
Zambia is a landlocked country located in Southern Africa, to the east of Angola. It has a total area of 752,618 square kilometres, of which 9 220 km² is water.

The Zambezi is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. The area of its basin is 1,390,000 square kilometres (540,000 sq mi), slightly less than half of the Nile's. The 2,574-kilometre-long river (1,599 mi) rises in Zambia and flows through eastern Angola, along the north-eastern border of Namibia and the northern border of Botswana, then along the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe to Mozambique, where it crosses the country to empty into the Indian Ocean.

The Cuando River is a river in south-central Africa flowing through Angola and Namibia's Caprivi Strip and into the Linyanti Swamp on the northern border of Botswana. Below the swamp, the river is called the Linyanti River and, farther east, the Chobe River, before it flows into the Zambezi River.
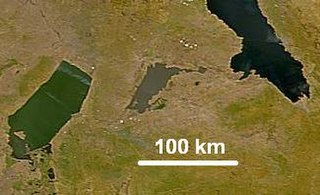
Lake Mweru Wantipa or Mweru-wa-Ntipa meaning "muddy lake" is a lake and swamp system in the Northern Province of Zambia. It has been regarded in the past as something of mystery, displaying fluctuations in water level and salinity which were not entirely explained by variation in rainfall levels; it has been known to dry out almost completely. This is compounded by its remoteness and it not receiving the same attention from geographers and geologists as its larger and more accessible neighbours, Lake Tanganyika, 25 km east, and Lake Mweru, 40 km west, with which its name is sometimes confused.

The Luangwa River is one of the major tributaries of the Zambezi River, and one of the four biggest rivers of Zambia. The river generally floods in the rainy season and then falls considerably in the dry season. It is one of the biggest unaltered rivers in Southern Africa and the 20,000 square miles that make up the surrounding valley are home to abundant wildlife.

The Kafue River is the longest river lying wholly within Zambia at about 1,600 kilometres (990 mi) long. Its water is used for irrigation and for hydroelectric power. It is the largest tributary of the Zambezi, and of Zambia's principal rivers, it is the most central and the most urban. More than 50% of Zambia's population live in the Kafue River Basin and of these around 65% are urban.

Mongu is the capital of Western Province in Zambia and was the capital of the formerly-named province and historic state of Barotseland. Its population is 179,585, and it is also the headquarters of Mongu District.
Luambe National Park is located in the Eastern Province of Zambia. The park is situated north-east of the famous South Luangwa National Park, and south of the North Luangwa National Park. Like its neighbours, it is located in the Luangwa River rift valley.
A Dambo is a class of complex shallow wetlands in central, southern and eastern Africa, particularly in Zambia and Zimbabwe. They are generally found in higher rainfall flat plateau areas, and have river-like branching forms which in themselves are not very large, but combined add up to a large area. Dambos have been estimated to comprise 12.5% of the area of Zambia. Similar African words include mbuga, matoro (Mashonaland), vlei, fadama (Nigeria), and bolis ; the French bas-fond and German Spültal have also been suggested as referring to similar grassy wetlands.

Chilubi District with headquarters at Chilubi is located in Northern Province, Zambia. It covers the north-east Bangweulu Lake and Bangweulu swamps containing several islands including Chilubi Island, and some of the mainland northeast of the lake. As of the 2000 Zambian Census, the district had a population of 66,338 people.

The climate of Zambia in Central and Southern Africa is definitely tropical modified by altitude (elevation). In the Köppen climate classification, most of the country is classified as humid subtropical or tropical wet and dry, with small patches of semi-arid steppe climate in the south-west.
The biomes and ecoregions in the ecology of Zambia are described, listed and mapped here, following the World Wildlife Fund's Global 200 classification scheme for terrestrial ecoregions, and the WWF freshwater bioregion classification for rivers, lakes and wetlands. Zambia is in the Afrotropic biogeographic realm of the scheme. Three terrestrial biomes are well represented in the country . The distribution of the biomes and ecoregions is governed mainly by the physical environment, especially climate.
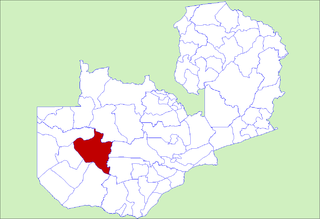
Kaoma District with headquarters at Kaoma, Zambia is located in the north-east corner of Western Province. As of the 2000 Zambian Census, the district had a population of 162,568 people. The population lives mainly around Kaoma town and the northern parts of the district along the Luena and Luampa Rivers. Its south-western portion is relatively uninhabited being very sandy with little water available in the dry season.

Mongu District is a district of Zambia with headquarters at Mongu. As of the 2000 Zambian Census, the district had a population of 162,002 people. More than a quarter of whom live in Mongu town; the remainder live on the floodplain or its edge. East of the Lui River, the population is very low due to the absence of surface water in the dry season.
The River Lumi is located in northern Tanzania and southern Kenya in Coast Province. It originates on the east side of Mawenzi, and flows so close to the River Rombo as almost to form a fork. The Lumi, however, maintains its southerly direction, and may thus be said to represent the upper course of the Ruvu, one of tho two main sources of the Pangani River. It flows around the Lake Chala and the Taveta town in the west and empties into the Lake Jipe. The fish species Barbus sp. 'Pangani' has only been found in the river's N'joro Springs, situated in the upper Pangani River drainage basin.
Lumi is the Finnish and Estonian word for snow, and the Albanian word for river.













