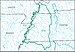
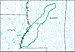
A hydrological code or hydrologic unit code is a sequence of numbers or letters that identify a hydrological feature like a river, river reach, lake, or area like a drainage basin or catchment.
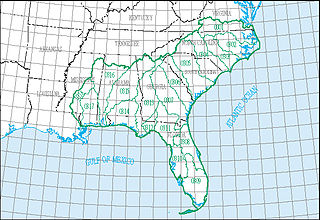
The South Atlantic–Gulf water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.
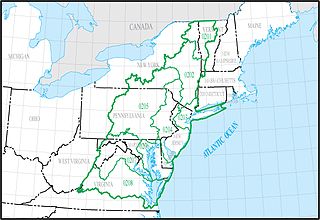
The Mid Atlantic water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.

The Upper Mississippi water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.
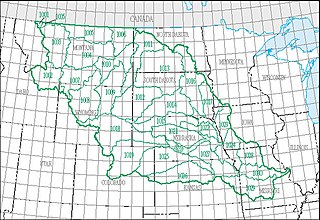
The Missouri water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.

The Great Lakes water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.

The Ohio water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.
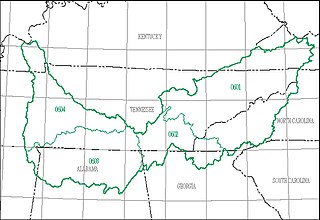
The Tennessee water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.

The Rio Grande water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.
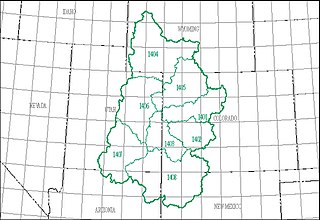
The Upper Colorado water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.
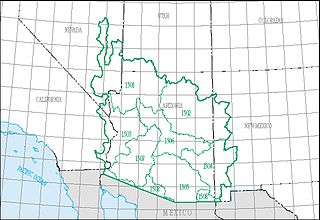
The Lower Colorado water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.
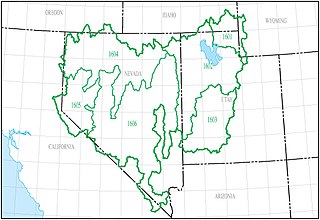
The Great Basin water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.
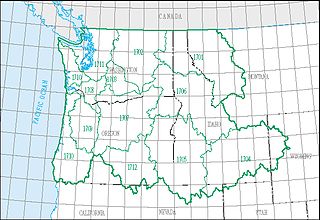
The Pacific Northwest water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.
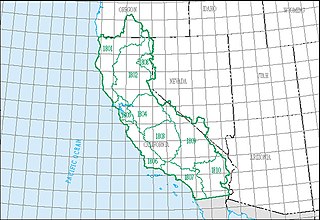
The California water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.
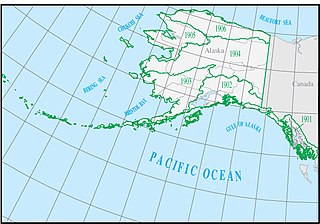
The Alaska water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.

The Hawaii water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.

The Souris–Red–Rainy region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.
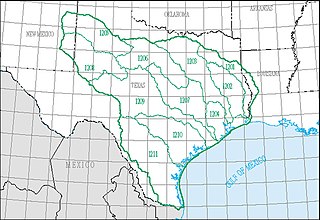
The Texas–Gulf water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.
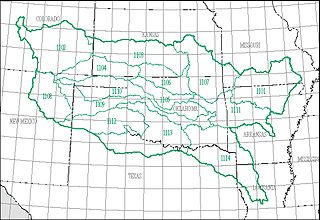
The Arkansas–White–Red water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.