
Apocynaceae is a family of flowering plants that includes trees, shrubs, herbs, stem succulents, and vines, commonly known as the dogbane family, because some taxa were used as dog poison Members of the family are native to the European, Asian, African, Australian, and American tropics or subtropics, with some temperate members. The former family Asclepiadaceae is considered a subfamily of Apocynaceae and contains 348 genera. A list of Apocynaceae genera may be found here.

Alstonia is a widespread genus of evergreen trees and shrubs, of the family Apocynaceae. It was named by Robert Brown in 1811, after Charles Alston (1685–1760), professor of botany at Edinburgh from 1716 to 1760.

Triosteum, commonly known in American English as horse-gentian or, less commonly, feverwort, and, in Standard Chinese as 莛子藨属, is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Caprifoliaceae. A genus of six species in total, it has three species native to North America, and three more in eastern Asia.

Indole alkaloids are a class of alkaloids containing a structural moiety of indole; many indole alkaloids also include isoprene groups and are thus called terpene indole or secologanin tryptamine alkaloids. Containing more than 4100 known different compounds, it is one of the largest classes of alkaloids. Many of them possess significant physiological activity and some of them are used in medicine. The amino acid tryptophan is the biochemical precursor of indole alkaloids.

Iridoids are a type of monoterpenoids in the general form of cyclopentanopyran, found in a wide variety of plants and some animals. They are biosynthetically derived from 8-oxogeranial. Iridoids are typically found in plants as glycosides, most often bound to glucose.
In enzymology, a loganate O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Camptothecin (CPT) is a topoisomerase inhibitor. It was discovered in 1966 by M. E. Wall and M. C. Wani in systematic screening of natural products for anticancer drugs. It was isolated from the bark and stem of Camptotheca acuminata, a tree native to China used in traditional Chinese medicine. It has been used clinically more recently in China for the treatment of gastrointestinal tumors. CPT showed anticancer activity in preliminary clinical trials, especially against breast, ovarian, colon, lung, and stomach cancers. However, it has low solubility and adverse effects have been reported when used therapeutically, so synthetic and medicinal chemists have developed numerous syntheses of camptothecin and various derivatives to increase the benefits of the chemical, with good results. Four CPT analogues have been approved and are used in cancer chemotherapy today, topotecan, irinotecan, belotecan, and trastuzumab deruxtecan. Camptothecin has also been found in other plants including Chonemorpha fragrans.

Alstonia constricta, commonly known as quinine bush or bitterbark, is an endemic Australian endemic shrub or small tree of the family Apocynaceae.
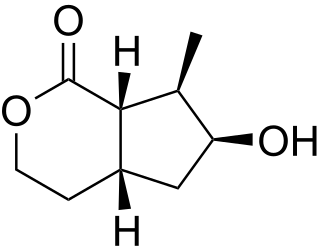
Boonein is an iridoid isolated from Alstonia boonei, a medicinal tree of West Africa.
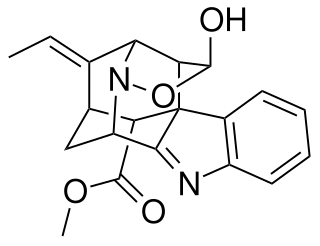
Nareline is a bio-active alkaloid isolated from Alstonia boonei, a medicinal tree of West Africa.

Picrinine is a bio-active alkaloid from Alstonia boonei, a medicinal tree of West Africa.
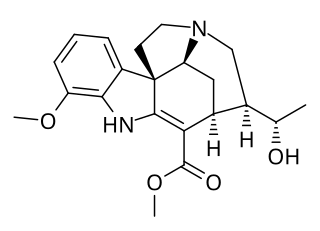
Scholarine is an alkaloid isolated initially from Alstonia scholaris by Banerji and Siddhanta. Subsequently, it was obtained from the West African tree Alstonia boonei. The derivative N-Formylscholarine has been isolated from the fruit pods of Alstonia scholaris.

Pseudoakuammigine is a bio-active alkaloid from Alstonia boonei, a medicinal tree from West Africa.
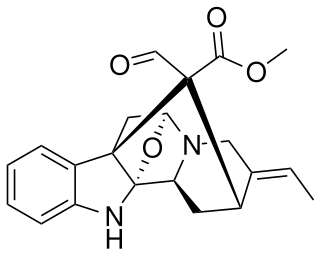
Picralinal is a bio-active alkaloid from Alstonia scholaris, a medicinal tree of West Africa.

Scholaricine is an alkaloid that has been isolated from Alstonia boonei, a tree of West Africa.
Alstonia boonei is a very large, deciduous, tropical-forest tree belonging to the Dogbane Family (Apocynaceae). It is native to tropical West Africa, with a range extending into Ethiopia and Tanzania. Its common name in the English timber trade is cheese wood, pattern wood or stool wood while its common name in the French timber trade is emien.

Tabersonine is a terpene indole alkaloid found in the medicinal plant Catharanthus roseus and also in the genus Voacanga. Tabersonine is hydroxylated at the 16 position by the enzyme tabersonine 16-hydroxylase (T16H) to form 16-hydroxytabersonine. The enzyme leading to its formation is currently unknown. Tabersonine is the first intermediate leading to the formation of vindoline one of the two precursors required for vinblastine biosynthesis.
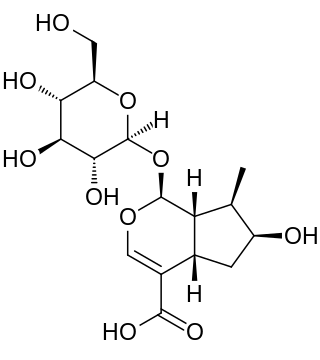
Loganic acid is an iridoid. Loganic acid is synthesized from 7-deoxyloganic acid by the enzyme 7-deoxyloganic acid hydroxylase (7-DLH). It is a substrate for the enzyme loganate O-methyltransferase for the production of loganin.

Harpagoside is a natural product found in the plant Harpagophytum procumbens, also known as devil's claw. It is the active chemical constituent responsible for the medicinal properties of the plant, which have been used for centuries by the Khoisan people of southern Africa to treat diverse health disorders, including fever, diabetes, hypertension, and various blood related diseases.

Alstonia congensis, is a tree within the Apocynaceae family and one of two African species within the Alstonia genus, the other being the Alstonia boonei De Wild. Both have similar morphological characteristics.



















