National flag
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1966-present | Flag of Ghana | A horizontal triband of red, gold, and green, charged with a black star in the centre. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] |
The following is a list of flags associated with Ghana. For more information about the current national flag, see flag of Ghana.
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1966-present | Flag of Ghana | A horizontal triband of red, gold, and green, charged with a black star in the centre. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1966-present | Flag of the president of Ghana | A horizontal triband of red, gold, and green, charged with a black star in the centre with a gold rim. |
 | 1964-1966 | Flag of the president of Ghana | An electric blue field with the government emblem in the centre. |
 | 1966-present | Flag of the president of Ghana | A navy blue field with the government emblem in the centre. [11] |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1935-present | Flag of the Ashanti people | A horizontal tricolour of gold, black, green and white with the Golden Stool stationed in the middle of flag. [12] |
 | ?-present | Flag of the Ewe people | A horizontal tricolour of green (top), red and green with 3 golden stars in the red stripe. [13] |
 | ?-present | Flag of the Hausa people | A white field with the Dagin Arewa star in the centre. [14] |
 | ?-present | Flag of the Yoruba people | A blue field with a white disc off-centre toward the hoist and 2 green rings and a golden spear inside the disc. [15] |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1992-present | Flag of the Ghanan National Democratic Congress | 4 horizontal stripes of black, red, white and green with the emblem in the centre. [16] |
 | 1966-present | Flag of the Convention People's Party | |
 | 2017-present | Flag of Western Togoland | |
| Link to file | 1992-present | Flag of the People's National Convention | |
| Link to file | 2006-2012 | Flag of the Democratic Freedom Party |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1964-1966 | Civil ensign of Ghana | A red field with the national flag, fimbriated in black, in the canton. |
 | 1966-present | Civil ensign of Ghana | A red field with the national flag, fimbriated in black, in the canton. [17] |
 | 1964-1966 | Naval ensign of Ghana | Red St. George's Cross on white centrrensign, with the national flag in canton. |
 | 1966-present | Naval ensign of Ghana | Red St. George's Cross on white centrrensign, with the national flag in canton. [18] |
 | 1964-1966 | Air Force ensign of Ghana | A light-blue field with the national flag in canton charged in the fly with a red, white and green roundel. |
 | 1966-present | Air Force ensign of Ghana | A light-blue field with the national flag in canton charged in the fly with a red, yellow and green roundel. [19] |
 | 1964-1966 | Civil Air ensign of Ghana | A light-blue field with the national flag in canton charged in the fly with a black five-pointed star. |
 | 1966-present | Civil Air ensign of Ghana | A light-blue field with the national flag in canton charged in the fly with a black five-pointed star. [20] |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 2002 | Emmanuel Enoch Agbozo's proposal | |
 | 1914 | Proposed flag of German Togoland | A tricolour, made of three equal horizontal bands coloured black (top), white, and red (bottom) with the emblem of Togoland in the centre. [21] |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1482-1485 | Flag of the Kingdom of Portugal (Portuguese Gold Coast) | Five blue escutcheons each charged with an undetermined number of bezants on a white field. Border: red with yellow castles and a green cross of the Order of Aviz. |
 | 1485-1495 | Flag of the Kingdom of Portugal (Portuguese Gold Coast) | Five blue escutcheons each charged with 5 bezants on a white field. Border: red with 7 yellow castles. |
 | 1495-1521 | Flag of the Kingdom of Portugal (Portuguese Gold Coast) | A white field with the Portuguese coat of arms in the centre. |
 | 1521-1578 | Flag of the Kingdom of Portugal (Portuguese Gold Coast) | A white field with the Portuguese coat of arms in the centre. |
 | 1578-1640 | Flag of the Kingdom of Portugal (Portuguese Gold Coast) | A white field with the Portuguese coat of arms in the centre. |
 | 1612-1795 | The Prince's Flag of the Dutch Republic (Dutch Gold Coast) | A horizontal tricolour of orange, white and blue. |
 | 1616-1640 | Flag of the Kingdom of Portugal (Portuguese Gold Coast) (Putative Flag) | A white field with the Portuguese coat of arms in the centre. |
 | 1631-1637 1663-1700 | Flag of the Kingdom of England (English Gold Coast) | A white field with centred red cross. |
 | 1640-1642 | Flag of the Kingdom of Portugal (Portuguese Gold Coast) | A white field with the Portuguese coat of arms in the centre. |
 | 1650–1658 1660–1663 | Flag of the Kingdom of Sweden (Swedish Gold Coast) | Blue with a yellow Nordic cross that extends to the edges of the flag. Overall ratio, including the tails. |
 | 1652–1672 | States Flag of the Dutch Republic (Dutch Gold Coast) | A horizontal tricolour of red, white and blue. |
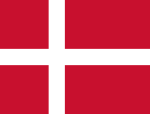 | 1658–1850 | Flag of Denmark–Norway and the Kingdom of Denmark (Danish Gold Coast) | A red field charged with a white Nordic cross that extends to the edges; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side. |
 | 1663-1700 | Flag of the Royal African Company | A white field with centred red cross with a chess themed border. [22] |
 | 1682-1721 | Flag of the Holy Roman Empire (Brandenburger/Prussian Gold Coast). | A black double-headed eagle with haloes on a yellow field. |
 | 1682-1701 | Flag of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (Brandenburger Gold Coast). | 7 horizontal stripes alternating black and white; with a red eagle off-centred toward the hoist. |
 | 1684-1701 | Flag of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (Brandenburger Gold Coast). | A white field with a red crowned eagle off-centred toward the hoist. [23] |
 | 1701-1721 | Flag of the Kingdom of Prussia (Prussian Gold Coast). | A black eagle holding a sword and rod on a white field, a crown on top. |
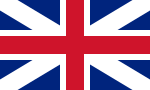 | 1750-1801 | Flag of the Kingdom of Great Britain | A superimposition of the flags of England and Scotland |
 | 1795–1813 | Flag of the French First Republic and the First French Empire (French occupied Dutch Gold Coast) | A vertical tricolour of blue, white, and red. |
 | 1795–1806 | Flag of the Batavian Republic | A horizontal triband of red, white and blue with the Republic’s emblem in the canton. |
 | 1801-1960 | Flag of the United Kingdom | A superimposition of the flags of England and Scotland with the Saint Patrick's Saltire (representing Ireland). |
 | 1806-1872 | Flag of the Kingdom of Holland, the Sovereign Principality of the United Netherlands, the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and the Kingdom of the Netherlands (Dutch Gold Coast) | A horizontal tricolour of red, white and blue. |
 | 1870-1877 | Flag of the British West Africa | A blue ensign defaced with the emblem of the West African Settlements. [24] |
 | 1877-1957 | Flag of the British Gold Coast | A blue ensign defaced with the emblem of the Gold Coast. [25] |
 | 1884-1916 | Flag of the German Empire (German Togoland) | A tricolour, made of three equal horizontal bands coloured black (top), white, and red (bottom) |
 | 1884-1916 | Colonial flag of the German Empire | A tricolour, made of three equal horizontal bands coloured black (top), white, and red (bottom) with the Reichsadler in the centre. |
 | 1916-1956 | Flag of the British Togoland | A blue ensign defaced with an elephant. |
 | 1935-1957 | Flag of the Ashanti Empire | A horizontal tricolour of gold, black, green and white with the Golden Stool stationed in the middle of flag. |
 | 1957-1964 | Flag of the Dominion of Ghana and 1st Flag of Ghana | A horizontal triband of red, gold, and green, charged with a black star in the centre. [26] |
 | 1958-1961 | Flag of the Union of African States | A horizontal triband of red, gold, and green, charged with 2 black stars on the yellow band. [27] |
 | 1961-1962 | Flag of the Union of African States | A horizontal triband of red, gold, and green, charged with 3 black stars on the yellow band. |
 | 1964-1966 | 2nd flag of Ghana | A horizontal triband of red, white, and green, charged with a black star in the centre. [28] [29] |

Ghana, officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It lies adjacent to the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing a border with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and Togo in the east. Ghana covers an area of 239,567 km2 (92,497 sq mi), spanning diverse ecologies, from coastal savannas to tropical rainforests. With nearly 35 million inhabitants, Ghana is the second-most populous country in West Africa. The capital and largest city is Accra; other significant cities include Kumasi, Tamale, and Sekondi-Takoradi. In 1957 Ghana became the first colony in Sub-Saharan Africa to achieve sovereignty, under the leadership of Kwame Nkrumah.

Pan-African colours is a term that may refer to two different sets of colours:

"God Bless Our Homeland Ghana" is the national anthem of Ghana; it was adopted in 1957 when Ghana declared its independence from the United Kingdom.

The national flag of Ghana consists of a horizontal triband of red, yellow, and green. It was designed in replacement of the British Gold Coast's Blue Ensign.

Ampe is a simple but energy-driven game played by school-age children. It originated from Ghana and also played in other neighbouring countries. It is played by two or more people and requires no equipment.

The Black Star of Africa is a black five-pointed star symbolizing Africa in general and Ghana in particular. The Black Star Line, founded in 1919 by Marcus Garvey as part of the Back-to-Africa movement, modelled its name on that of the White Star Line, changing the colour from white to black to symbolise ownership by black people rather than white people. The black star became a symbol of Pan-Africanism and anti-colonialism. Described as the "Lodestar of African Freedom", the black star was used in 1957 by Theodosia Okoh in the design of the Flag of Ghana.

Susanna Al-Hassan or Susan Alhassan was a Ghanaian author and politician, who in 1961 became Ghana's first female to be appointed minister. She was the first African woman to hold a cabinet portfolio and became the member of parliament for the then Northern Region parliamentary constituency between 1960 and 1966. She also wrote several children's books.

Ghana gained independence from the British on 6 March 1957. It is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations. The country became a republic on July 1, 1960.
2015 in Ghana lists events of note that happened in the Ghana in the year 2015.
Theodosia Salome Okoh was a Ghanaian teacher and artist known for designing Ghana's national flag in 1957. She exhibited her artwork internationally. She also played a leading role in the development of hockey in Ghana. Her grandson is Ian Jones-Quartey, creator of OK K.O.! Let's Be Heroes, and her granddaughter-in-law is Rebecca Sugar, creator of Steven Universe.

The Independence Day of Ghana is a national holiday celebrated yearly. This day is an official state holiday for the citizens of Ghana both within and in the diaspora to honour and celebrate the Heroes of Ghana who led the country to attain its independence. The Independence Day is celebrated on March 6 every year. Independence Day is also remembrance of the day that marks the declaration of Ghanaian independence from the British colonial rule. The first Prime Minister of Ghana, Kwame Nkrumah, became the Head of Government from 1957 to 1960. On Wednesday, 6 March 1957 Kwame Nkrumah declared to the people of Ghana about their freedom, he added that, "the African People are capable of managing their own affairs and Ghana our beloved country is free forever." Ghana was the first country in sub-Saharan Africa to achieve its independence from European colonial rule. Many Ghanaians who have had the opportunity to serve as president have remembered the occasion and made Ghana Independence Day a public holiday to celebrate. Granting the day as a national holiday is well recognized such that, if 6 March of a year fell on a weekend of the Independence Day celebration, the working day that follows which is a Monday will be granted and observed as a holiday by the whole nation. Many Presidents from other African countries and Europe have been invited to Ghana to join in the celebration either as Guest Speakers or Invited Guests since the reign of former President Kwame Nkrumah till now.
Letitia Eva Takyibea Obeng was the first Ghanaian woman to obtain a degree in zoology and the first to be awarded a doctorate. She is described as "the grandmother of female scientists in Ghana".
Okoh may refer to:
Paul Okoh was a Ghanaian diplomat and a member of the New Patriotic Party of Ghana. He is currently Ghana's ambassador to Egypt.

GhanaWeb, founded as GhanaHomePage, is a Ghananian portal, content curation and syndication website covering news, politics, business, sports, entertainment, opinions and general information about Ghana. It was launched by GhanaWeb B.V., a privately-owned Dutch company in 1999. It also offers background information, classifieds, radio stations and a social network for Ghanaians and the Diaspora.

The Greater Accra Regional Minister is the Ghana government official who is responsible for overseeing the administration of the Greater Accra Region of Ghana. The region was initially an administrative district within the Eastern Region of Ghana. The region was formally created by law in July 1982 by Provisional National Defence Council government through the Greater Accra Region Law as a legally separate region. Currently, the southern boundary of the Greater Accra Region is the Atlantic Ocean. To the east is the Volta Region, Central Region to the west and the Eastern Region to the north. There are currently sixteen administrative regions in Ghana.

The Western Togoland Rebellion is an ongoing separatist revolt led by the Ewe nationalist organization Western Togoland Restoration Front (WTRF) against the government of Ghana. The group seeks the independence of former British Togoland.

The Spelling Bee is an annual spelling bee held in Ghana since 2007.

Flag families are sets of national flags with similarities in their design, often based on a shared history, culture, or influence. Families do not include flags with coincidental similarities. Flags may be in multiple flag families. Only twelve current national flags existed before the 19th century, when large-scale flag use began. Seven of these flags are the inspiration for more than 130 current national flags and ensigns.