Related Research Articles

Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery to end users or its storage, using for example, the pumped-storage method.

Renewable energy is energy from renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind power, and hydropower. Bioenergy and geothermal power are also significant in some countries. Some also consider nuclear power a renewable power source, although this is controversial. Renewable energy installations can be large or small and are suited for both urban and rural areas. Renewable energy is often deployed together with further electrification. This has several benefits: electricity can move heat and vehicles efficiently and is clean at the point of consumption. Variable renewable energy sources are those that have a fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power. In contrast, controllable renewable energy sources include dammed hydroelectricity, bioenergy, or geothermal power.

Energy development is the field of activities focused on obtaining sources of energy from natural resources. These activities include the production of renewable, nuclear, and fossil fuel derived sources of energy, and for the recovery and reuse of energy that would otherwise be wasted. Energy conservation and efficiency measures reduce the demand for energy development, and can have benefits to society with improvements to environmental issues.
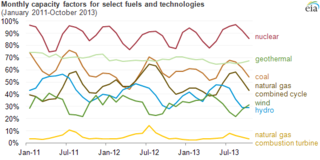
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full nameplate capacity over the relevant period. The capacity factor can be calculated for any electricity producing installation, such as a fuel consuming power plant or one using renewable energy, such as wind, the sun or hydro-electric installations. The average capacity factor can also be defined for any class of such installations, and can be used to compare different types of electricity production.

Renewable energy progress in the European Union (EU) is driven by the European Commission's 2023 revision of the Renewable Energy Directive, which raises the EU's binding renewable energy target for 2030 to at least 42.5%, up from the previous target of 32%. Effective since November 20, 2023, across all EU countries, this directive aligns with broader climate objectives, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030 and achieving climate neutrality by 2050. Additionally, the Energy 2020 strategy exceeded its goals, with the EU achieving a 22.1% share of renewable energy in 2020, surpassing the 20% target.
The natural environment, commonly referred to simply as the environment, is all living and non-living things that occur naturally on Earth or some part of it. This includes complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive human intervention, including all vegetation, animals, microorganisms, rocks, atmosphere and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries. And it includes universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water, and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism, not originating from human activity.

Renewable energy commercialization involves the deployment of three generations of renewable energy technologies dating back more than 100 years. First-generation technologies, which are already mature and economically competitive, include biomass, hydroelectricity, geothermal power and heat. Second-generation technologies are market-ready and are being deployed at the present time; they include solar heating, photovoltaics, wind power, solar thermal power stations, and modern forms of bioenergy. Third-generation technologies require continued R&D efforts in order to make large contributions on a global scale and include advanced biomass gasification, hot-dry-rock geothermal power, and ocean energy. In 2019, nearly 75% of new installed electricity generation capacity used renewable energy and the International Energy Agency (IEA) has predicted that by 2025, renewable capacity will meet 35% of global power generation.

According to data from the US Energy Information Administration, renewable energy accounted for 8.4% of total primary energy production and 21% of total utility-scale electricity generation in the United States in 2022.

Renewable energy in Spain, comprising bioenergy, wind, solar, and hydro sources, accounted for 15.0% of the Total Energy Supply (TES) in 2019. Oil was the largest contributor at 42.4% of the TES, followed by gas, which made up 25.4%.

The renewable-energy industry is the part of the energy industry focusing on new and appropriate renewable energy technologies. Investors worldwide are increasingly paying greater attention to this emerging industry. In many cases, this has translated into rapid renewable energy commercialization and considerable industry expansion. The wind power, solar power and hydroelectric power industries provide good examples of this.

The electricity sector in Sri Lanka has a national grid which is primarily powered by hydroelectric power and thermal power, with sources such as photovoltaics and wind power in early stages of deployment. Although potential sites are being identified, other power sources such as geothermal, nuclear, solar thermal and wave power are not used in the power generation process for the national grid.

Policy makers often debate the constraints and opportunities of renewable energy.

Despite the historic usage of wind power to drain water and grind grain, the Netherlands today lags 21 of the 26 other member states of the European Union in the consumption of energy from renewable sources. In 2022, the Netherlands consumed just 15% of its total energy from renewables. According to statistics published by Eurostat, it was the last among the EU countries in the shift away from global warming-inducing energy sources. The leading renewable sources in the country are biomass, wind, solar and both geothermal and aerothermal power. In 2018 decisions were made to replace natural gas as the main energy source in the Netherlands with increased electrification being a major part of this process.
Under its commitment to the EU renewable energy directive of 2009, France has a target of producing 23% of its total energy needs from renewable energy by 2020. This figure breaks down to renewable energy providing 33% of energy used in the heating and cooling sector, 27% of the electricity sector and 10.5% in the transport sector. By the end of 2014, 14.3% of France's total energy requirements came from renewable energy, a rise from 9.6% in 2005.

Renewable energy in Taiwan contributed to 8.7% of national electricity generation as of end of 2013. The total installed capacity of renewable energy in Taiwan by the end of 2013 was 3.76 GW.

Renewables supply a quarter of energy in Turkey, including heat and electricity. Some houses have rooftop solar water heating, and hot water from underground warms many spas and greenhouses. In parts of the west hot rocks are shallow enough to generate electricity as well as heat. Wind turbines, also mainly near western cities and industry, generate a tenth of Turkey’s electricity. Hydropower, mostly from dams in the east, is the only modern renewable energy which is fully exploited. Hydropower averages about a fifth of the country's electricity, but much less in drought years. Apart from wind and hydro, other renewables; such as geothermal, solar and biogas; together generated almost a tenth of Turkey’s electricity in 2022. Türkiye has ranked 5th in Europe and 12th in the world in terms of installed capacity in renewable energy. The share of renewables in Türkiye’s installed power reached to 54% at the end of 2022.
Denmark is a leading country in renewable energy production and usage. Renewable energy sources collectively produced 81% of Denmark's electricity generation in 2022, and are expected to provide 100% of national electric power production from 2030. Including energy use in the heating/cooling and transport sectors, Denmark is expected to reach 100% renewable energy in 2050, up from the 34% recorded in 2021.

Renewable energy in South Africa is energy generated in South Africa from renewable resources, those that naturally replenish themselves—such as sunlight, wind, tides, waves, rain, biomass, and geothermal heat. Renewable energy focuses on four core areas: electricity generation, air and water heating/cooling, transportation, and rural energy services. The energy sector in South Africa is an important component of global energy regimes due to the country's innovation and advances in renewable energy. South Africa's greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions is ranked as moderate and its per capita emission rate is higher than the global average. Energy demand within the country is expected to rise steadily and double by 2025.
References
- ↑ Omar Ellabban, Haitham Abu-Rub, Frede Blaabjerg, Renewable energy resources: Current status, future prospects and their enabling technology. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 39, (2014), 748–764, p 749, doi : 10.1016/j.rser.2014.07.113.
- ↑ REN21 (2010). Renewables 2010 Global Status Report p. 15.
- ↑ REN21 (2014). Renewables 2014: Global Status Report (PDF). pp. 13, 17, 21, 25. ISBN 978-3-9815934-2-6. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 September 2014.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)