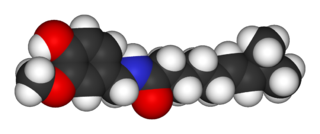
Capsaicin (8-methyl-N-vanillyl-6-nonenamide) is an active component of chili peppers, which are plants belonging to the genus Capsicum. It is a chemical irritant and neurotoxin for mammals, including humans, and produces a sensation of burning in any tissue with which it comes into contact. Capsaicin and several related amides (capsaicinoids) are produced as secondary metabolites by chili peppers, probably as deterrents against certain mammals and fungi. Pure capsaicin is a hydrophobic, colorless, highly pungent, crystalline to waxy solid compound.

Cercospora capsici is a fungal plant pathogen that causes leaf spot, known as frogeye spot, on peppers.

Phytophthora capsici is an oomycete plant pathogen that causes blight and fruit rot of peppers and other important commercial crops. It was first described by L. Leonian at the New Mexico State University Agricultural Experiment Station in Las Cruces in 1922 on a crop of chili peppers. In 1967, a study by M. M. Satour and E. E. Butler found 45 species of cultivated plants and weeds susceptible to P. capsici In Greek, Phytophthora capsici means "plant destroyer of capsicums". P. capsici has a wide range of hosts including members of the families Solanaceae and Cucurbitaceae as well as Fabaceae.
Colletotrichum capsici is a species of fungus and plant pathogen which causes leaf blight on Chlorophytum borivilianum, basil, chickpea and pepper as well as dieback in pigeonpea and anthracnose in poinsettia.
Lysinibacillus sphaericus is a Gram-positive, mesophilic, rod-shaped bacterium commonly found on soil. It can form resistant endospores that are tolerant to high temperatures, chemicals and ultraviolet light and can remain viable for long periods of time. It is of particular interest to the World Health Organization due to the larvicide effect of some strains against two mosquito genera, more effective than Bacillus thuringiensis, frequently used as a biological pest control. L. sphaericus cells in a vegetative state are also effective against Aedes aegypti larvae, an important vector of yellow fever and dengue viruses.

Capsidiol is a terpenoid compound that accumulates in tobacco Nicotiana tabacum and chili pepper Capsicum annuum in response to fungal infection. Capsidiol is categorized under the broad term of phytoalexin, a class of low molecular weight plant secondary metabolites that are produced during infection. Phytoalexins are also characterized as a part of a two pronged response to infection which involves a short term response consisting of production of free radicals near the site of infection and a long term response involving the production of hormones and an increase in enzymes to biosynthesize phytoalexins such as capsidiol.
Lysinibacillus fusiformis is a gram-positive, rod-shaped bacterium of the genus Lysinibacillus. Scientists have yet to completely characterize this microbe's pathogenic nature. Though little is known about this organism, several genome sequencing projects for various strains of L. fusiformis are currently underway.
Trichoderma theobromicola is a species of endophytic fungus in the family Hypocreaceae. It was first isolated from the trunk of a healthy cacao tree in Amazonian Peru. It produces a volatile antibiotic that inhibits development of M. roreri.
An attract-kill pattern is an interaction between plant roots and pathogen, which plays an important role in suppression of Phytophthora disease in intercropping systems. The recent research from Key Laboratory of Agro-Biodiversity and Pest Management of Education Ministry of China indicated that maize roots attracted the zoospores of Phytophthora capsici and inhibited their motility. Then a large amount of cystospores closed to maize roots were lysed. The phenomenon has been widely found in various interactions between roots of non-host plant and Phytophthora.
Lysinibacillus alkalisoli is a Gram-positive, aerobic and motile bacterium from the genus of Lysinibacillus which has been isolated from saline-alkaline soil from Hanggin Banner.
Lysinibacillus antri is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, endospore-forming and motile bacterium from the genus of Lysinibacillus which has been isolade from soil from a karst cave in Xingyi county.
Lysinibacillus composti is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, endospore-forming and motile bacterium from the genus of Lysinibacillus which has been isolated from compost.
Lysinibacillus contaminans is a Gram-positive, aerobic and endospore-forming bacterium from the genus of Lysinibacillus which has been isolated from surface water.
Lysinibacillus endophyticus is a Gram-positive, aerobic and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus of Lysinibacillus which has been isolated from the root of a maize plant. Lysinibacillus endophyticus produces indole-3-acetic acid.
Lysinibacillus meyeri is a Gram-positive bacterium from the genus of Lysinibacillus which has been isolated from a medical practice.
Lysinibacillus parviboronicapiens is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, spore-forming and motile bacterium from the genus of Lysinibacillus which has been isolated from soil.
Lysinibacillus tabacifolii is a Gram-positive, strictly aerobic and endospore-forming bacterium from the genus of Lysinibacillus which has been isolated from leaves of the plant Nicotiana tabacum.
Lysinibacillus telephonicus is a Gram-positive, aerobic, rod-shaped, endospore-forming and motile bacterium from the genus of Lysinibacillus which has been isolated from the screen of a cellular phone.
Lysinibacillus timonensis is a bacterium from the genus of Lysinibacillus which has been isolated from human skin.
Lysinibacillus xylanilyticus is a Gram-positive, aerobic, xylan-degrading, endospore-forming and motile bacterium from the genus of Lysinibacillus which has been isolated from forest humus from the Gyeryong Mountain.



