Luba | |
|---|---|
 Luba, 2013 | |
| Coordinates: 3°27′N8°33′E / 3.450°N 8.550°E Coordinates: 3°27′N8°33′E / 3.450°N 8.550°E | |
| Country | |
| Province | Bioko Sur |
| Elevation | 181 m (594 ft) |
| Population (2012) | |
| • City | 7,739 |
| • Metro | 24,000 |
| Climate | Am |
Luba (formerly San Carlos) (pop. 7,000) is the second-largest town on Bioko in Equatorial Guinea, a port for the logging industry on the island's west coast beneath volcanic peaks. Attractions in Luba include several beaches and a colonial hospital.
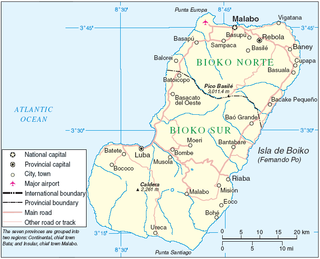
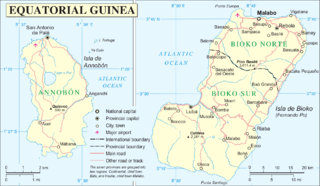
Bioko is an island 32 km (20 mi) off the west coast of Africa, and the northernmost part of Equatorial Guinea. Its population was 334,463 at the 2015 census and it covers an area of 2,017 km2 (779 sq mi). The island is located off Cameroon, in the Bight of Bonny portion of the Gulf of Guinea. Its geology is volcanic; its highest peak is Pico Basile at 3,012 m (9,882 ft).

Equatorial Guinea, officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea, is a country located on the west coast of Central Africa, with an area of 28,000 square kilometres (11,000 sq mi). Formerly the colony of Spanish Guinea, its post-independence name evokes its location near both the Equator and the Gulf of Guinea. Equatorial Guinea is the only sovereign African state in which Spanish is the official language. As of 2015, the country had an estimated population of 1,222,245.

A port is a maritime commercial facility which may comprise one or more wharves where ships may dock to load and discharge passengers and cargo. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, some ports, such as Hamburg, Manchester and Duluth, are many miles inland, with access from the sea via river or canal.
The city may be reached either by sea or by a main road linking Luba to the country's capital, Malabo. The road is now[ clarification needed ] accessible; it takes about an hour to drive from Malabo to Luba. In 1999, a free port opened near the town, creating deepwater access for larger and oil industry vessels, an alternative to the congested port of Malabo for re-supplying on fuel, water and other materials. [1] As of 2010 a new highway was under construction from Luba via Belebú Balachá through the Luba Crater Scientific Reserve to Ureca near the south coast. [2]

Malabo is the capital of Equatorial Guinea and the province of Bioko Norte. It is located on the north coast of the island of Bioko, formerly known by the Bubis, its indigenous inhabitants, as Etulá, and as Fernando Pó by the Europeans. The city has a population of approximately 187,302 inhabitants.

Belebú Balachá is a community on Bioko island in Equatorial Guinea. It is south of Luba, the second-largest town on the island, and just north of the Luba Crater Scientific Reserve. As of 2010 a new highway was under construction through the reserve from Belebu to Ureca but it cannot be confirmed if the highway was built.