
Domitian was Roman emperor from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavian dynasty. Described as "a ruthless but efficient autocrat", his authoritarian style of ruling put him at sharp odds with the Senate, whose powers he drastically curtailed.

Galba was Roman emperor, ruling for 7 months from 8 June AD 68 to 15 January 69. He was the first emperor in the Year of the Four Emperors and assumed the throne following Emperor Nero's suicide.

The Julio-Claudian dynasty comprised the first five Roman emperors: Augustus, Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius, and Nero.

Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus was a Roman emperor and the final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his death in AD 68.

Otho was Roman emperor, ruling for three months from 15 January to 16 April 69. He was the second emperor of the Year of the Four Emperors.

Aulus Vitellius was Roman emperor for eight months, from 19 April to 20 December AD 69. Vitellius became emperor following the quick succession of the previous emperors Galba and Otho, in a year of civil war known as the Year of the Four Emperors. Vitellius added the honorific Germanicus to his name instead of Caesar upon his accession. Like his predecessor, Otho, Vitellius attempted to rally public support to his cause by honoring and imitating Nero who remained popular in the empire.
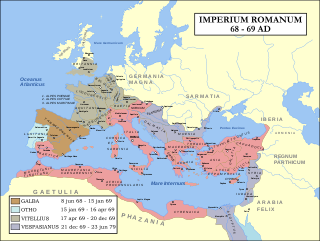
AD 69 (LXIX) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the consulship of Galba and Vinius. The denomination AD 69 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The 60s decade ran from January 1, AD 60, to December 31, AD 69.
Ofonius Tigellinus was a prefect of the Roman imperial bodyguard, known as the Praetorian Guard, from 62 until 68, during the reign of emperor Nero. Tigellinus gained imperial favour through his acquaintance with Nero's mother Agrippina the Younger, and was appointed prefect upon the death of his predecessor Sextus Afranius Burrus, a position Tigellinus held first with Faenius Rufus and then Nymphidius Sabinus.

Gordian III was Roman emperor from 238 to 244. At the age of 13, he became the youngest sole emperor of the united Roman Empire. Gordian was the son of Antonia Gordiana and Junius Balbus, who died before 238. Antonia Gordiana was the daughter of Emperor Gordian I and sister of Emperor Gordian II. Very little is known of his early life before his acclamation.

The Praetorian Guard was the imperial guard of the Imperial Roman army that served various roles for the Roman emperor including being a bodyguard unit, counterintelligence, crowd control and gathering military intelligence.

The Year of the Four Emperors, AD 69, was the first civil war of the Roman Empire, during which four emperors ruled in succession: Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian. It is considered an important interval, marking the transition from the Julio-Claudians, the first imperial dynasty, to the Flavian dynasty. The period witnessed several rebellions and claimants, with shifting allegiances and widespread turmoil in Rome and the provinces.

The Flavian dynasty, lasting from AD 69 to 96, was the second dynastic line of emperors to rule the Roman Empire following the Julio-Claudians, encompassing the reigns of Vespasian and his two sons, Titus and Domitian. The Flavians rose to power during the civil war of AD 69, known as the Year of the Four Emperors; after Galba and Otho died in quick succession, Vitellius became emperor in mid 69. His claim to the throne was quickly challenged by legions stationed in the eastern provinces, who declared their commander Vespasian emperor in his place. The Second Battle of Bedriacum tilted the balance decisively in favor of the Flavian forces, who entered Rome on 20 December, and the following day, the Roman Senate officially declared Vespasian emperor, thus commencing the Flavian dynasty. Although the dynasty proved to be short-lived, several significant historic, economic and military events took place during their reign.
Gaius Licinius Mucianus was a Roman general, statesman and writer. He is considered to have played a role behind the scenes in the elevation of Vespasian to the throne.
The Battle of Bedriacum refers to two battles fought during the Year of the Four Emperors near the village of Bedriacum, about 35 kilometers (22 mi) from the town of Cremona in northern Italy. The fighting in fact took place between Bedriacum and Cremona, and the battles are sometimes called "First Cremona" and "Second Cremona".
Gaius Nymphidius Sabinus was a Prefect of the Praetorian Guard during the rule of Emperor Nero from AD 65 until his death in 68. He shared this office together with Ofonius Tigellinus, replacing his previous colleague Faenius Rufus. During the second half of the 60s, Nero grew increasingly unpopular with the people and the army, leading to a number of rebellions which ultimately caused his downfall and suicide in 68. Nymphidius took part in the final conspiracy against Nero and persuaded the Praetorian Guard to desert him, but when he attempted to have himself declared emperor, he was killed by his own soldiers.
Cornelius Fuscus was a Roman general who fought campaigns under the Emperors of the Flavian dynasty. He first distinguished himself as one of Vespasian's most ardent supporters during the civil war of 69 AD, known as the Year of the Four Emperors. Vespasian's son Domitian employed Fuscus as prefect of the Praetorian Guard, a post he held from 81 until his death.

Nerva was a Roman emperor from 96 to 98. Nerva became emperor when aged almost 66, after a lifetime of imperial service under Nero and the succeeding rulers of the Flavian dynasty. Under Nero, he was a member of the imperial entourage and played a vital part in exposing the Pisonian conspiracy of 65. Later, as a loyalist to the Flavians, he attained consulships in 71 and 90 during the reigns of Vespasian and Domitian, respectively. On 18 September 96, Domitian was assassinated in a palace conspiracy involving members of the Praetorian Guard and several of his freedmen. On the same day, Nerva was declared emperor by the Roman Senate. As the new ruler of the Roman Empire, he vowed to restore liberties which had been curtailed during the autocratic government of Domitian.
Fabius Valens of Anagnia was a Roman commander favoured by Nero. Valens was an undisciplined character but not without talent; he tried to portray himself as witty by behaving frivolously.
Antonius Novellus was a politician of ancient Rome who served as one of the Roman emperor Otho's principal generals, though he possessed no influence with the soldiery.
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Greenhill, William Alexander (1870). "Antonius". In Smith, William (ed.). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology . Vol. 1. p. 628.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Greenhill, William Alexander (1870). "Antonius". In Smith, William (ed.). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology . Vol. 1. p. 628.











