See also
This article includes a building-related list of lists.
The following are lists of hydroelectric power stations based on the four methods of hydroelectric generation:

Hydropower, also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of a water source to produce power. Hydropower is a method of sustainable energy production.

A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electrical grid.

Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power systems for load balancing. The method stores energy in the form of gravitational potential energy of water, pumped from a lower elevation reservoir to a higher elevation. Low-cost surplus off-peak electric power is typically used to run the pumps. During periods of high electrical demand, the stored water is released through turbines to produce electric power. Although the losses of the pumping process make the plant a net consumer of energy overall, the system increases revenue by selling more electricity during periods of peak demand, when electricity prices are highest. If the upper lake collects significant rainfall or is fed by a river then the plant may be a net energy producer in the manner of a traditional hydroelectric plant.
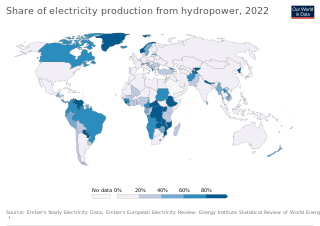
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity produced from hydropower. In 2020 hydropower generated one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh, which was more than all other renewables combined and also more than nuclear power.

The Palmiet Pumped Storage Scheme consists of two 200 megawatts (270,000 hp) turbine units located 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) upstream of the Kogelberg Dam on the Palmiet River near Cape Town, South Africa. The pumped-storage hydroelectricity plant is capable of responding to a surge in peak power demand in minutes. At night, excess power on the grid generated by conventional coal and nuclear plants is used to pump water to the Upper Reservoir overlooking Gordon's Bay.
The Shoalhaven Scheme is a dual-purpose water supply and Pumped-storage Hydroelectricity scheme located on the South Coast region of New South Wales, Australia.

The Murray Region Hydroelectric Power Stations refers to two of the original seven hydroelectric power stations, both located near the town of Khancoban in the Snowy Mountains region of New South Wales, Australia. The two power stations are part of the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro. Although both power stations are physically located in New South Wales, since 1 July 2008 all power generated has been allocated to the Victorian region of the National Electricity Market. The stations are not located on the Murray River.

Tumut Hydroelectric Power Station is a series of three of the original four, now five hydroelectric power stations on the Tumut River in New South Wales, Australia, that are part of the Snowy Mountains Scheme.

Sir Adam Beck Hydroelectric Generating Stations are two hydroelectric generating stations in Niagara Falls, Ontario, Canada. Sir Adam Beck Generating Station I, Sir Adam Beck Generating Station II and the Sir Adam Beck Pump Generating Station are all owned by Ontario Power Generation. Following the development of several smaller generating stations around Niagara Falls in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the Province of Ontario authorized the construction of the first major publicly owned generating station in the province. At the time it was built, it was the largest hydroelectric generating station in the world.

Run-of-river hydroelectricity (ROR) or run-of-the-river hydroelectricity is a type of hydroelectric generation plant whereby little or no water storage is provided. Run-of-the-river power plants may have no water storage at all or a limited amount of storage, in which case the storage reservoir is referred to as pondage. A plant without pondage is subject to seasonal river flows, thus the plant will operate as an intermittent energy source. Conventional hydro uses reservoirs, which regulate water for flood control, dispatchable electrical power, and the provision of fresh water for agriculture.
The Ingula Pumped Storage Scheme is a pumped-storage power station in the escarpment of the Little Drakensberg range straddling the border of the KwaZulu-Natal and Free State provinces, South Africa. It is about 22 km (14 mi) North-East of Van Reenen.

Hydroelectric power in the United States is, as of 2019, the second-largest renewable source of energy in both generation and nominal capacity. In 2019, hydroelectric power produced 38% of the total renewable electricity, and 6.6% of the total U.S. electricity.

India is 5th globally for installed hydroelectric power capacity. As of 31 March 2020, India's installed utility-scale hydroelectric capacity was 46,000 MW, or 12.3% of its total utility power generation capacity. Additional smaller hydroelectric power units with a total capacity of 4,683 MW have been installed. India's hydroelectric power potential is estimated at 148,700 MW at 60% load factor. In the fiscal year 2019–20, the total hydroelectric power generated in India was 156 TWh with an average capacity factor of 38.71%.

The Grand'Maison Dam is an embankment dam on L'Eau d'Olle, a tributary of the Romanche River. It is located in Vaujany of Isère within the French Alps. The primary purpose of the dam is to serve as the upper reservoir for a pumped-storage hydroelectric scheme where Lac du Verney located lower in the valley is the lower reservoir. The dam was constructed between 1978 and 1985 with its power station being commissioned in 1987. With an installed capacity of 1,800 MW, it is the largest hydroelectric power station in France.

The Linth–Limmern Power Stations are a system of hydroelectric power stations located south of Linthal in the canton of Glarus, Switzerland. The system uses five reservoirs and four power stations at steep variations in altitude.

As of 2018, hydroelectric power stations in the United Kingdom accounted for 1.87 GW of installed electrical generating capacity, being 2.2% of the UK's total generating capacity and 4.2% of UK's renewable energy generating capacity. This includes four conventional hydroelectric power stations and run-of-river schemes for which annual electricity production is approximately 5,000 GWh, being about 1.3% of the UK's total electricity production. There are also pumped-storage hydroelectric power stations providing a further 2.8 GW of installed electrical generating capacity, and contributing up to 4,075 GWh of peak demand electricity annually.
Hydroelectricity is the second most important renewable energy source after solar energy in Japan with an installed capacity of 50.0 gigawatt (GW) as of 2019. According to the International Hydropower Association Japan was the world's sixth largest producer of hydroelectricity in 2020. Most of Japanese hydroelectric power plants are pumped-storage plants. Conventional hydropower plants account for about 20 GW out of the total installed capacity as of 2007.

The Okawachi Pumped Storage Power Station is a large pumped-storage hydroelectric power station in Kamikawa Town in the Kanzaki District of Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan. With a total installed capacity of 1,280 megawatts (1,720,000 hp), it is one of the largest pumped-storage power stations in Japan. The facility is run by the Kansai Electric Power Company (KEPCO). The power plant started operation in October 1992 and all four units were commissioned by June 1995.
The Shintoyone Pumped Storage Power Station is a large pumped-storage hydroelectric power plant in Toyone, Kitashitara, Aichi Prefecture, Japan. With an installed capacity of 1,125 megawatts (1,509,000 hp), the plant is one of the largest pumped-storage power stations in Japan.