
The heterotrichs are a class of ciliates. They typically have a prominent adoral zone of membranelles circling the mouth, used in locomotion and feeding, and shorter cilia on the rest of the body. Many species are highly contractile, and are typically compressed or conical in form. These include some of the largest protozoa, such as Stentor and Spirostomum, as well as many brightly pigmented forms, such as certain Blepharisma.

A trochophore is a type of free-swimming planktonic marine larva with several bands of cilia.

The green honeycreeper is a small bird in the tanager family. It is found in the tropical New World from southern Mexico south to Brazil, and on Trinidad. It is the only member of the genus Chlorophanes. The purplish honeycreeper, a bird from Venezuela known only from the type specimen, is now thought to be an intergeneric hybrid between the green honeycreeper and either the red-legged honeycreeper or the blue dacnis.

Thaumetopoeidae is a small family of moths in the order Lepidoptera. The genera in this family have been historically treated as a subfamily within Notodontidae (Thaumetopoeinae), and this subfamily has been raised to the family status.

The Polycladida represents a highly diverse clade of free-living marine flatworms. They are known from the littoral to the sublittoral zone, and many species are common from coral reefs. Only a few species are found in freshwater habitats.

The white-faced spiny tree-rat, Echimys chrysurus, is a spiny rat species from South America. It is found in Brazil, French Guiana, Guyana and Suriname.
The long-tailed armored tree-rat, Makalata macrura, is a spiny rat species from South America. It is found in Brazil, with a population in Ecuador which is referable either to this species or to Makalata didelphoides. Initially considered a large form of the latter species, it actually represents a distinct species as supported by morphological and molecular characters.

Monoxenous development, or monoxeny, characterizes a parasite whose development is restricted to a single host species.

Arbutus andrachne, commonly called the Greek strawberry tree, is an evergreen shrub or small tree in the family Ericaceae, native to the Mediterranean region and the Middle East.
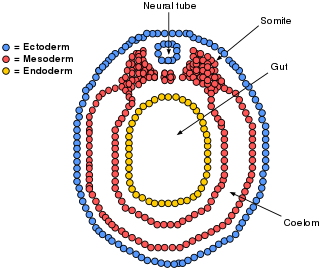
Enterocoely describes both the process by which some animal embryos develop and the origin of the cells involved. In enterocoely, a mesoderm is formed in a developing embryo, in which the coelom appears from pouches growing and separating from the digestive tract. As the incipient coelomic epithelium originates from archenteral diverticula, the endoderm therefore gives rise to the mesodermal cells.
Neusticomys is a genus of semiaquatic South American rodents in the family Cricetidae.

Psammomys is a genus of rodents in the family Muridae.

Amaurospiza is a genus of birds. The generic name is derived from the Ancient Greek amauros, meaning "dusky", and σπίζα (spíza), a catch-all term for finch-like birds.

Geospiza is a genus of bird in the family Thraupidae. All species in the genus are endemic to the Galápagos Islands. Together with related genera, they are collectively known as Darwin's finches. Although in the past, they were classified in the bunting and American sparrow family Emberizidae, more recent studies have shown they belong in the tanager family.
The Peruvian tree rat is a species of rodent in the family Echimyidae. It is found in northeastern Peru and adjacent Ecuador, where it is found in the Amazon rainforest. It is nocturnal and arboreal.
Plagiodontia is a genus of rodent in the family Capromyidae.

Euphorbia leuconeura, the Madagascar jewel, is a species of plant in the family Euphorbiaceae. It is endemic to Madagascar. Its natural habitat is forest undergrowth in rocky areas. It can grow to a height of 1.8 m (6 ft), as a branching small tree, and propagates by shooting its seeds several feet into the air. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Loxodes is a genus of karyorelictean ciliates, belonging to family Loxodidae. It is the only known karyorelictean ciliate that lives in freshwater habitats.
Protoheterotrichida is an order of karyorelict ciliates. It contains the family Geleiidae.

Heteroxeny, or heteroxenous development, characterizes a parasite whose development involves several host species.














