
Kenneth David Buchizya Kaunda, also known as KK, is a Zambian former politician who served as the first President of Zambia from 1964 to 1991.
This article deals with the history of the country now called Zambia from prehistoric times to the present.

Zambia is one of Sub-Saharan Africa's most highly urbanized countries. About one-half of the country's 16 million people are concentrated in a few urban zones strung along the major transportation corridors, while rural areas are under-populated. Unemployment and underemployment are serious problems. National GDP has actually doubled since independence, but due in large part to high birth rates and AIDS per capita annual incomes are currently at about two-thirds of their levels at independence. As of 2015 the GDP per capita stands at $4,300. Zambia is one of the fastest growing economies in Africa and its capital, Lusaka is the fastest growing city in the Southern African Development Community (SADC).

After independence in 1964 the foreign relations of Zambia were mostly focused on supporting liberation movements in other countries in Southern Africa, such as the African National Congress and SWAPO. During the Cold War Zambia was a member of the Non-Aligned Movement.
"Stand and Sing of Zambia, Proud and Free" is the national anthem of Zambia. The tune is taken from the hymn "Nkosi Sikelel' iAfrika", which was composed by South African Enoch Sontonga, in 1897. The lyrics were composed after Zambian independence to specifically reflect Zambia, as opposed to Sontonga's lyrics which refer to Africa as a whole.

The flag of Zambia is the national flag of Zambia. It was adopted upon independence on 24 October 1964. Before that, Zambia was the British protectorate of Northern Rhodesia and used a defaced Blue Ensign as its flag.

Zambia is divided into 10 provinces for administrative purposes. Each province is headed by a minister appointed by the President and there are ministries of central government for each province. The administrative head of the province is the Permanent Secretary, appointed by the President. There are Deputy Permanent Secretary, heads of government departments and civil servants at the provincial level.

The Southern Africa-Indian Ocean Division of Seventh-day Adventists is a sub-entity of the General Conference of Seventh-day Adventists, which coordinates the Church's activities in the southern portion of Africa, which include the nations of Angola, Ascension Island, Botswana, Comoro Islands, Lesotho, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Réunion, São Tomé and Príncipe, Seychelles, South Africa, Swaziland, Zambia, Zimbabwe; as well as St. Helena and Tristan da Cunha, territories of the United Kingdom, and the Kerguelen Islands, territory of France. Its headquarters is in Johannesburg, South Africa. The Division membership as of June 30, 2017 is 3,779,368.

The music of Zambia has a rich heritage which falls roughly into three categories: traditional, popular and Christian.

The Zambia national football team represents Zambia in association football and is governed by the Football Association of Zambia (FAZ). During the 1980s, they were known as the KK 11, after founding president Dr. Kenneth Kaunda ("KK") who ruled Zambia from 1964 to 1991. After the country adopted multiparty politics, the side was nicknamed Chipolopolo, the "Copper Bullets".
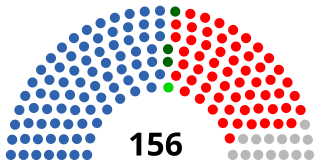
The National Assembly is Zambia's unicameral legislative body. Between 1972 and 1990, Zambia was a one-party state with the United National Independence Party (UNIP) as the sole legal party.

The Football Association of Zambia (FAZ) is the governing body of football in Zambia. It was founded in 1929 and affiliated to FIFA in 1964. It is also a member of the Confederation of African Football and the Council of Southern Africa Football Associations. It organizes the Zambian Premier League and the national team.

Zambia has several major indigenous languages, all of them members of the Bantu family. English is the official language and the major language of business and education.

The diplomatic relationship between the United States of America and Zambia can be characterized as warm and cooperative. Several U.S. administrations cooperated closely with Zambia's first president, Kenneth Kaunda, in hopes of facilitating solutions to the conflicts in Rhodesia (Zimbabwe), Angola, and Namibia. The United States works closely with the Zambian Government to defeat the HIV/AIDS pandemic that is ravaging Zambia, to promote economic growth and development, and to effect political reform needed to promote responsive and responsible government. The United States is also supporting the government's efforts to root out corruption. Zambia is a beneficiary of the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA). The U.S. Government provides a variety of technical assistance and other support that is managed by the Department of State, U.S. Agency for International Development, Millennium Challenge Account (MCA) Threshold Program, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Department of Treasury, Department of Defense, and Peace Corps. The majority of U.S. assistance is provided through the President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), in support of the fight against HIV/AIDS.
Lusaka is the capital and largest city of Zambia. One of the fastest developing cities in southern Africa, Lusaka is in the southern part of the central plateau at an elevation of about 1,279 metres (4,196 ft). As of 2010, the city's population was about 1.7 million, while the urban population is 2.4 million. Lusaka is the centre of both commerce and government in Zambia and connects to the country's four main highways heading north, south, east and west. English is the official language of the city, and Nyanja and Bemba are also common.

Visitors to Zambia must obtain a visa from one of the Zambian diplomatic missions unless they come from one of the visa exempt countries or countries whose citizens are eligible for visa on arrival. Visitors may alternatively obtain an electronic visa. All visitors must hold a passport valid for at least 6 months. As of November 2014 Zambia and Zimbabwe also offer a universal visa.

Edgar Chagwa Lungu is a Zambian politician who has been the President of Zambia since January 2015. Under President Michael Sata, Lungu served as Minister of Justice and Minister of Defence. Following Sata's death in October 2014, Lungu was adopted as the candidate of the ruling Patriotic Front for the January 2015 presidential by-election, which was to determine who would serve out the remainder of Sata's term. In the election, he narrowly defeated opposition candidate Hakainde Hichilema and took office on 25 January 2015.
The Military ranks of Zambia are the military insignia used by the Zambian Defence Force. Being a member of the Commonwealth of Nations, Zambia shares a rank structure similar to that of the United Kingdom. Zambia is a landlocked country, and does therefore not possess a navy.















