Africa is a continent comprising 63 political territories, representing the largest of the great southward projections from the main mass of Earth's surface. Within its regular outline, it comprises an area of 30,368,609 km2 (11,725,385 sq mi), excluding adjacent islands. Its highest mountain is Kilimanjaro; its largest lake is Lake Victoria.
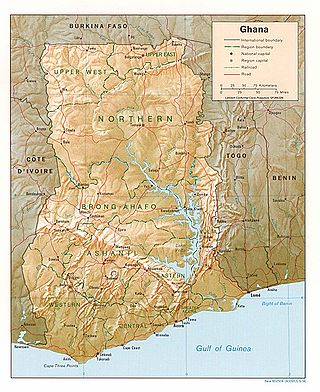
Ghana is a West African country in Africa, along the Gulf of Guinea.

The geography of Iraq is diverse and falls into five main regions: the desert, Upper Mesopotamia, the northern highlands of Iraq, Lower Mesopotamia, and the alluvial plain extending from around Tikrit to the Persian Gulf.

Nicaragua is a country in Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean, between Costa Rica and Honduras. Nicaragua is the largest country in Central America in square kilometers.

Somalia is a country located in the Horn of Africa which officially consists of the intra-46th meridian east territory, the seven federal member states, namely Galmudug, Hirshabelle, Jubaland, South West, Puntland, and the municipality of Benadir. It is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, the Gulf of Aden to the north, the Somali Sea and Guardafui Channel to the east, and Kenya to the southwest. With a land area of 637,657 square kilometers, Somalia's terrain consists mainly of plateaus, plains and highlands. Its coastline is more than 3,333 kilometers in length, the longest of mainland Africa. It has been described as being roughly shaped "like a tilted number seven".

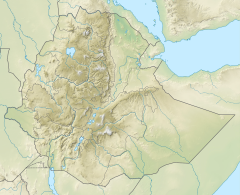
Ethiopia is located in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Eritrea to the north, Djibouti and Somalia to the east, Sudan and South Sudan to the west, and Kenya to the south. Ethiopia has a high central plateau, the Abyssinian Highlands that varies from 1,290 to 3,000 m above sea level, with some 25 mountains whose peaks rise over 4,000 meters (13,200ft), the highest being Ras Dashen at 4,543 meters (14,538ft).

The Awash River is a major river of Ethiopia. Its course is entirely contained within the boundaries of Ethiopia and empties into a chain of interconnected lakes that begin with Lake Gargori and end with Lake Abbe on the border with Djibouti, some 100 kilometres from the head of the Gulf of Tadjoura. The Awash River is the principal stream of an endorheic drainage basin covering parts of the Amhara, Oromia and Somali Regions, as well as the southern half of the Afar Region. The Awash River basin, spanning 23 administrative zones, covers 10% of Ethiopia's area.

The Ethiopian Highlands is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below 1,500 m (4,900 ft), while the summits reach heights of up to 4,550 m (14,930 ft). It is sometimes called the "Roof of Africa" due to its height and large area. It is the only country in the region with such a high elevated surface. This elevated surface is bisected diagonally by the Great East African Rift System which extends from Syria to Mozambique across the East African Lakes. Most of the Ethiopian Highlands are part of central and northern Ethiopia, and its northernmost portion reaches into Eritrea.

The Clarence River is a river situated in the Northern Rivers district of New South Wales, Australia. It rises on the eastern slopes of the Great Dividing Range, in the Border Ranges west of Bonalbo, near Rivertree at the junction of Koreelah Creek and Maryland River, on the watershed that marks the border between New South Wales and Queensland. It flows generally south, south east and north east, and is joined by twenty-four tributaries including Tooloom Creek and the Mann, Nymboida, Cataract, Orara, Coldstream, Timbarra, and Esk rivers. It descends 256 metres (840 ft) over the course of its 394-kilometre (245 mi) length and empties into the Coral Sea in the South Pacific Ocean, between Iluka and Yamba.
The Nguru Mountains are a mountain range in Morogoro Region, Tanzania, Africa. They are part of the Eastern Arc Mountains. The mountains are predominantly covered with rainforest, home to 83 species of birds and African violets. Several forest reserves are located in the mountains.

The Cascades ecoregion is a Level III ecoregion designated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the U.S. states of Washington, Oregon, and California. Somewhat smaller than the Cascade mountain range for which it is named, the ecoregion extends north to Snoqualmie Pass, near Seattle, and south to Hayden Pass, near the Oregon-California border, including the peaks and western slopes of most of the High Cascades. A discontiguous section is located on Mount Shasta in California.
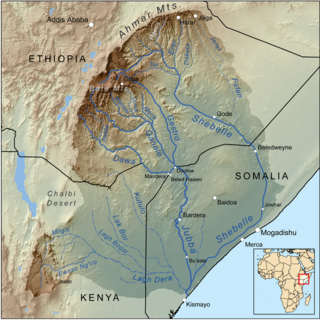
The Dawaro River is found in East Africa, covering an area of 58,961 km2. It flows through three major countries: Kenya, Ethiopia, and Somalia, with 81% found in Ethiopian territory. It is known for its complex geological environment, evident through its diverse lithology and structural framework, coming from the river's closeness to multiple volcanic-tectonic events. The wide river has gentle slopes either side of its exposed bedrock. The Dawa river flows south east to form part of both the Ethiopia–Somalia border and the Ethiopia–Kenya border. Awata, Digati, and Mormora are the only significant off-flowing rivers to Dawa.

The Eastern Anatolian montane steppe is a temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion. It is located in the Armenian Highlands, covering parts of eastern Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan, southern Georgia, and northwestern Iran.
The Nguu Mountains are a mountain range in Tanga Region of Tanzania. The Nguu Mountains are part of the Eastern Arc Mountains. The mountains are covered in woodland, grassland, and forest.

Simret is a municipality in the Tanqua Millash district of the Tigray Region, Ethiopia, which comprises the longest cave of Tigray in Zeyi, as well as Ras Alula’s birthplace in Mennewe. The municipality centre is in Dengolo village. Until January 2020, Simret belonged to the Dogu'a Tembien district.

Selam is a tabia or municipality in the Dogu'a Tembien district of the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. The tabia centre is in Addi Werho village, located approximately 3 km to the northeast of the woreda town Hagere Selam.

The Central Yakutian Lowland or the Central Yakutian Lowlands, also known as the Central Yakut Plain or the Vilyuy Lowland, is a low alluvial plain in Siberia, Russia.

The Selenga Highlands are a mountainous area in Buryatia and the southwestern end of Zabaykalsky Krai, Russia.

The Jordanian Highlands is a mountain range in Jordan. It extends north and south through the western portion of the country, between the Red Sea-Dead Sea depression to the west and a plateau to the east. The highlands are home to most of Jordan's population and large cities.

The Likouala-aux-Herbes is a river in the Republic of the Congo. It is a tributary of the Sangha River, which in turn is a tributary of the Congo River. It gives its name to the Likouala Department.