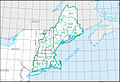
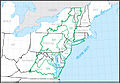
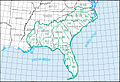
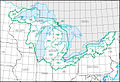
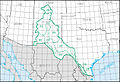
Region HUC [ 3] Region name [ 3] Region description [ 4] Region location [ 3] Region size [ 3] Region population Region map 01 New England region The drainage within the United States that ultimately discharges into: the Bay of Fundy the Atlantic Ocean within and between the states of Maine and Connecticut Long Island Sound north of the New York -Connecticut state line the Riviere St. Francois , a tributary of the Saint Lawrence River Includes all of Maine , New Hampshire and Rhode Island , and parts of Connecticut , Massachusetts , New York , and Vermont . 73,753 sq mi (191,020 km 2 ) 14,500,000 HUC01 02 Mid Atlantic region The drainage within the United States that ultimately discharges into: the Atlantic Ocean within and between the states of New York and Virginia Long Island Sound south of the New York -Connecticut State Line the Riviere Richelieu , a tributary of the Saint Lawrence River Includes all of Delaware and New Jersey and the District of Columbia , and parts of Connecticut , Maryland , Massachusetts , New York , Pennsylvania , Vermont , Virginia , and West Virginia . 106,334 sq mi (275,400 km 2 ) 50,800,000 HUC02 03 South Atlantic–Gulf region The drainage that ultimately discharges into: the Atlantic Ocean within and between the states of Virginia and Florida the Gulf of Mexico within and between the states of Florida and Louisiana the associated waters Includes all of Florida and South Carolina , and parts of Alabama , Georgia , Louisiana , Mississippi , North Carolina , Tennessee , and Virginia . 279,664 sq mi (724,330 km 2 ) 55,900,000 HUC03 04 Great Lakes region The drainage within the United States that ultimately discharges into: the Great Lakes system, including the lake surfaces, bays, and islands the Saint Lawrence River to the Riviere Richelieu drainage boundary. Includes parts of Illinois , Indiana , Michigan , Minnesota , New York , Ohio , Pennsylvania , and Wisconsin . 141,984 sq mi (367,740 km 2 ) 15,200,000 HUC04 05 Ohio region The drainage of the Ohio River Basin, excluding the Tennessee River Basin. Includes parts of Illinois , Indiana , Kentucky , Maryland , New York , North Carolina , Ohio , Pennsylvania , Tennessee , Virginia and West Virginia . 162,916 sq mi (421,950 km 2 ) 27,000,000 HUC05 06 Tennessee region The drainage of the Tennessee River Basin. Includes parts of Alabama , Georgia , Kentucky , Mississippi , North Carolina , Tennessee , and Virginia . 40,908 sq mi (105,950 km 2 ) 5,400,000 HUC06 07 Upper Mississippi region The drainage of the Mississippi River Basin above the confluence with the Ohio River , excluding the Missouri River Basin. Includes parts of Illinois , Indiana , Iowa , Michigan , Minnesota , Missouri , South Dakota , and Wisconsin . 189,968 sq mi (492,010 km 2 ) 26,100,000 HUC07 08 Lower Mississippi region The drainage of: the Mississippi River below its confluence with the Ohio River , excluding the Arkansas , Red , and White River Basins above the points of highest backwater effect of the Mississippi River in those basins coastal streams that ultimately discharge into the Gulf of Mexico from the Pearl River Basin boundary to the Sabine River and Sabine Lake drainage boundary. Includes parts of Arkansas , Kentucky , Louisiana , Mississippi , Missouri , and Tennessee . 106,741 sq mi (276,460 km 2 ) 10,400,000 HUC08 09 Souris-Red-Rainy region The drainage within the United States of the Lake of the Woods and the Rainy , Red , and Souris River Basins that ultimately discharges into Lake Winnipeg and Hudson Bay . Includes parts of Minnesota , North Dakota , and South Dakota . 90,759 sq mi (235,060 km 2 ) 1,000,000 HUC09 10 Missouri region The drainage within the United States of: the Missouri River Basin the Saskatchewan River Basin several small closed basins . Includes all of Nebraska and parts of Colorado , Iowa , Kansas , Minnesota , Missouri , Montana , North Dakota , South Dakota , and Wyoming . 520,960 sq mi (1,349,300 km 2 ) 13,000,000 HUC10 11 Arkansas-White-Red region The drainage of the Arkansas , White , and Red River Basins above the points of highest backwater effect of the Mississippi River . Includes all of Oklahoma and parts of Arkansas , Colorado , Kansas , Louisiana , Missouri , New Mexico , and Texas . 247,988 sq mi (642,290 km 2 ) 11,300,000 HUC11 12 Texas-Gulf region The drainage that discharges into the Gulf of Mexico from and including Sabine Pass to the Rio Grande Basin boundary. Includes parts of Louisiana , New Mexico , and Texas . 181,886 sq mi (471,080 km 2 ) 25,200,000 HUC12 13 Rio Grande region The drainage within the United States of: the Rio Grande Basin the San Luis Valley , North Plains, Plains of San Agustin , Mimbres River , Estancia, Jornada Del Muerto , Tularosa Valley , Salt Basin, and other closed basins . Includes parts of Colorado , New Mexico , and Texas . 132,517 sq mi (343,220 km 2 ) 3,000,000 HUC13 14 Upper Colorado region The drainage of: the Colorado River Basin above the Lee Ferry compact point which is one mile below the mouth of the Paria River the Great Divide closed basin. Includes parts of Arizona , Colorado , New Mexico , Utah , and Wyoming . 113,347 sq mi (293,570 km 2 ) 1,800,000 HUC14 15 Lower Colorado region The drainage within the United States of: the Colorado River Basin below the Lee Ferry compact point which is one mile below the mouth of the Paria River streams that originate within the United States and ultimately discharge into the Gulf of California the Animas Valley , Willcox Playa , and other smaller closed basins . Includes parts of Arizona , California , Nevada , New Mexico , and Utah . 140,146 sq mi (362,980 km 2 ) 9,900,000 HUC15 16 Great Basin region The drainage of the Great Basin that discharges into the states of Utah and Nevada . Includes parts of California , Idaho , Nevada , Oregon , Utah , and Wyoming . 141,717 sq mi (367,050 km 2 ) 3,900,000 HUC16 17 Pacific Northwest region The drainage within the United States that ultimately discharges into: the Strait of Georgia and of Strait of Juan de Fuca the Pacific Ocean within the states of Oregon and Washington ; and that part of the Great Basin whose discharge is into the state of Oregon . Includes all of Washington and parts of California , Idaho , Montana , Nevada , Oregon , Utah , and Wyoming . 302,334 sq mi (783,040 km 2 ) 14,100,000 HUC17 18 California region The drainage within the United States that ultimately discharges into the Pacific Ocean within the state of California; and those parts of the Great Basin , or other closed basins , that discharge into the state of California . Includes parts of California , Nevada , and Oregon . 168,579 sq mi (436,620 km 2 ) 38,900,000 HUC18 19 Alaska region The drainage within the state of Alaska . Includes all of Alaska . 720,535 sq mi (1,866,180 km 2 ) 720,000 HUC19 20 Hawaii region The drainage within the state of Hawaii . Includes all of Hawaii . 6,428 sq mi (16,650 km 2 ) 1,400,000 HUC20 21 Caribbean region The drainage within: the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico the Virgin Islands of the United States other United States Caribbean outlying areas. Includes land areas over which the United States has some degree of interest, jurisdiction, or sovereignty. 3,582 sq mi (9,280 km 2 ) 3,400,000 HUC21 22 South Pacific region Guam , the Northern Mariana Islands , and American Samoa 496.48 sq mi (1,285.9 km 2 ) 280,000