
Żary County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lubusz Voivodeship, western Poland, on the German border. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Żary, which lies 43 km (27 mi) south-west of Zielona Góra and 123 km (76 mi) south of Gorzów Wielkopolski. The county contains three other towns: Lubsko, lying 21 km (13 mi) north-west of Żary, Jasień, lying 16 km (10 mi) north-west of Żary, and Łęknica, 30 km (19 mi) west of Żary.

Słubice County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lubusz Voivodeship, western Poland, on the German border. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Słubice, which lies 63 km (39 mi) south-west of Gorzów Wielkopolski and 79 km (49 mi) north-west of Zielona Góra. The county contains three other towns: Rzepin, lying 19 km (12 mi) east of Słubice, Ośno Lubuskie, lying 25 km (16 mi) north-east of Słubice, and Cybinka, 24 km (15 mi) south-east of Słubice.

Krosno County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lubusz Voivodeship, western Poland, on the German border. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is the town of Krosno Odrzańskie, which lies 30 km (19 mi) west of Zielona Góra and 79 km (49 mi) south of Gorzów Wielkopolski. The only other town is Gubin which is the biggest town in the county. It is situated on the German border 28 km (17 mi) west of Krosno Odrzańskie.

Kościerzyna County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Pomeranian Voivodeship, northern Poland. It came into being on 1 January 1999 as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and only town is Kościerzyna, which lies 51 kilometres (32 mi) south-west of the regional capital Gdańsk. Its borders equal approximately the borders of the old Marquessate of Berent in the German Empire.

Cieszyn County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Silesian Voivodeship, southern Poland, on the Czech and Slovak border. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998.

Tomaszów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lublin Voivodeship, eastern Poland, on the border with Ukraine. It was established on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Tomaszów Lubelski, which lies 107 kilometres (66 mi) south-east of the regional capital Lublin. The only other towns in the county are Tyszowce, lying 28 km (17 mi) north-east of Tomaszów, and Łaszczów, lying 25 km (16 mi) east of Tomaszów.

Siemiatycze County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Podlaskie Voivodeship, north-eastern Poland, on the border with Belarus. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Siemiatycze, which lies 80 kilometres (50 mi) south of the regional capital Białystok. The only other town in the county is Drohiczyn, lying 15 km (9 mi) west of Siemiatycze.

Garwolin County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Masovian Voivodeship, east-central Poland. It came into being on 1 January 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Garwolin, which lies 56 kilometres (35 mi) south-east of Warsaw. The county contains three other towns: Łaskarzew, 13 km (8 mi) south of Garwolin, Pilawa, 10 km (6 mi) north-west of Garwolin, and Żelechów, 22 km (14 mi) south-east of Garwolin.

Przasnysz County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Masovian Voivodeship, east-central Poland. It came into being on 1 January 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Przasnysz, which lies 90 kilometres (56 mi) north of Warsaw. The only other town in the county is Chorzele, lying 26 km (16 mi) north of Przasnysz. The county covers an area of 1,217.82 square kilometres (470.2 sq mi). As of 2019, its total population is 52,616, out of which the population of Przasnysz is 17,264, that of Chorzele is 3,088, and the rural population is 32,324.

Płońsk County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Masovian Voivodeship, east-central Poland. It came into being on 1 January 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Płońsk, which lies 63 kilometres (39 mi) north-west of Warsaw. The only other town in the county is Raciąż, lying 25 km (16 mi) north-west of Płońsk.
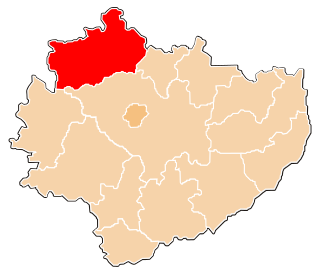
Końskie County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Końskie, which lies 38 kilometres (24 mi) north of the regional capital Kielce. The only other town in the county is Stąporków, lying 11 km (7 mi) south-east of Końskie.

Koło County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Koło, which lies 119 kilometres (74 mi) east of the regional capital Poznań. The county contains three other towns: Kłodawa, 21 km (13 mi) east of Koło, Dąbie, 19 km (12 mi) south-east of Koło, and Przedecz, 21 km (13 mi) north-east of Koło.
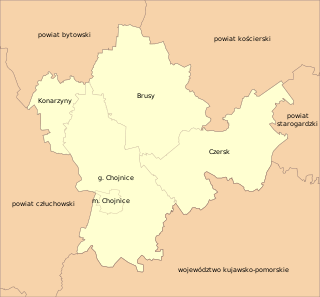
Chojnice County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Pomeranian Voivodeship, northern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Chojnice, which lies 103 kilometres (64 mi) south-west of the regional capital Gdańsk. The county also contains the towns of Czersk, lying 30 km (19 mi) east of Chojnice, and Brusy, 24 km (15 mi) north-east of Chojnice.

Kluczbork County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Opole Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Kluczbork, which lies 41 kilometres (25 mi) north-east of the regional capital Opole. The county also contains the towns of Wołczyn, lying 12 km (7 mi) west of Kluczbork, and Byczyna, 15 km (9 mi) north of Kluczbork.

Olesno County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Opole Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Olesno, which lies 42 kilometres (26 mi) north-east of the regional capital Opole. The county contains three other towns: Praszka, 20 km (12 mi) north of Olesno, Dobrodzień, 17 km (11 mi) south of Olesno, and Gorzów Śląski, 18 km (11 mi) north of Olesno.

Strzelce County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Opole Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Strzelce Opolskie, which lies 31 kilometres (19 mi) south-east of the regional capital Opole. The county contains four other towns: Zawadzkie, 19 km (12 mi) north-east of Strzelce Opolskie, Kolonowskie, 19 km (12 mi) north-east of Strzelce Opolskie, Leśnica, 11 km (7 mi) south-west of Strzelce Opolskie, and Ujazd, 14 km (9 mi) south-east of Strzelce Opolskie.

Częstochowa County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Silesian Voivodeship, southern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is the city of Częstochowa, although the city is not part of the county. The only towns in Częstochowa County are Blachownia, which lies 11 km (7 mi) west of Częstochowa, and Koniecpol, 40 km (25 mi) east of Częstochowa.

Myszków County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Silesian Voivodeship, southern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Myszków, which lies 44 kilometres (27 mi) north-east of the regional capital Katowice. The county also contains the towns of Żarki, lying 7 km (4 mi) north-east of Myszków, and Koziegłowy, 11 km (7 mi) west of Myszków.
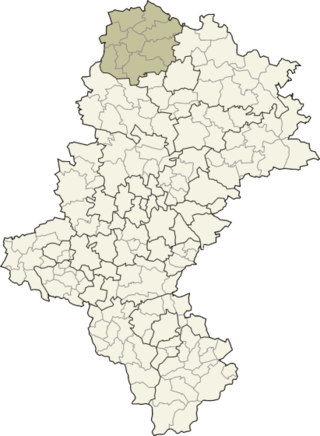
Kłobuck County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Silesian Voivodeship, southern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Kłobuck, which lies 75 kilometres (47 mi) north of the regional capital Katowice. The only other town in the county is Krzepice, lying 16 km (10 mi) west of Kłobuck.

Tarnowskie Góry County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Silesian Voivodeship, southern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Tarnowskie Góry, which lies 25 kilometres (16 mi) north-west of the regional capital Katowice. The county contains three other towns: Radzionków, 8 km (5 mi) south of Tarnowskie Góry, Kalety, 14 km (9 mi) north of Tarnowskie Góry, and Miasteczko Śląskie, 5 km (3 mi) north-east of Tarnowskie Góry.
























