Related Research Articles
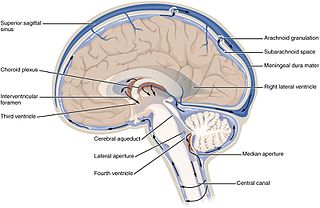
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.

In a mixture of gases, each constituent gas has a partial pressure which is the notional pressure of that constituent gas as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture.

Oligoclonal bands (OCBs) are bands of immunoglobulins that are seen when a patient's blood serum, or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is analyzed. They are used in the diagnosis of various neurological and blood diseases. Oligoclonal bands are present in the CSF of more than 95% of patients with clinically definite multiple sclerosis.
Reference ranges for blood tests are sets of values used by a health professional to interpret a set of medical test results from blood samples. Reference ranges for blood tests are studied within the field of clinical chemistry, the area of pathology that is generally concerned with analysis of bodily fluids.

Lumbar puncture (LP), also known as a spinal tap, is a medical procedure in which a needle is inserted into the spinal canal, most commonly to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for diagnostic testing. The main reason for a lumbar puncture is to help diagnose diseases of the central nervous system, including the brain and spine. Examples of these conditions include meningitis and subarachnoid hemorrhage. It may also be used therapeutically in some conditions. Increased intracranial pressure is a contraindication, due to risk of brain matter being compressed and pushed toward the spine. Sometimes, lumbar puncture cannot be performed safely. It is regarded as a safe procedure, but post-dural-puncture headache is a common side effect if a small atraumatic needle is not used.

The choroid plexus, or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. Regions of the choroid plexus produce and secrete most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the central nervous system. The choroid plexus consists of modified ependymal cells surrounding a core of capillaries and loose connective tissue. Multiple cilia on the ependymal cells move to circulate the cerebrospinal fluid.

Glycine encephalopathy is a rare autosomal recessive disorder of glycine metabolism. After phenylketonuria, glycine encephalopathy is the second most common disorder of amino acid metabolism. The disease is caused by defects in the glycine cleavage system, an enzyme responsible for glycine catabolism. There are several forms of the disease, with varying severity of symptoms and time of onset. The symptoms are exclusively neurological in nature, and clinically this disorder is characterized by abnormally high levels of the amino acid glycine in bodily fluids and tissues, especially the cerebrospinal fluid.

Tauopathies are a class of neurodegenerative diseases characterized by the aggregation of abnormal tau protein. Hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins causes them to dissociate from microtubules and form insoluble aggregates called neurofibrillary tangles. Various neuropathologic phenotypes have been described based on the anatomical regions and cell types involved as well as the unique tau isoforms making up these deposits. The designation 'primary tauopathy' is assigned to disorders where the predominant feature is the deposition of tau protein. Alternatively, diseases exhibiting tau pathologies attributed to different and varied underlying causes are termed 'secondary tauopathies'. Some neuropathologic phenotypes involving tau protein is Alzheimer's disease, Pick disease, Progressive supranuclear palsy, and corticobasal degeneration.

Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the CNS in which activated immune cells invade the central nervous system and cause inflammation, neurodegeneration, and tissue damage. The underlying cause is currently unknown. Current research in neuropathology, neuroimmunology, neurobiology, and neuroimaging, together with clinical neurology, provide support for the notion that MS is not a single disease but rather a spectrum.

Xanthochromia, from the Greek xanthos (ξανθός) "yellow" and chroma (χρώμα) "colour", is the yellowish appearance of cerebrospinal fluid that occurs several hours after bleeding into the subarachnoid space caused by certain medical conditions, most commonly subarachnoid hemorrhage. Its presence can be determined by either spectrophotometry or simple visual examination. It is unclear which method is superior.
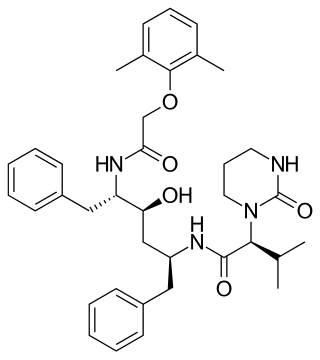
Lopinavir is an antiretroviral of the protease inhibitor class. It is used against HIV infections as a fixed-dose combination with another protease inhibitor, ritonavir (lopinavir/ritonavir).

Neurogranin is a calmodulin-binding protein expressed primarily in the brain, particularly in dendritic spines, and participating in the protein kinase C signaling pathway. Neurogranin has recently been found in aortic endothelial cells and cardiomyocytes. Neurogranin is the main postsynaptic protein regulating the availability of calmodulin, binding to it in the absence of calcium. Phosphorylation by protein kinase C lowers its binding ability. NRGN gene expression is controlled by thyroid hormones. Human neurogranin consists of 78 amino acids.

A medical laboratory or clinical laboratory is a laboratory where tests are conducted out on clinical specimens to obtain information about the health of a patient to aid in diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease. Clinical medical laboratories are an example of applied science, as opposed to research laboratories that focus on basic science, such as found in some academic institutions.

The CSF tap test, sometimes lumbar tap test or Miller Fisher Test, is a medical test that is used to decide whether shunting of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) would be helpful in a patient with suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH). The test involves removing 30-50 ml of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) through a lumbar puncture, after which motor and cognitive function is clinically reassessed. The name "Fisher test" is after C. Miller Fisher, a Canadian neurologist working in Boston, Massachusetts, who described the test.

A cerebrospinal fluid leak is a medical condition where the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that surrounds the brain and spinal cord leaks out of one or more holes or tears in the dura mater. A CSF leak is classed as either spontaneous (primary), having no known cause, or nonspontaneous (secondary) where it is attributed to an underlying condition. Causes of a primary CSF leak are those of trauma including from an accident or intentional injury, or arising from a medical intervention known as iatrogenic. A basilar skull fracture as a cause can give the sign of CSF leakage from the ear nose or mouth. A lumbar puncture can give the symptom of a post-dural-puncture headache.
CSF albumin is a measurement used to determine the levels of albumin in cerebrospinal fluid.

Lymphocytic pleocytosis is an abnormal increase in the amount of lymphocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It is usually considered to be a sign of infection or inflammation within the nervous system, and is encountered in a number of neurological diseases, such as pseudomigraine, Susac's syndrome, and encephalitis. While lymphocytes make up roughly a quarter of all white blood cells (WBC) in the body, they are generally rare in the CSF. Under normal conditions, there are usually less than 5 white blood cells per μL of CSF. In a pleocytic setting, the number of lymphocytes can jump to more than 1,000 cells per μL. Increases in lymphocyte count are often accompanied by an increase in cerebrospinal protein concentrations in addition to pleocytosis of other types of white blood cells.

The glymphatic system is a system for waste clearance in the central nervous system (CNS) of vertebrates. According to this model, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flows into the paravascular space around cerebral arteries, combining with interstitial fluid (ISF) and parenchymal solutes, and exiting down venous paravascular spaces. The pathway consists of a para-arterial influx route for CSF to enter the brain parenchyma, coupled to a clearance mechanism for the removal of interstitial fluid (ISF) and extracellular solutes from the interstitial compartments of the brain and spinal cord. Exchange of solutes between CSF and ISF is driven primarily by arterial pulsation and regulated during sleep by the expansion and contraction of brain extracellular space. Clearance of soluble proteins, waste products, and excess extracellular fluid is accomplished through convective bulk flow of ISF, facilitated by astrocytic aquaporin 4 (AQP4) water channels.
Several biomarkers for diagnosis of multiple sclerosis, disease evolution and response to medication are under research. While most of them are still under research, there are some of them already well stablished:
Anne Cross is an American neurologist and neuroimmunologist and the Section Head of Neuroimmunology at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Missouri. Cross holds the Manny and Rosalyn Rosenthal–Dr. John L. Trotter Endowed Chair in Neuroimmunology at Washington University in St. Louis School of Medicine and co-directs the John L Trotter Multiple Sclerosis Clinic at Barnes-Jewish Hospital. Cross is a leader in the field of neuroimmunology and was the first to discover the role of B cells in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis (MS) in animals and then in humans. Cross now develops novel imaging techniques to observe inflammation and demyelination in the central nervous systems of MS patients for diagnosis and disease management.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 PATHOLOGY 425 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF] Archived 2005-10-27 at the Wayback Machine at the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine at the University of British Columbia. By Dr. G.P. Bondy. Retrieved November 2011 [ dead link ]
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Normal Reference Range Table Archived 2011-12-25 at the Wayback Machine from The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas. Used in Interactive Case Study Companion to Pathologic basis of disease.
- 1 2 Department of Chemical Pathology at the Chinese University of Hong Kong Archived 2015-01-05 at the Wayback Machine , in turn citing: Roberts WL et al. Reference Information for the Clinical Laboratory. In Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics, 4th edn. Burtis CA, Ashwood ER and Bruns DE eds. Elsevier Saunders 2006; 2251 - 2318
- ↑ Felgenhauer K (1974). "Protein size and CSF composition". Klin. Wochenschr. 52 (24): 1158–64. doi:10.1007/BF01466734. PMID 4456012. S2CID 19776406.
- 1 2 Lab Manual for SFGH > PROTEIN, CSF - IgG INDEX Archived 2015-01-05 at the Wayback Machine at The University of California, San Francisco. Last updated 10/4/2010.
- 1 2 Standardization of procedures and methods in neuroimmunology Archived 2013-10-21 at the Wayback Machine from the Italian Association of Neuroimmunology. Retrieved January, 2012
- 1 2 3 4 Derived from mmHg values using 0.133322 kPa/mmHg