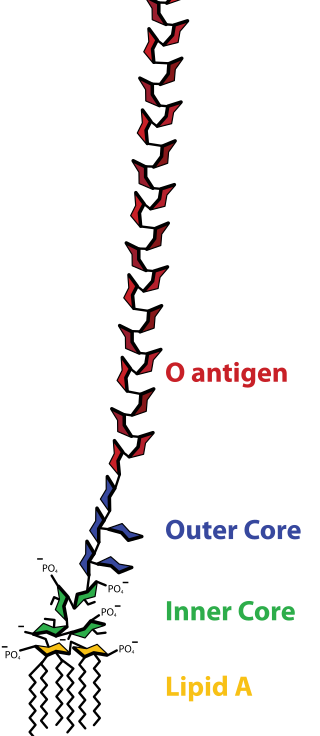
Lipopolysaccharide, now more commonly known as endotoxin, is a collective term for components of the outermost membrane of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria, such as E. coli and Salmonella with a common structural architecture. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of three parts: an outer core polysaccharide termed the O-antigen, an inner core oligosaccharide and Lipid A, all covalently linked. In current terminology, the term endotoxin is often used synonymously with LPS, although there are a few endotoxins that are not related to LPS, such as the so-called delta endotoxin proteins produced by Bacillus thuringiensis.

Septic shock is a potentially fatal medical condition that occurs when sepsis, which is organ injury or damage in response to infection, leads to dangerously low blood pressure and abnormalities in cellular metabolism. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) defines septic shock as a subset of sepsis in which particularly profound circulatory, cellular, and metabolic abnormalities are associated with a greater risk of mortality than with sepsis alone. Patients with septic shock can be clinically identified by requiring a vasopressor to maintain a mean arterial pressure of 65 mm Hg or greater and having serum lactate level greater than 2 mmol/L (>18 mg/dL) in the absence of hypovolemia. This combination is associated with hospital mortality rates greater than 40%.

Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single-spanning receptors usually expressed on sentinel cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, that recognize structurally conserved molecules derived from microbes. Once these microbes have reached physical barriers such as the skin or intestinal tract mucosa, they are recognized by TLRs, which activate immune cell responses. The TLRs include TLR1, TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9, TLR10, TLR11, TLR12, and TLR13. Humans lack genes for TLR11, TLR12 and TLR13 and mice lack a functional gene for TLR10. The receptors TLR1, TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, and TLR10 are located on the cell membrane, whereas TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9 are located in intracellular vesicles.
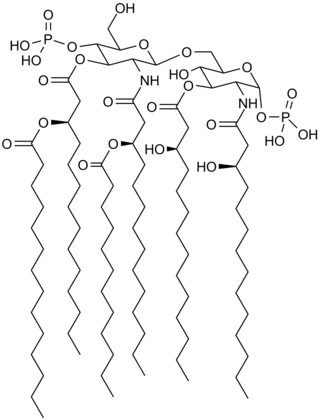
Lipid A is a lipid component of an endotoxin held responsible for the toxicity of gram-negative bacteria. It is the innermost of the three regions of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS), also called endotoxin molecule, and its hydrophobic nature allows it to anchor the LPS to the outer membrane. While its toxic effects can be damaging, the sensing of lipid A by the immune system may also be critical for the onset of immune responses to gram-negative infection, and for the subsequent successful fight against the infection.

Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) also known as CD283 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TLR3 gene. TLR3 is a member of the toll-like receptor family of pattern recognition receptors of the innate immune system. TLR3 recognizes double-stranded RNA in endosomes, which is a common feature of viral genomes internalised by macrophages and dendritic cells.

TIR domain containing adaptor molecule 1 is an adapter in responding to activation of toll-like receptors (TLRs). It mediates the rather delayed cascade of two TLR-associated signaling cascades, where the other one is dependent upon a MyD88 adapter.

Toll-like receptor 5, also known as TLR5, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the TLR5 gene. It is a member of the toll-like receptor (TLR) family. TLR5 is known to recognize bacterial flagellin from invading mobile bacteria. It has been shown to be involved in the onset of many diseases, including Inflammatory bowel disease due to the high expression of TLR in intestinal lamina propria dendritic cells. Recent studies have also shown that malfunctioning of TLR5 is likely related to rheumatoid arthritis, osteoclastogenesis, and bone loss. Abnormal TLR5 functioning is related to the onset of gastric, cervical, endometrial and ovarian cancers.

Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), also designated as CD284, is a key activator of the innate immune response and plays a central role in the fight against bacterial infections. TLR4 is a transmembrane protein of approximately 95 kDa that is encoded by the TLR4 gene.

Lymphocyte antigen 96, also known as "Myeloid Differentiation factor 2 (MD-2)," is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LY96 gene.

High mobility group box 1 protein, also known as high-mobility group protein 1 (HMG-1) and amphoterin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HMGB1 gene.

Ibudilast is an anti-inflammatory drug used mainly in Japan, which acts as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, inhibiting the PDE4 subtype to the greatest extent, but also showing significant inhibition of other PDE subtypes.

Bruce Alan Beutler is an American immunologist and geneticist. Together with Jules A. Hoffmann, he received one-half of the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, for "discoveries concerning the activation of innate immunity." Beutler discovered the long-elusive receptor for lipopolysaccharide. He did so by identifying spontaneous mutations in the gene coding for mouse Toll-like receptor 4 (Tlr4) in two unrelated strains of LPS-refractory mice and proving they were responsible for that phenotype. Subsequently, and chiefly through the work of Shizuo Akira, other TLRs were shown to detect signature molecules of most infectious microbes, in each case triggering an innate immune response.

Single Ig IL-1-related receptor (SIGIRR), also called Toll/Interleukin-1 receptor 8 (TIR8) or Interleukin-1 receptor 8 (IL-1R8), is transmembrane protein encoded by gene SIGIRR, which modulate inflammation, immune response, and tumorigenesis of colonic epithelial cells.
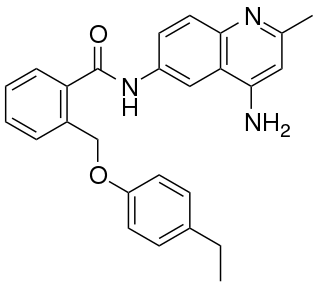
JTC-801 is an opioid analgesic drug used in scientific research.

Eritoran is a synthetic lipid that inhibits the receptor TLR4. It was developed as a potential treatment for severe sepsis, an excessive inflammatory response to an infection. It failed a five year Phase III clinical trial, the results of which were published in 2013, and as of 2014 was no longer being developed.
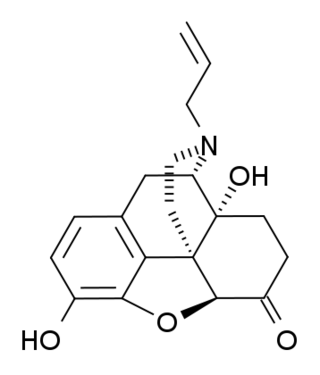
(+)-Naloxone (dextro-naloxone) is a drug which is the opposite enantiomer of the opioid antagonist drug (−)-naloxone. Unlike (−)-naloxone, (+)-naloxone has no significant affinity for opioid receptors, but instead has been discovered to act as a selective antagonist of Toll-like receptor 4. This receptor is involved in immune system responses, and activation of TLR4 induces glial activation and release of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α and Interleukin-1.
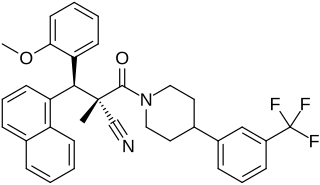
WAY-204688, also known as SIM-688, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) inhibitor which was originated by ArQule and Wyeth and was under development by Wyeth for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, non-specific inflammation, and sepsis but was never marketed. It is a "pathway-selective" estrogen receptor (ER) ligand which inhibits NF-κB with an IC50Tooltip half-maximal inhibitory concentration of 122 nM and with maximal inhibition relative to estradiol of 94%. Inhibition of NF-κB by WAY-204688 appears to be dependent on agonism of the ERα, as it is reversed by the ERα antagonist fulvestrant, but is not dependent on the ERβ. In contrast to the case of NF-κB inhibition, WAY-204688 produces only slight elevation of creatine kinase in vitro, a measure of classical estradiol effects. It reached phase I clinical trials prior to the discontinuation of its development.
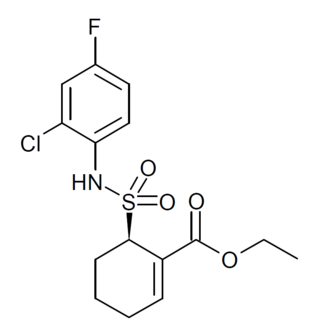
Resatorvid (TAK-242) is a cyclohexane derivative that was invented by scientists at Takeda in a drug discovery campaign to identify inhibitors of the receptor TLR4. It binds directly to cysteine residue 747 intracellularly, preventing TLR4 binding with TIRAP and thus preventing downstream signal transduction.

TLR4-IN-C34 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). In animal studies it blocks TLR4-mediated cytokine release and has antiinflammatory effects.

VGX-1027 (GIT-27) is a drug which acts as an immunomodulator. It acts by blocking downstream signalling of the Toll-like receptors TLR2, TLR4 and TLR6, and thereby reducing production of various cytokines, including interleukins and TNF-α. In animal studies it has antiinflammatory effects and has been investigated for conditions such as arthritis and lung inflammation.



















