
Macedonian is a South Slavic language spoken as a first language by around two million people, principally in North Macedonia and its diaspora, with a smaller number of speakers throughout the transnational region of Macedonia. It is the official language of North Macedonia and a recognized minority language in parts of Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Romania, and Serbia.
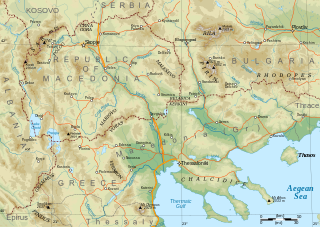
Macedonia is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time; however, it came to be defined as the modern geographical region by the mid 19th century. Today the region is considered to include parts of six Balkan countries: Greece, North Macedonia, Bulgaria, Albania, Serbia, and Kosovo. It covers approximately 67,000 square kilometres (25,869 sq mi) and has a population of 4.76 million.
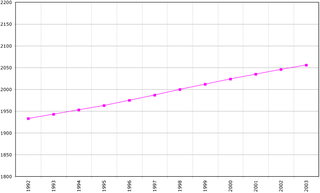
This article is about the demographic features of the population of North Macedonia, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

The foreign relations of North Macedonia since its independence in 1991 have been characterized by the country's efforts to gain membership in international organizations such as NATO and the European Union and to gain international recognition under its constitutional name, overshadowed by a long-standing, dead-locked dispute with neighboring Greece. Greek objections to the country's name have led to it being admitted to the United Nations and several other international fora only under the provisional designation Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia.

Skopje is the capital and largest city of North Macedonia. It is the country's political, cultural, economic, and academic centre.

Macedonia, also called Macedon, was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal Argead dynasty, which was followed by the Antipatrid and Antigonid dynasties. Home to the ancient Macedonians, the earliest kingdom was centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula, and bordered by Epirus to the west, Paeonia to the north, Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south.
Macedonians or Macedonian people are a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group native to the region of Macedonia. They speak the Macedonian language, a South Slavic language. About two thirds of all ethnic Macedonians live in North Macedonia and there are also communities in a number of other countries.

Central Macedonia is one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece, consisting of the central part of the geographical and historical region of Macedonia. With a population of almost 1.9 million, it is the second most populous in Greece after Attica.

Goran Pandev is a Macedonian professional footballer who plays as a forward for Italian club Genoa. He is the captain of the North Macedonia national football team, and is the country's all-time top scorer with 34 goals.

Macedonia is a geographic and administrative region of Greece, in the southern Balkans. Macedonia is the largest and second-most-populous Greek region, with a population of 2.38 million in 2017. The region is highly mountainous, with most major urban centres such as Thessaloniki and Kavala being concentrated on its southern coastline. Together with Thrace, and sometimes also Thessaly and Epirus, it is part of Northern Greece. Greek Macedonia encompasses entirely the southern part of the region of Macedonia, making up 51% of the total area of the region. It also contains Mount Athos, an autonomous monastic region of Greece. Macedonia forms part of Greece's national frontier with three countries: Bulgaria to the northeast, North Macedonia to the north, and Albania to the northwest.

The Macedonian Greek Catholic Church is a Byzantine Rite sui juris Eastern Catholic Church in full union with the Catholic Church which uses the Macedonian language in the liturgy.

KF Renova is a football club based in the village of Džepčište, Tetovo, North Macedonia competing in the Macedonian First League.
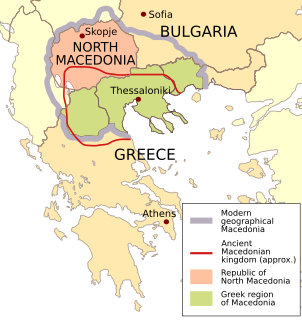
The use of the name "Macedonia" was disputed between the Southeast European countries of Greece and North Macedonia. Pertinent to its background is an early 20th-century multifaceted dispute and armed conflict that formed part of the background to the Balkan Wars. The specific naming dispute, although an existing issue in Yugoslav–Greek relations since World War II, was reignited after the breakup of Yugoslavia and the newly gained independence of the former Socialist Republic of Macedonia in 1991. Since then, it was an ongoing issue in bilateral and international relations until it was settled with the Prespa agreement in June 2018, the subsequent ratification by the Macedonian and Greek parliaments in late 2018 and early 2019, and the official renaming of Macedonia to North Macedonia in February 2019.

In North Macedonia, the most common religion is Orthodox Christianity, practiced by most of the ethnic Macedonians. The vast majority of the Orthodox Christians in the country belong to the Macedonian Orthodox Church, which declared autocephaly from the Serbian Orthodox Church in 1967.
This is a list of flags which have been, or are still today, used on the territory of North Macedonia or by ethnic Macedonians.

The accession of North Macedonia to the European Union (EU) has been on the current agenda for future enlargement of the EU since 2005, when it became a candidate for accession. Republic of Macedonia submitted its membership application in 2004, thirteen years after its independence from Yugoslavia.
The 2009–10 Macedonian First League was the 18th season of the Macedonian First Football League, the highest football league of Macedonia. It began on 1 August 2009 and ended on 19 May 2010. Makedonija Gjorche Petrov were the defending champions having won their first Macedonian championship last season.

North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a country in the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. It gained its independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. A landlocked country, North Macedonia has borders with Kosovo to the northwest, Serbia to the northeast, Bulgaria to the east, Greece to the south, and Albania to the west. It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical region of Macedonia. The capital and largest city, Skopje, is home to roughly a quarter of the country's 2.06 million inhabitants. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians, a South Slavic people. Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks, Romani, Serbs, Bosniaks, and Aromanians.

Israel–North Macedonia relations refer to the bilateral political relations between the State of Israel and the Republic of North Macedonia.
The Administration for Security and Counterintelligence, commonly referred to by the acronym UBK, was the domestic counterintelligence and security agency of North Macedonia. Its headquarters are located in Skopje, and the agency is under jurisdiction of the Ministry of Internal Affairs.















