de Lis with the royal coat of arms in the center. |
 | 1790-1794 | Flag of The Kingdom of France and The French First Republic | A vertical tricolour of red, white and blue. |
 | 1794-1803 | Flag of The French First Republic | A vertical tricolour of blue, white and red. |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1733 | Flag of Sweden | A blue 3-pointed swallowtail field charged with a yellow Nordic cross that extends to the edges; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side. |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1639-1649 1672-1674 | Flag of England | A white field with centred red cross. |
 | 1649-1651 | Flag of The Commonwealth of England | St George's Cross and an Irish Harp juxtaposed. [8] |
 | 1651-1654 | Flag of The Commonwealth of England | St George's Cross and St Andrew's cross quartered. |
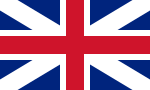 | 1762-1781 | Flag of The Kingdom of Great Britain | A superimposition of the flags of England and Scotland |
 | 1803-1962 | Flag of The United Kingdom | A superimposition of the flags of England and Scotland with the Saint Patrick's Saltire (representing Ireland). |
 | 1886-1903 | Flag of The British Windward Islands | A blue ensign with the arms of The Windward Islands. [9] |
 | 1889–1958 | Flag of The Colony of Trinidad and Tobago | A blue ensign with the arms of Trinidad & Tobago. [10] |
 | 1903-1953 | Flag of The British Windward Islands | A blue ensign with the arms of The Windward Islands. [11] |
 | 1953-1958 | Flag of The British Windward Islands | A blue ensign with the arms of The Windward Islands. |
 | 1958–1962 | Flag of The West Indies Federation | A blue field with four white horizontal wavy bars (the top pair of bars being parallel and the lower pair also parallel) and an orange sun in the center. [12] |
 | 1958–1962 | Flag of The Colony of Trinidad and Tobago | A blue ensign with the arms of Trinidad & Tobago. [13] |
 | 1962–1976 | Royal Flag of Trinidad and Tobago | the coat of arms of Trinidad and Tobago in banner form, which depicts the colours of the national flag. The gold ships represent the three ships Christopher Columbus used on his voyage. The two birds above are hummingbirds. A blue disc of the crowned letter "E", surrounded by a garland of gold roses defaced the flag, which is taken from the Queen's Personal Flag. [14] |