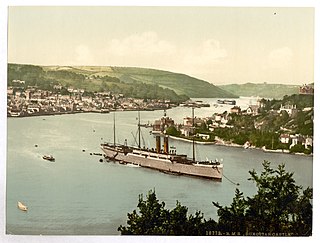Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill was a British statesman, military officer, and writer who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 and again from 1951 to 1955. Apart from 1922 to 1924, he was a member of Parliament (MP) from 1900 to 1964 and represented a total of five constituencies. Ideologically an adherent to economic liberalism and imperialism, he was for most of his career a member of the Conservative Party, which he led from 1940 to 1955. He was a member of the Liberal Party from 1904 to 1924.

Ladysmith is a town in the Uthukela District of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. It lies 230 kilometres (140 mi) north-west of Durban and 365 kilometres (227 mi) south-east of Johannesburg. Important industries in the area include food processing, textiles, and tyre production. Ladysmith is the seat for both the Alfred Duma Local Municipality and Uthukela District Municipality.

Major John Strange Spencer-Churchill, known as Jack Churchill, was the younger son of Lord Randolph Churchill and his wife Jennie, and the brother of former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom Sir Winston Churchill.

The Battle of Spion Kop was a military engagement between British forces and two Boer Republics, the South African Republic and the Orange Free State, during the campaign by the British to relieve the besieged city Ladysmith during the initial months of the Second Boer War. The battle was fought 23–24 January 1900 on the hilltop of Spioen Kop(a), about 38 km (24 mi) west-southwest of Ladysmith and resulted in a Boer victory.

George Warrington Steevens was a British journalist and writer.

The siege of Ladysmith was a protracted engagement in the Second Boer War, taking place between 2 November 1899 and 28 February 1900 at Ladysmith, Natal.

General Sir James Aylmer Lowthorpe Haldane, was a Scottish soldier who rose to high rank in the British Army.

My Early Life, also known in the US as A Roving Commission: My Early Life, is a 1930 book by Winston Churchill. It is an autobiography from his birth in 1874 to around 1902. The book closes with mention of his marriage in 1908, stating that he lived happily ever after.
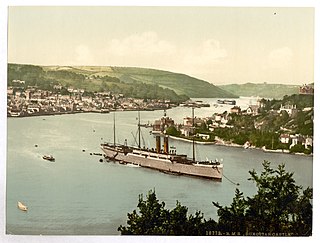
RMS Dunottar Castle was a Royal Mail Ship that went into service with the Castle Line in 1890 on the passenger and mail service between Britain and South Africa. In 1913 the ship was sold to the Royal Mail Steam Packet Company as the Caribbean. After the outbreak of the First World War she served as HMS Caribbean, first as a troop ship and then as an armed merchant cruiser, until she sank in a storm off the Scottish coast on 27 September 1915.

Jan Willem Boudewijn Gunning, was a Dutch physician, who served as the director of both the Staatsmuseum and what was then known as the Pretoria Zoological Gardens.

Winston Churchill, in addition to his careers as a soldier and politician, was a prolific writer under the variant of his full name 'Winston S. Churchill'. After being commissioned into the 4th Queen's Own Hussars in 1895, Churchill gained permission to observe the Cuban War of Independence, and sent war reports to The Daily Graphic. He continued his war journalism in British India, at the Siege of Malakand, then in the Sudan during the Mahdist War and in southern Africa during the Second Boer War.

Ian Hamilton's March is a book written by Winston Churchill. It is a description of his experiences accompanying the British army during the Second Boer War, continuing after the events described in London to Ladysmith via Pretoria.

The Relief of Ladysmith consisted of multiple efforts to relieve the city of Ladysmith by General Sir Redvers Buller. Buller and the Natal Field Force attempted to relieve the city through multiple offensive actions. The city had been under siege since 2 November, 1899, and Britain had sent General Buller to relieve the city. After consolidating his Forces at Estcourt through most of November and early December, he began his relief of the city. The attempts to relieve the city started on 15 December at the Battle of Colenso, in which the British forces were repelled by the Boers on the Tugela River. The next two attempts were repulsed by the Boers, however at the Battle of Pieters Hill in February 1900, the Boers were eventually beaten from the city and forced to withdraw to Botha's Pass near Newcastle. Buller and his Forces entered the city on February 28, 1900, officially ending the Siege of Ladysmith.

Lieutenant-General Sir William Penn Symons KCB was a British Army officer who was mortally wounded as he commanded his forces at the Battle of Talana Hill during the Second Boer War. While his forces won the battle, they had to abandon their position and fall back to Ladysmith. Symons and the more severely wounded were left to the Boers; he died three days later.. A monument to his valour was raised in Victoria Park, Saltash, Cornwall, UK.
Major General Sir Geoffrey Barton, of the 7th Regiment of Foot, served the British Army from 1862 until 1904. Although he saw service in Ireland, Hong Kong and India, the majority of his campaigns were on the African continent. During the Second Boer War he was put in command of the 6th Brigade of the South Natal Field Force, taking part in the Relief of Ladysmith and the Relief of Mafeking. When he retired to Scotland he took an interest in local politics, the Red Cross Society and the Boy Scout Movement.
The Natal Field Force (NFF) was a multi-battalion field force originally formed by Major-General Sir George Pomeroy Colley in Natal for the First Boer War. It was later re-established for the Second Boer War (1899–1902) and commanded by Major-General Sir Redvers Buller VC GCB GCMG.
The South African Light Horse regiment of the British Army were raised in Cape Colony in 1899 and disbanded in 1907.

The early life of Winston Churchill covers the period from his birth on 30 November 1874 to 31 May 1904 when he formally crossed the floor of the House of Commons, defecting from the Conservative Party to sit as a member of the Liberal Party.

The Battle of Chieveley took place on 15 November 1899, and was an ambush on a British armored train travelling from Estcourt to Colenso in a reconnaissance mission. Boer forces under the command of Louis Botha, which comprised primarily the Italian Volunteer Legion, ambushed the armored train, and derailed it, taking most of the British soldiers prisoner. Commanding the British forces on the armored train was Colonel Charles James Long, who had received reports a day earlier about Boers in the area, hence the reason for sending out the armored train.

The Northern Natal Offensive was a military invasion of the Northern region of Natal by the Boers of the Transvaal and the Orange Free State during the Second Boer War. It was part of a larger offensive by the Boers into the British colonies, with other invasions occurring in Bechuanaland and the Cape Colony. The Boers invaded on 12 October, after Paul Kruger had declared war a day earlier. The Boers initially had success with this offensive, besieging Ladysmith, and reaching as far south as Estcourt in November 1899. The goal of the offensive for the Boers was to reach the port city of Durban and the capital of Pietermartizburg in order hopefully force the British into peace negotiations. However, with Redvers Buller's reinforcements arriving that same month, the Boers retreated to the Tugela River. Multiple attempts were made by Buller to relieve Ladysmith, but to no avail. However, the fourth attempt in February 1900 expelled the Boers from their position at the Battle of the Pieters. Scattered fighting from March-May 1900 continued, with the Boers being expelled from Natal completely at the Battle of Laing's Nek. With the Boers out of Natal, the offensive ended.