
Electric power transmission is the bulk movement of electrical energy from a generating site, such as a power plant, to an electrical substation. The interconnected lines which facilitate this movement are known as a transmission network. This is distinct from the local wiring between high-voltage substations and customers, which is typically referred to as electric power distribution. The combined transmission and distribution network is part of electricity delivery, known as the electrical grid.

Electric power distribution is the final stage in the delivery of electric power; it carries electricity from the transmission system to individual consumers. Distribution substations connect to the transmission system and lower the transmission voltage to medium voltage ranging between 2 kV and 35 kV with the use of transformers. Primary distribution lines carry this medium voltage power to distribution transformers located near the customer's premises. Distribution transformers again lower the voltage to the utilization voltage used by lighting, industrial equipment and household appliances. Often several customers are supplied from one transformer through secondary distribution lines. Commercial and residential customers are connected to the secondary distribution lines through service drops. Customers demanding a much larger amount of power may be connected directly to the primary distribution level or the subtransmission level.

The electric power industry covers the generation, transmission, distribution and sale of electric power to the general public and industry. The commercial distribution of electric power started in 1882 when electricity was produced for electric lighting. In the 1880s and 1890s, growing economic and safety concerns lead to the regulation of the industry. What was once an expensive novelty limited to the most densely populated areas, reliable and economical electric power has become an essential aspect for normal operation of all elements of developed economies.
Transpower New Zealand Limited (TPNZ) is the state-owned enterprise responsible for electric power transmission in New Zealand. It performs two major functions in the New Zealand electricity market. As the owner of the National Grid it provides the infrastructure of electric power transmission that allows consumers to have access to generation from a wide range of sources, and enables competition in the wholesale electricity market; as System Operator it manages the real-time operation of the grid and the physical operation of the electricity market.

Hydro-Québec's electricity transmission system is an international electric power transmission system centred in Quebec, Canada. The system pioneered the use of very high voltage 735-kilovolt (kV) alternating current (AC) power lines that link the population centres of Montreal and Quebec City to distant hydroelectric power stations like the Daniel-Johnson Dam and the James Bay Project in northwestern Quebec and the Churchill Falls Generating Station in Labrador.
OAO FGC UES is a state-owned energy company located in Moscow, Russia. It is the country's largest transmission grid company. The company is listed at the Moscow and London stock exchanges with 80.13% of shares owned by Rosseti.

An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:
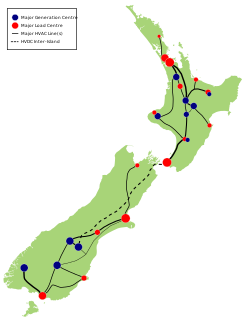
The National Grid is the nationwide system of electric power transmission in New Zealand. The national electricity transmission grid is owned, operated, and maintained by state-owned enterprise Transpower New Zealand, although some lines are owned by local distribution companies and leased to Transpower. In total, the national grid contains 11,803 kilometres (7,334 mi) of high-voltage lines and 178 substations.

PAO Rosseti is a Russian power company, comprises interregional and regional distribution grid companies (IDGCs/RDGCs), research and development institutes, design and construction institutes, and construction and sales entities. Ninety-seven subsidiaries of IDGCs/RDGCs are based in 69 constituent entities of the Russian Federation. The company was created as a result of the reorganization of RAO UES.

Russia is the fourth largest generator and consumer of electricity in the world. Its 440 power stations have a combined installed generation capacity of 220 GW.

Electricity Ashburton Limited, trading as EA Networks is a co-operatively-owned electricity distribution company, based in Ashburton, New Zealand.

A low-voltage network or secondary network is a part of electric power distribution which carries electric energy from distribution transformers to electricity meters of end customers. Secondary networks are operated at a low voltage level, which is typically equal to the mains voltage of electric appliances.

Creos Luxembourg S.A. owns and manages electricity networks and natural gas pipelines in the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. In this capacity, the company plans, constructs and maintains high, medium and low-voltage electricity networks and high, medium and low-pressure natural gas pipelines, which it owns or which it is responsible for managing.
Kawanda–Birembo High Voltage Power Line is a high voltage electricity power line, under construction, connecting the high voltage substation at Kawanda, in Uganda to another high voltage substation at Birembo, in Rwanda.
The Nkenda–Fort Portal–Hoima High Voltage Power Line is a high voltage electricity power line, in operation, connecting the high voltage substation at Nkenda, Kasese District, to another high voltage substation at Kabaale, Buseruka sub-county, Hoima District, all in the Western Region of Uganda.
The Masaka–Mutukula–Mwanza High Voltage Power Line is a proposed high voltage electricity power line, connecting the high voltage substation at Masaka, in Masaka District, in the Central Region of Uganda, to another high voltage substation at Mwanza, in Mwanza Region, in the Republic of Tanzania.
The Achwa 1 Hydroelectric Power Station (A1HPS), also Achwa I Hydroelectric Power Station, is a hydroelectric power station currently under construction (2020) in Uganda, with a planned installed capacity of 41 megawatts (55,000 hp).
The Hoima–Kinyara–Kafu High Voltage Power Line is a planned high voltage electricity power line, connecting the high voltage substation at Kabaale, Buseruka sub-county, Hoima District, in the Western Region of Uganda to another high voltage substation at Kafu, Nakasongola District, in the Central Region of Uganda. On the way, the power line passes through Kinyara Sugar Works, in Masindi District.
The Mirama–Kabale High Voltage Power Line is a high voltage electricity power line, connecting the high voltage substation in the town of Mirama Hills, in the Western Region to another high voltage substation in te city of Kabale, also in the Western Region of Uganda.
The Kishapu Solar Power Station is a proposed 50 MW (67,000 hp) solar power plant in Tanzania. The power station is under development by Tanzania Electric Supply Company Limited (TANESCO), the national electricity monopoly utility company. The energy will be integrated into the national grid, also operated by TANESCO. The solar farm will be developed in phases to capacity of 150 megawatts. When completed and commissioned, it will be the largest, grid-ready solar power station in the country.











