
The Buthidae are the largest family of scorpions, containing about 100 genera and 1339 species as of 2022. A few very large genera are known, but a high number of species-poor or monotypic ones also exist. New taxa are being described at a rate of several new species per year. They have a [cosmopolitan] distribution throughout tropical and subtropical environments worldwide. Together with four other families, the Buthidae make up the superfamily Buthoidea. The family was established by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1837.
Bark scorpion may refer to:
Ludwig Glauert MBE was a British-born Australian paleontologist, herpetologist and museum curator. He is known for work on Pleistocene mammal fossils, and as a museum curator who played an important role in natural science of Western Australia.

The Kimberley rock monitor is a medium-sized species of monitor lizard in the family Varanidae. The species is native to Northern Australia. Also known as Glauert's monitor or the Kakadu sand goanna, it belongs to the subgenus Odatria.

Urodacus is a genus of scorpion belonging to the family Urodacidae. It was described by German naturalist Wilhelm Peters in 1861. The type species is U. novaehollandiae. Its species are native to Australia, and dig burrows. The genus was placed in its own family in 2000. Before this, the group had been a subfamily Urodacinae within the family Scorpionidae.
Lychas ceylonensis is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae. It is endemic to Sri Lanka. The name is derived from the old name of Sri Lanka (Ceylon). The species has similarities with Lychas srilankensis, but can be differentiated by physical differences and differing habitats: L. srilankensis coming from a humid regions, whereas L. ceylonensis comes from dry formations closer to the center of the island.

Lychas srilankensis is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae. It is endemic to Sri Lanka.
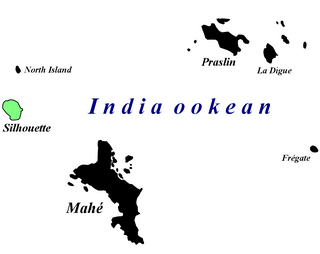
Afrolychas braueri, commonly known as the Seychelles forest scorpion, is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae. It is currently thought to survive only on Silhouette Island, Seychelles, although the species was historically found on two additional Seychellois islands. This scorpion lives in leaf litter in forests that are largely unaffected by invasive plant species. It is a small yellowish-brown scorpion with three prominent keels on the dorsal surface of its mesosoma, which distinguishes it from other scorpions. While not much is known about the Seychelles forest scorpion's ecology due to the paucity of sightings, it is known to rely solely on its venom to capture its prey and defend its young. Its venom is not dangerous to humans.
Afrolychas is a genus of scorpion in the family Buthidae. There are two species in this genus, both of which used to belong to the genus Lychas. The genus was described in 2019 by František Kovařík. The genus name Afrolychas is a reference to the African range of its species and the fact that the two species used to be members of the genus Lychas. Afrolychas's closest relatives are believed to be the scorpions in the genus Pseudolychas. Afrolychas braueri is one of the rarest scorpions in the world, as it is listed as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List.

Lychas is a genus of scorpions belonging to the family Buthidae. It is one of the most widespread genus of the scorpions, where the species are found throughout in Africa and Seychelles, and in the Oriental region from India to Melanesia.
Lychas buchari, also known as the yellow sand scorpion or Buchar's scorpion, is a species of small scorpion in the Buthidae family. It is native to Australia, and was first described in 1997 by Czech arachnologist Frantisek Kovarik.

Lychas marmoreus, also known as the marbled scorpion, little marbled scorpion or bark scorpion, is a species of small scorpion in the Buthidae family. It is native to Australia, and was first described in 1845 by German arachnologist Carl Ludwig Koch.
Marbled scorpion may refer to various Australian scorpions, including:
Lychas mjobergi is a species of scorpion in the Buthidae family. It is endemic to Australia, and was first described in 1916 by German naturalist Karl Kraepelin following the collection of specimen material from the Kimberley region of Western Australia by Swedish zoologist Eric Mjöberg, for which the species was named.

Lychas variatus, also known as the marbled scorpion or splendid marbled scorpion, is a species of small scorpion in the Buthidae family. It is native to Australia and New Guinea, and was first described in 1877 by Swedish arachnologist Tamerlan Thorell.

Cercophonius is a genus of six species of Australian scorpions, often termed wood scorpions, in the family Bothriuridae.
Cercophonius kershawi, also known as the mallee wood scorpion, is a species of scorpion in the Bothriuridae family. It is native to south-eastern Australia, and was first described in 1930 by Australian paleontologist and Western Australian Museum curator Ludwig Glauert.
Urodacus varians is a species of scorpion in the Urodacidae family. It is endemic to Australia, and was first described in 1963 by Australian paleontologist and Western Australian Museum curator Ludwig Glauert.








