The Lower Mainland is a name commonly applied to the region surrounding and including Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. As of 2016, 2,759,365 people, lived in the region; sixteen of the province's thirty most populous municipalities are located there. Islands contained within rivers in the region are considered to be part of the Lower Mainland.

Leduc is a city in the province of Alberta, Canada. It is 33 kilometres (21 mi) south of the provincial capital of Edmonton and is part of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region.

Alberta is a Canadian province. Located in Western Canada, the province has an area of 661,190 square kilometres (255,290 sq mi) and is bounded to the south by the U.S. state of Montana along 49° north for 298 kilometres (185 mi); to the east at 110° west by the province of Saskatchewan for 1,223 kilometres (760 mi); and at 60° north the Northwest Territories for 644 kilometres (400 mi). The southern half of the province borders British Columbia along the Continental Divide of the Americas on the peaks of the Rocky Mountains, while the northern half borders British Columbia along the 120th meridian west.

Fort Chipewyan, commonly referred to as Fort Chip, is a hamlet in northern Alberta, Canada, within the Regional Municipality (RM) of Wood Buffalo. It is located on the western tip of Lake Athabasca, adjacent to Wood Buffalo National Park, approximately 223 kilometres (139 mi) north of Fort McMurray.

Jasper is a specialized municipality in western Alberta, Canada. It is the commercial centre of Jasper National Park, located in the Canadian Rockies within the Athabasca River valley. Jasper is approximately 362 kilometres (225 mi) west of Edmonton and 290 kilometres (180 mi) north of Banff, Alberta, at the intersection of Highway 16 and Highway 93.
A regional municipality is a type of Canadian municipal government similar to and at the same municipal government level as a county, although the specific structure and servicing responsibilities may vary from place to place. Regional municipalities were formed in highly populated areas where it was considered more efficient to provide certain services, such as water, emergency services, and waste management over an area encompassing more than one local municipality. For this reason, regions may be involved in providing services to residents and businesses.

Peace River, originally named Peace River Crossing, and known as Rivière-la-Paix in French, is a town in northwestern Alberta, Canada, situated along the banks of the Peace River, at its confluence with the Smoky River, the Heart River and Pat's Creek. It is located 486 kilometres (302 mi) northwest of Edmonton, and 198 kilometres (123 mi) northeast of Grande Prairie, along Highway 2. It was known as the Village of Peace River Crossing between 1914 and 1916.

Métis in Alberta are Métis people, descendants of mixed First Nations/native Indian and white/European families, who live in the Canadian province of Alberta. The Métis are considered an aboriginal group under Canada's Constitution Act 1982 and make up a separate and distinct from the First Nations, and have different legal rights. In Alberta, unlike in the rest of Canada, Métis people have negotiated certain lands to be reserved for them, known today as the Eight Metis Settlements. These Metis Settlements Federated in 1975 to protect existing Metis Settlement lands following the Alberta Governments dissolution, by Order-In-Council of four Metis Settlements from 1950-1960. Following legal challenges by the Federation of Metis Settlements in 1975 for the lose of natural resource against Alberta, the Crown in Right of Alberta settled out of court for a suite of legislation that would see self-government, land, and money transferred to the newly formed government of the Metis Settlements General Council (MSGC), Canada’s only Metis self-govenernment. The Metis Settlements General Council is the legislator of the Federation of Metis Settlements. MSGC is the second largest land owner in the Province of Alberta.
British Columbia is the westernmost province of Canada, bordered by the Pacific Ocean. With an area of 944,735 square kilometres (364,764 sq mi) it is Canada's third-largest province. The province is almost four times the size of United Kingdom, two and one-half times larger than Japan and larger than every U.S. state except Alaska. It is bounded on the northwest by the U.S. state of Alaska, directly north by Yukon and the Northwest Territories, on the east by Alberta, and on the south by the U.S. states of Washington, Idaho, and Montana. Formerly part of the British Empire, the southern border of British Columbia was established by the 1846 Oregon Treaty. The province is dominated by mountain ranges, among them the Canadian Rockies but dominantly the Coast Mountains, Cassiar Mountains, and the Columbia Mountains. Most of the population is concentrated on the Pacific coast, notably in the area of Vancouver, located on the southwestern tip of the mainland, which is known as the Lower Mainland. It is the most mountainous province of Canada.

The Edmonton Metropolitan Region (EMR), also commonly referred to as the Alberta Capital Region, Greater Edmonton or Metro Edmonton, is a conglomeration of municipalities centred on Alberta's provincial capital of Edmonton.

Valleyview is a town in northwest Alberta, Canada within the Municipal District of Greenview No. 16 and Census Division No. 18.

The Municipal District of Peace No. 135 is a municipal district in northwestern Alberta, Canada. Located in Census Division No. 19, its municipal office is located outside but adjacent to the Village of Berwyn.

Central Alberta is a region located in the Canadian province of Alberta.

Western Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces and more commonly known as the West, is a region of Canada that includes the four provinces of Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta and British Columbia. British Columbia is culturally, economically, geographically, and politically distinct from the other parts of Western Canada and is often referred to as the "west coast" or "Pacific Canada", while Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba are grouped together as the Prairie Provinces and most commonly known as "The Prairies".
Environment and Parks is the Alberta provincial ministry of the Executive Council of Alberta responsible for environmental policy and sustainable resource development.

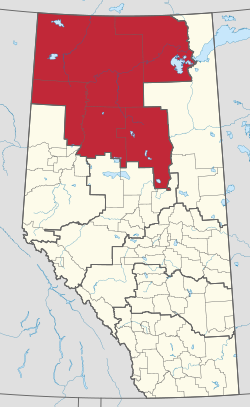
The Upper Peace Region is a land-use framework region in northern Alberta, Canada. One of seven in the province, each is intended to develop and implement a Regional Plan, complementing the planning efforts of member municipalities in order to coordinate future growth. Corresponding roughly to major watersheds while following municipal boundaries, these regions are managed by Alberta Environment and Parks.

The Red Deer Region is a land-use framework region in Alberta, Canada. One of seven in the province, each is intended to develop and implement a Regional Plan, complementing the planning efforts of member municipalities in order to coordinate future growth. Corresponding roughly to major watersheds while following municipal boundaries, these regions are managed by Alberta Environment and Parks.